Circular path ctp with tangential connection, Helical interpolation, Circular arc ctp – HEIDENHAIN TNC 426 (280 476) User Manual
Page 180: Polar radius, polar angle of the arc end point, Combination of a circular and a linear movement, 5 p ath cont ours — p olar coor dinat e s
HEIDENHAIN TNC 426, TNC 430
153
6.5 P
ath Cont
ours
—
P
olar Coor
dinat
e
s
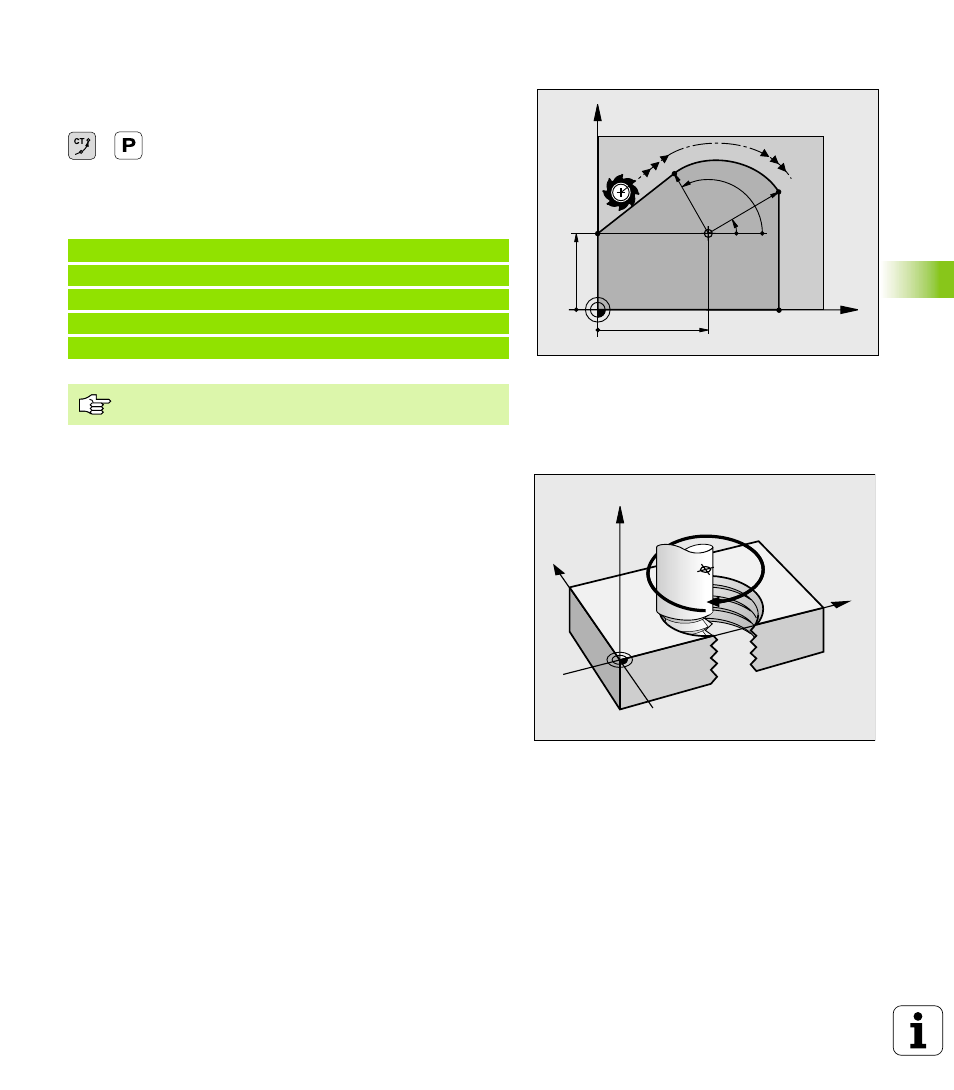
Circular path CTP with tangential connection
The tool moves on a circular path, starting tangentially from a
preceding contour element.
7
7
7
7
Polar coordinates radius PR:
Distance from the arc
end point to the pole CC
7
7
7
7
Polar coordinates angle PA:
Angular position of the
arc end point
Example NC blocks
Helical interpolation
A helix is a combination of a circular movement in a main plane and a
liner movement perpendicular to this plane.
A helix is programmed only in polar coordinates.
Application
n
Large-diameter internal and external threads
n
Lubrication grooves
Calculating the helix
To program a helix, you must enter the total angle through which the
tool is to move on the helix in incremental dimensions, and the total
height of the helix.
For calculating a helix that is to be cut in a upward direction, you need
the following data:
12 CC X+40 Y+35
13 L X+0 Y+35 RL F250 M3
14 LP PR+25 PA+120
15 CTP PR+30 PA+30
16 L Y+0
The pole CC is not the center of the contour arc!
X
Y
40
35
CC
30°
120°
R30
R25
Thread revolutions n
Thread revolutions + thread overrun at
the start and end of the thread
Total height h
Thread pitch P times thread revolutions n
Incremental total
angle IPA
Number of revolutions times 360° + angle for
beginning of thread + angle for thread
overrun
Starting coordinate Z
Pitch P times (thread revolutions + thread
overrun at start of thread)
Y
X
Z
CC
