Siemens Automation System S7-400 User Manual
Page 42
Installing the S7-400
2-26
Automation System S7-400 Hardware and Installation
A5E00850741-01
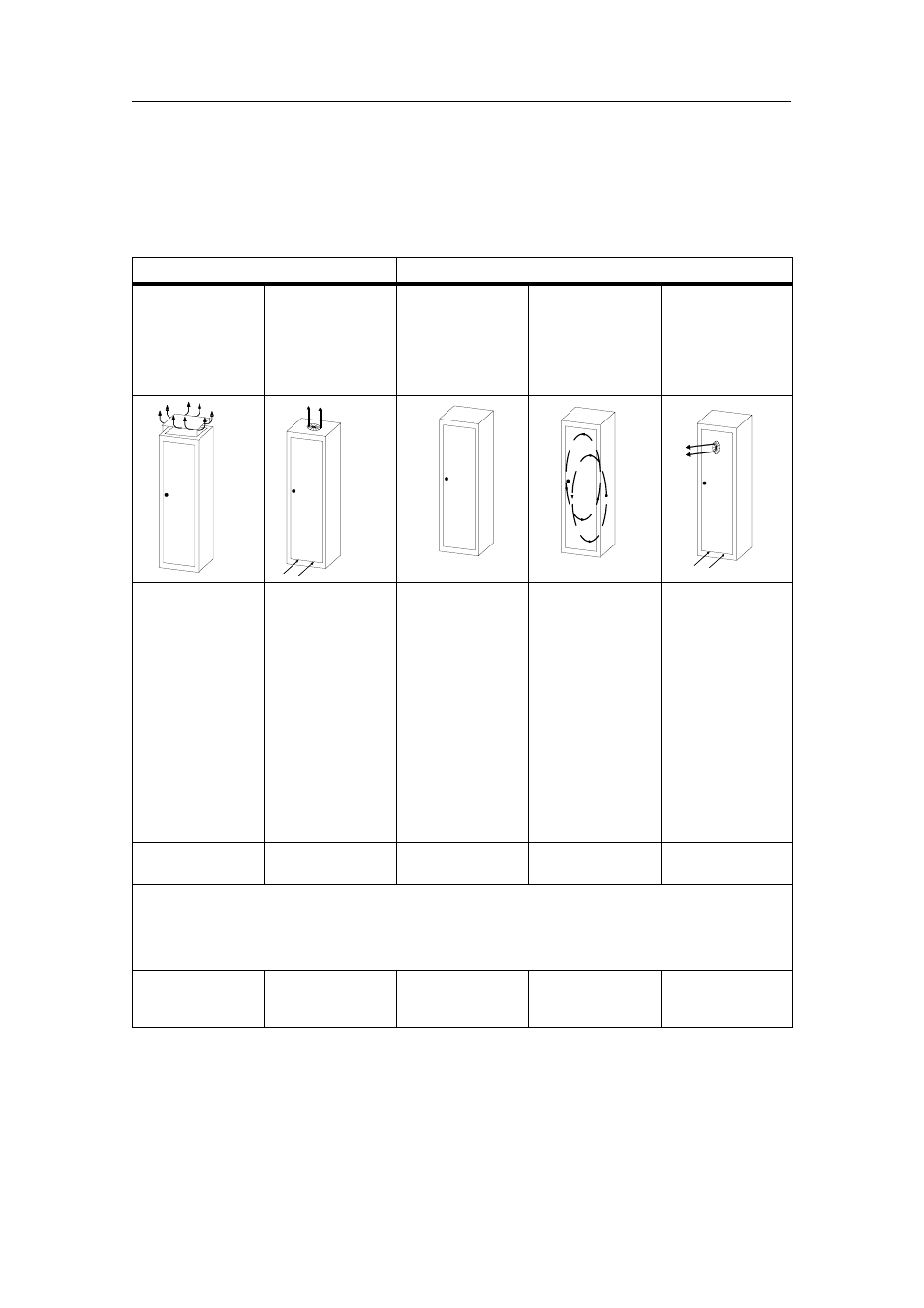
Table 2-1 provides an overview of the most common types of cabinet. You will also
find the principle of heat removal, as well as the estimated, maximum achievable
power loss removal and the degree of protection.
Table 2-1
Cabinet types
Open Cabinets
Closed Cabinets
Through-ventilatio
n by natural
convection
Increased
through-ventilation
Natural convection Forced circulation
using fan
subassembly,
enhanced natural
convection
Forced circulation
using heat
exchanger,
external ventilation
inside and outside
Heat removal
primarily by natural
thermal
convection, small
portion via the
cabinet wall
Increased heat
removal through
increased air
movement
Heat removal only
through the
cabinet wall; only
low power
dissipation
permissible. Heat
accumulation
usually occurs in
the top of the
cabinet.
Heat removal only
through the
cabinet wall.
Forced ventilation
of the internal air
results in improved
heat removal and
prevention of heat
accumulation.
Heat removal
through exchange
between heated
internal air and
cold external air.
The increased
surface of the
folded-area
sectional wall of
the heat
exchanger and
forced circulation
of internal and
external air permit
good heat output.
Degree of
protection IP 20
Degree of
protection IP 20
Degree of
protection IP 54
Degree of
protection IP 54
Degree of
protection IP 54
Typical removable power dissipation under the following boundary conditions:
•
Cabinet size 2200 x 600 x 600 mm
•
Difference between external and internal temperature of the cabinet: 20° C (for other temperature
differences, you must refer to the temperature characteristics of the cabinet manufacturer)
up to 700 W
up to 2700 W
(1400 W with very
fine filter)
up to 260 W
up to 360 W
up to 1700 W
