2 basic operations in "eit" processing, Basic operations in "eit" processing – FUJITSU FR family 32-bit microcontroller instruction manuel CM71-00101-5E User Manual
Page 58
34
CHAPTER 4 RESET AND "EIT" PROCESSING
4.2
Basic Operations in "EIT" Processing
Interrupts, exceptions and traps are similar operations applied under partially differing
conditions. Each "EIT" event involves terminating the execution of instructions, saving
information for restarting, and branching to a designated processing program.
■
Basic Operations in "EIT" Processing
The FR family device processes "EIT" events as follows.
(1) The vector table indicated by the table base register (TBR) and the number corresponding to the
particular "EIT" event are used to determine the entry address for the processing program for the
"EIT".
(2) For restarting purposes, the contents of the old program counter (PC) and the old program status (PS)
are saved to the stack area designated by the system stack pointer (SSP).
(3) After the processing flow is completed, the presence of new "EIT" sources is determined.
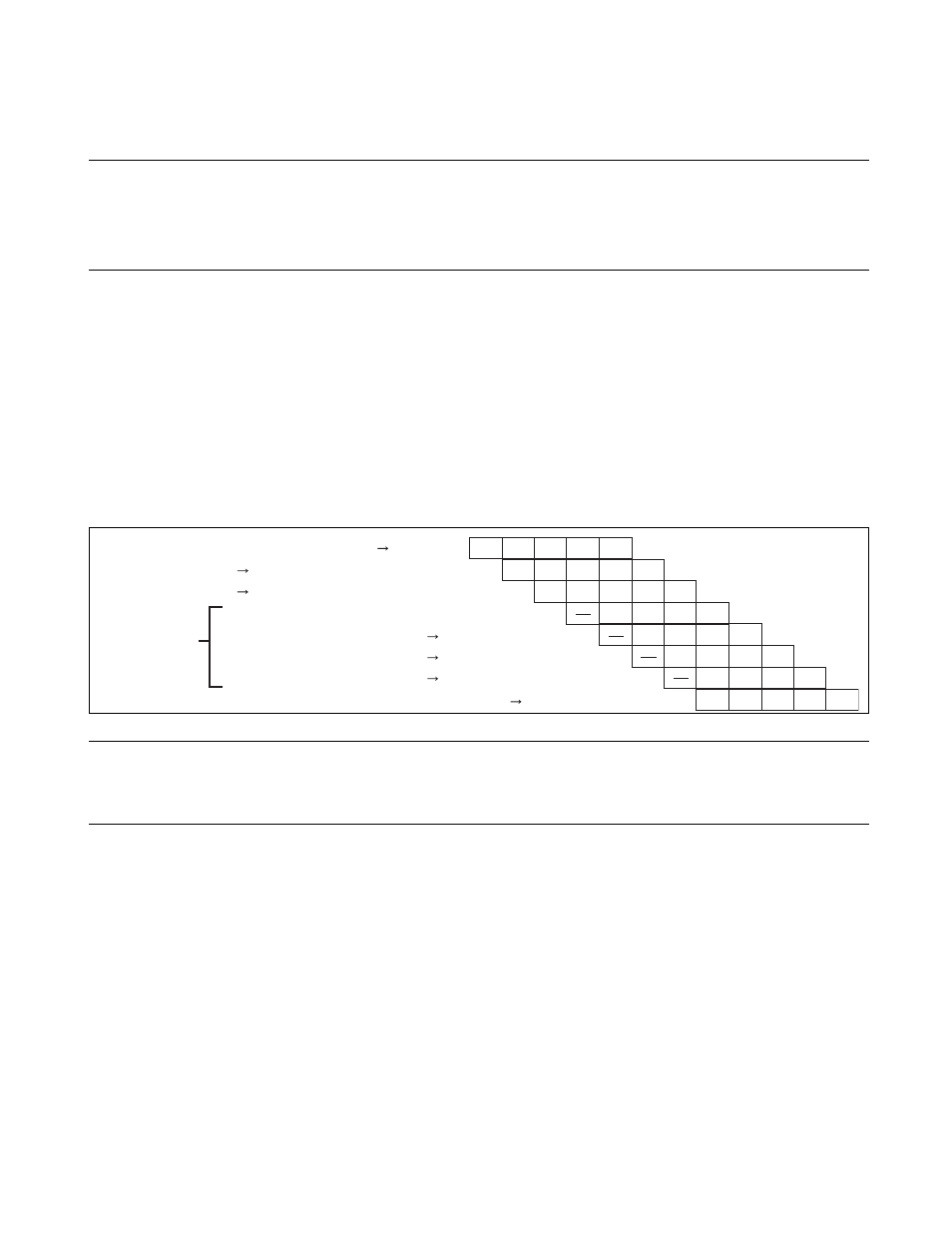
Figure 4.2-1 shows the operations in the "EIT" processing sequence.
Figure 4.2-1 "EIT" Processing Sequence
Note:
For a description of pipeline operations, see Section "5.1 Pipeline Operation".
Instruction at which EIT event is detected
Canceled instruction
EIT sequence
(1) Vector address calculation and new PC setting
(2) SSP update and PS save
(3) SSP update and PC save
(4) Detection of new EIT event
First instruction in EIT handler sequence (branching instruction)
Canceled instruction
IF
ID
EX
MA
WB
IF
ID
EX
MA
PC
ID(1) EX(1) MA(1) WB(1)
IF
ID
xxxx xxxx xxxx
IF
xxxx
xxxx
xxxx xxxx
ID(2) EX(2) MA(2) WB(2)
ID(3) EX(3) MA(3) WB(3)
ID(4) EX(4) MA(4) WB(4)
