Module do’s and dont’s – Vicor VI-J00 Family DC-DC Converters and Configurable Power Supplies User Manual
Page 6
Design Guide & Applications Manual
For VI-200 and VI-J00 Family DC-DC Converters and Configurable Power Supplies
VI-200 and VI-J00 Family Design Guide
Rev 3.5
vicorpower.com
Page 5 of 98
Apps. Eng. 800 927.9474
800 735.6200
Output OVP. The VI- / MI-200, with the exception of
VI- / MI-J00s, has an internal overvoltage protection circuit
that monitors the voltage across the output power pins. It
is designed to latch the converter off at 115 – 135% of
rated output voltage. It is not a crowbar circuit, and if a
module is trimmed above 110% of rated output voltage,
OVP may be activated. Do not backdrive the output of
the converter module to test the OVP circuit.
CAUTION: When trimming up VI-/ MI-J00 modules,
additional care should be taken as an improper
component selection could result in module failure.
Improper connection of the sense leads on VI-/ MI-J00
modules can also result in an excessive overvoltage
condition and module failure.
Input Reverse Voltage Protection. The module may be
protected against reverse input voltages by the addition of
a diode in series with the positive input, or a reverse
shunt diode with a fuse in series with the positive input.
See
, the Input Attenuator Module (IAM /MI-IAM)
provides input reverse voltage protection when used with
a current limiting device (fuse).
THERMAL / MECHANICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Baseplate. Operating temperature of the baseplate, as
measured at the center mounting slot on the –IN, –OUT
side, can not exceed rated maximum. ThermMate or
thermal compound should be used when mounting the
module baseplate to a chassis or heat sink. All six
mounting holes should be used. Number six (#6) machine
screws should be torqued to 5-7 in-lbs, and use of Belville
washers is recommended.
The module pins are intended for PCB mounting either by
wave soldering to a PCB or by insertion into one of the
recommended PCB socket solutions.
CAUTION: Use of discrete wires soldered directly
to the pins may cause intermittent or permanent
damage to the module; therefore, it is not
recommended as a reliable interconnection scheme
for production as a final released product. See
for packaging options designed for
discrete wire connections (BusMod, MegaMod).
In addition, modules that have been soldered into printed
circuit boards and have subsequently been removed
should not be reused.
THERMAL AND VOLTAGE HAZARDS
Vicor component power products are intended to be used
within protective enclosures. Vicor DC-DC converters
work effectively at baseplate temperatures, which could
be harmful if contacted directly. Voltages and high
currents (energy hazard) present at the pins and circuitry
connected to them may pose a safety hazard if contacted
or if stray current paths develop. Systems with removable
circuit cards or covers which may expose the converter(s)
or circuitry connected to the converters, should have proper
guarding to avoid hazardous conditions.
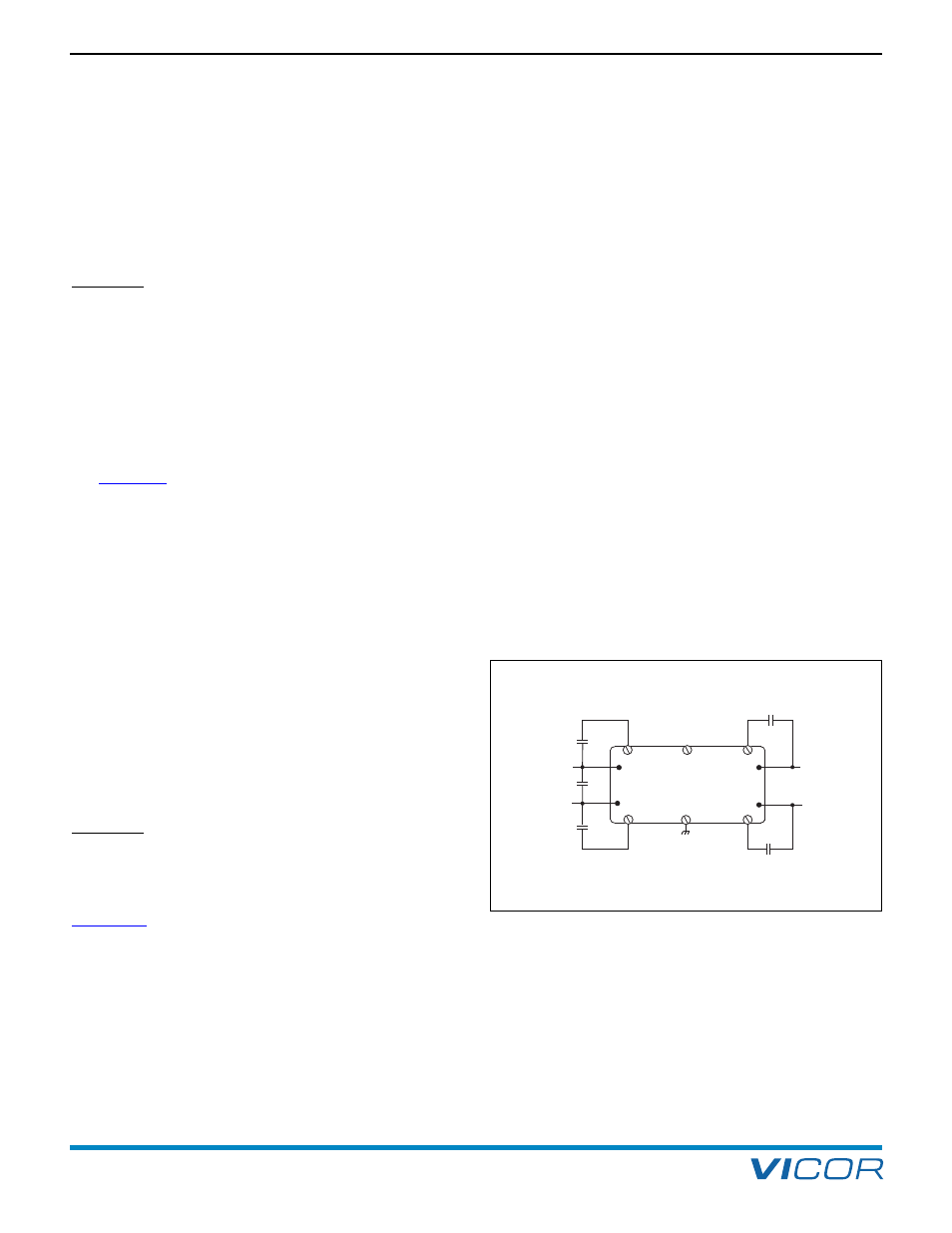
EMC CONSIDERATIONS
All applications utilizing DC-DC converters must be properly
bypassed, even if no EMC standards need to be met. Bypass
IN and OUT pins to each module baseplate as shown in
Figure 3–1. Lead length should be as short as possible.
Recommended values vary depending on the front end, if
any, that is used with the modules, and are indicated on the
appropriate data sheet. In most applications, C1a – C1b is a
4,700 pF Y-capacitor (Vicor Part # 01000) carrying the
appropriate safety agency approval; C2a – C2b is a 4,700 pF
Y-capacitor (Vicor Part # 01000) or a 0.01 µF ceramic
capacitor rated at 500 V. In PCB mount applications, each of
these components is typically small enough to fit under the
module baseplate flange.
Figure 3–1 — IN and OUT pins bypassed to the module baseplate
and input cap for low AC impedance
3. Module Do’s and Dont’s
+OUT
+IN
–IN
–OUT
Zero Current
Switching
Converter
C1a
C1b
C2a
C2b
C3
