2 f undamentals of p a th f unctions – HEIDENHAIN TNC 426 (280 476) User Manual
Page 157
130
6 Programming: Programming Contours
6.2 F
undamentals of P
a
th F
unctions
Entering more than three coordinates
The TNC can control up to 5 axes simultaneously. Machining with 5
axes, for example, moves 3 linear and 2 rotary axes simultaneously.
Such programs are too complex to program at the machine, however,
and are usually created with a CAD system.
Example:
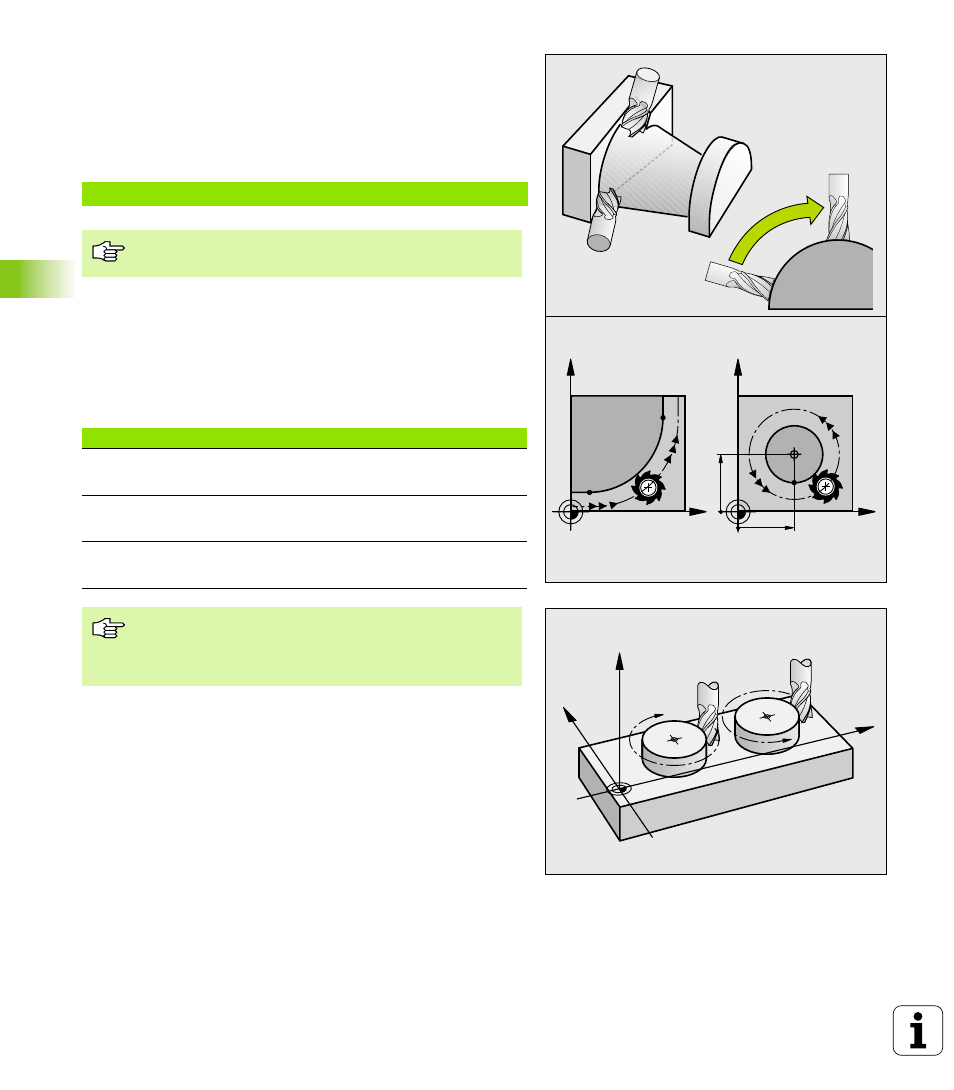
Circles and circular arcs
The TNC moves two axes simultaneously in a circular path relative to
the workpiece. You can define a circular movement by entering the
circle center CC.
When you program a circle, the TNC assigns it to one of the main
planes. This plane is defined automatically when you set the spindle
axis during a TOOL CALL:
Direction of rotation DR for circular movements
When a circular path has no tangential transition to another
contour element, enter the direction of rotation DR:
Clockwise direction of rotation: DR–
Counterclockwise direction of rotation: DR+
L X+20 Y+10 Z+2 A+15 C+6 R0 F100 M3
The TNC graphics cannot simulate movements in more
than three axes.
Tool axis
Main plane
Z
XY, also
UV, XV, UY
Y
ZX, also
WU, ZU, WX
X
YZ, also
VW, YW, VZ
You can program circles that do not lie parallel to a main
plane by using the function for tilting the working plane
(see “WORKING PLANE (Cycle 19),” page 330) or Q
parameters (see “Principle and Overview,” page 356).
X
Y
X
Y
CC
X
CC
Y
CC
CC
CC
DR–
DR+
X
Z
Y
