H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 103
93
Two types of CHAP authentication exist: one-way CHAP authentication and two-way CHAP
authentication. In one-way CHAP authentication, one side of the link acts as the authenticator and the
other acts as the authenticatee. In two-way authentication, each side serves as both the authenticator and
the authenticatee. Normally, one-way CHAP authentication is adopted.
In one-way CHAP authentication, the authenticator may or may not be configured with a username. H3C
recommends that you configure a username for the authenticator to identify the authenticator more
easily.
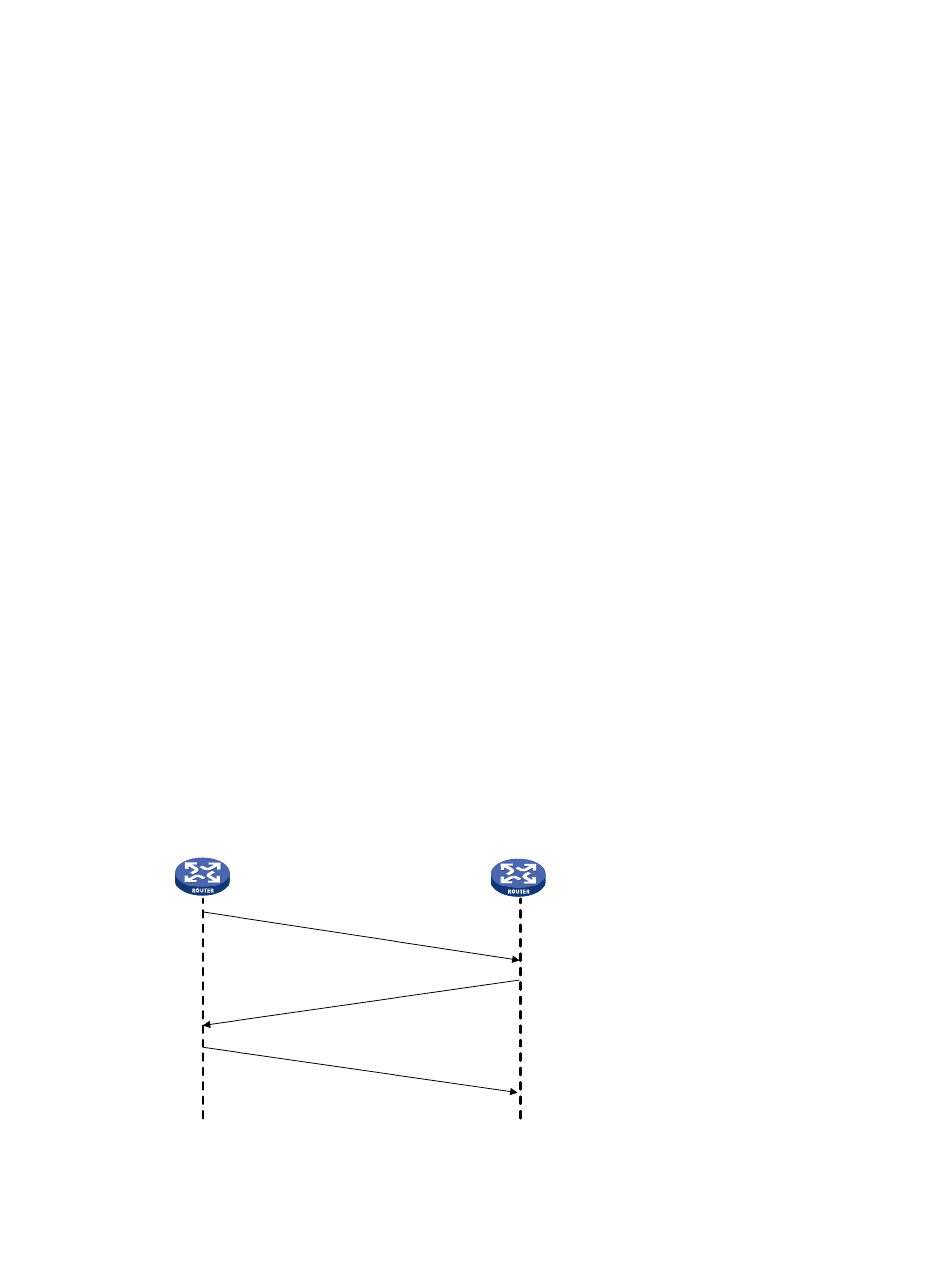
If the authenticator is configured with a username, CHAP authentication is performed in the following
workflow.
1.
The authenticator initiates an authentication by sending a randomly-generated packet (Challenge)
to the authenticatee. The packet carries the local username with it in addition.
2.
When the authenticatee receives the authentication request, it searches the local user list for the
password of the username carried in the received packet, encrypts the packet by using the MD5
algorithm, with the packet ID and the password as the parameters, and then sends the encrypted
packet and the local username to the authenticator (Response).
3.
The authenticator encrypts the original randomly-generated packet using the MD5 algorithm, with
the password of the authenticatee it maintains as the parameter, compares the encrypted packet
with the one received from the authenticatee, and returns an Acknowledge or Not Acknowledge
packet depending on the comparison result.
If the authenticator is not configured with a username, CHAP authentication is performed in the following
workflow.
1.
The authenticator initiates an authentication by sending a randomly-generated packet (Challenge)
to the authenticatee.
2.
When the authenticatee receives the authentication request, it encrypts the packet by using the
MD5 algorithm, with the packet ID and the default CHAP password as the parameters, and then
sends the encrypted packet and its own username to the authenticator (Response).
3.
The authenticator encrypts the original randomly-generated packet by using the MD5 algorithm,
with the password of the authenticatee it maintains as the parameter, compares the encrypted
packet with the one received from the authenticatee, and returns an Acknowledge or Not
Acknowledge packet depending on the comparison result.
Figure 26 CHAP authentication
Authenticator
Authenticatee
Challenge
Rsponse
Ack or Not Ack
- H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C WA3600 Series Access Points H3C WA2600 Series WLAN Access Points
