Rockwell Automation 1756-HSC ControlLogix High Speed Counter Module User Manual
Page 12
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-UM007C-EN-P - November 2011
12 1756-HSC Module Features
This user manual also details the Frequency operational modes that are
available depending on which one is required for your application. Frequency
can be calculated in one of three ways:
• frequency (rate measurement).
• period rate.
• continuous rate.
All three Frequency modes determine the frequency of input pulses by
counting pulses over a user-defined time interval. If the revolution is spinning
in a clockwise direction, the frequency is positive; in a counterclockwise
direction it’s decreasing (negative) frequency.
See
for more details on Frequency modes.
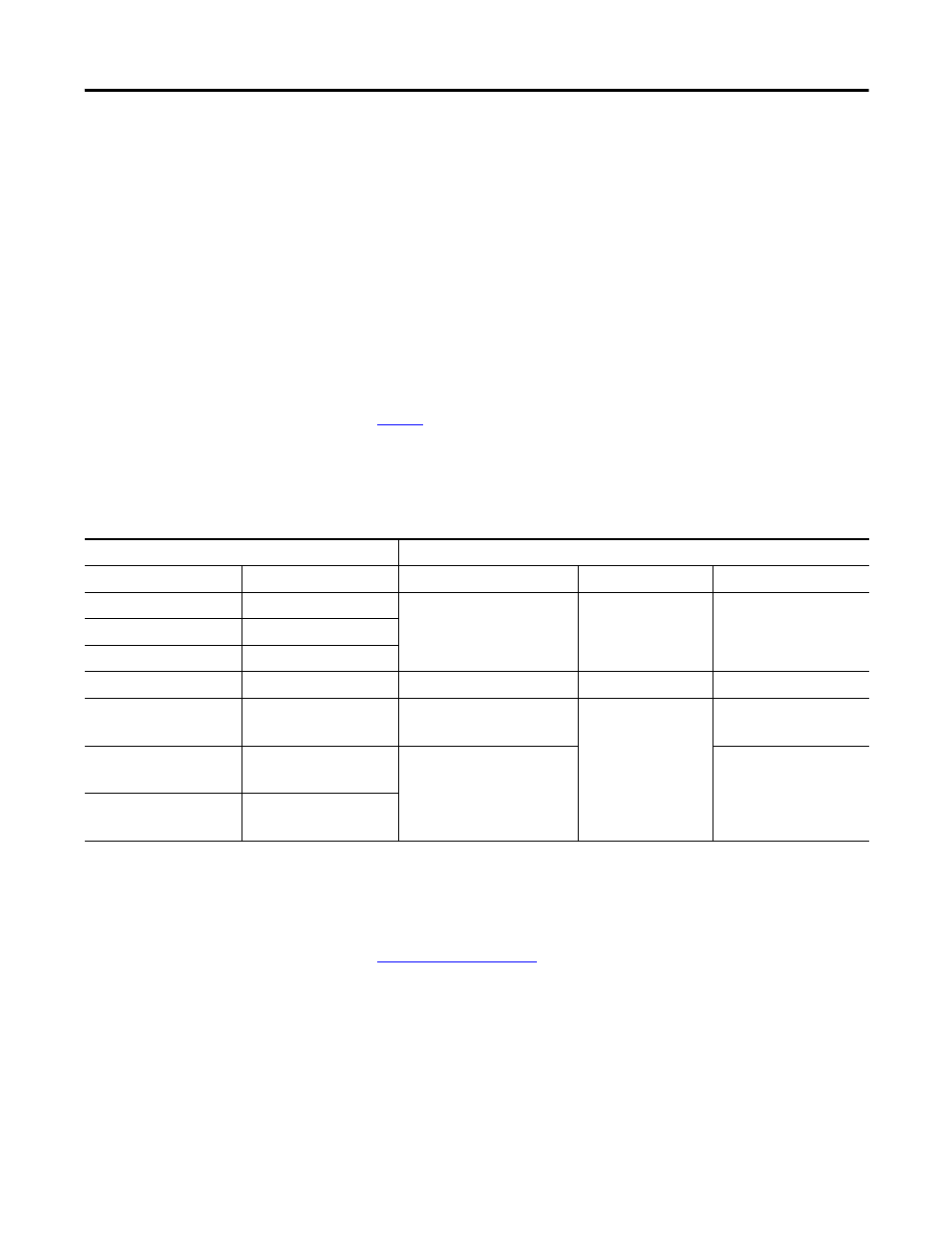
Pulse counts and frequency values are stored in one of three input tags (based
on the mode) as shown in the table.
See
in Appendix C for a list of tags.
Mode and Input Tag Values for the 1756-HSC/B Module
Comm Format = HSC Data-extended
Tags
Mode
Mode Description
Present Value
Stored Value
Totalizer
0
Counter
Accumulated count
Stored value
Directional frequency
(2)
1
Encoder X1
2
Encoder X4
3
Counter Not Used
N/A
N/A
N/A
4
Frequency
(Rate Measurement)
(1)
No. of input pulses occurring
in sample period
Frequency
Accumulated count
(3)
5
Frequency
(Period Rate)
No. of 4 MHz pulses
occurring in sample period
Accumulated count
6
Frequency
(Continuous Rate)
(1)
Modes where frequency controls the outputs.
(2)
B-input state defines direction (Counter mode).
(3)
Rollover/Preset settings apply.
