Raid 50 – Toshiba Magnia 560S User Manual
Page 47
RAID Levels
RAID Levels
29
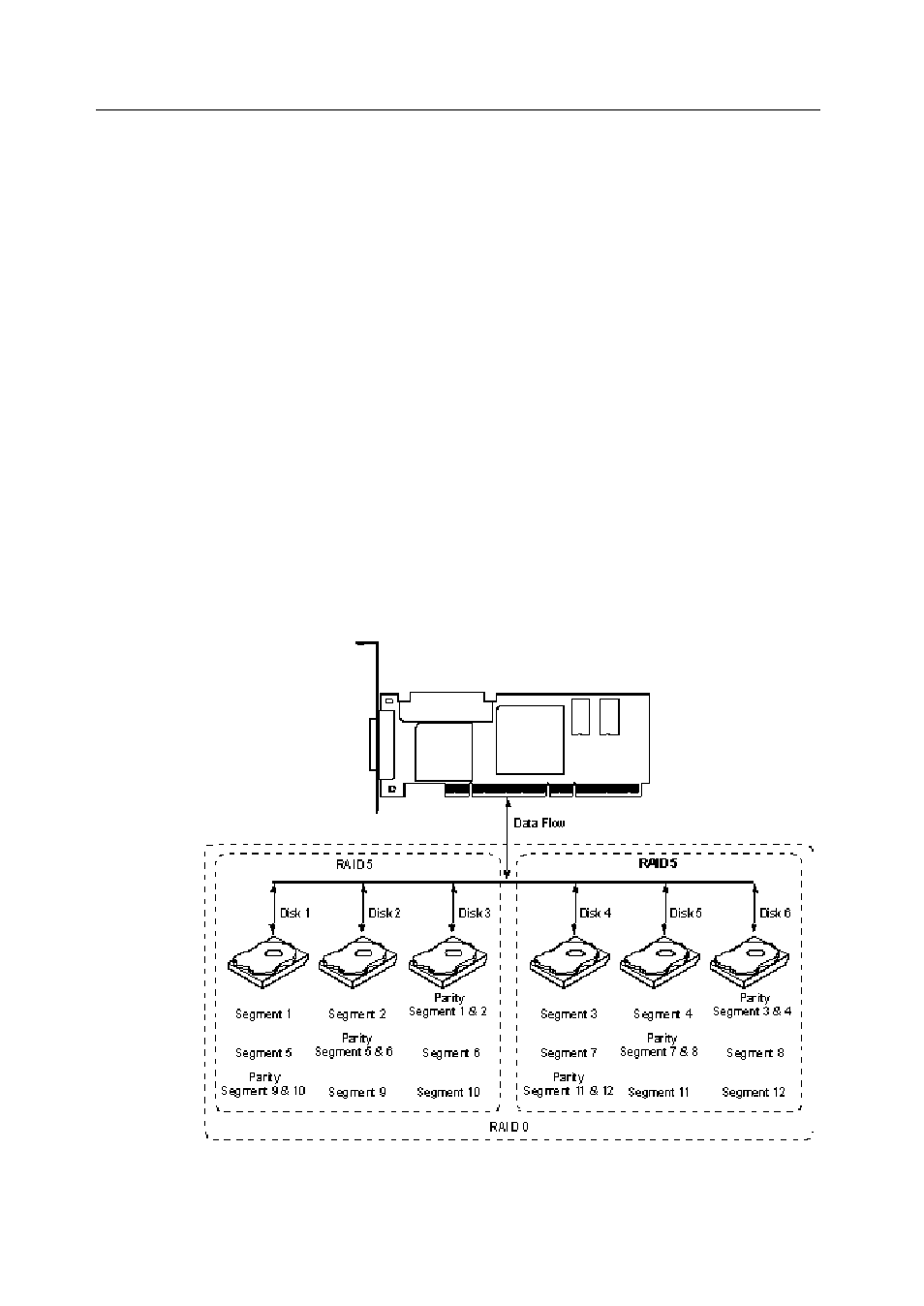
RAID 50
RAID 50 provides the features of both RAID 0 and RAID 5. RAID 50 includes both
parity and disk striping across multiple drives. RAID 50 is best implemented on two
RAID 5 disk arrays with data striped across both disk arrays. RAID 50 breaks up data
into smaller blocks, and then stripes the blocks of data to each RAID 5 raid set. RAID 5
breaks up data into smaller blocks, calculates parity by performing an exclusive-or on
the blocks, and then writes the blocks of data and parity to each drive in the array. The
size of each block is determined by the stripe size parameter, which is set during the
creation of the RAID set.
RAID 50 can sustain one to four drive failures while maintaining data integrity if each
failed disk is in a different RAID 5 array.
Uses
RAID 50 works best when used with data that requires high
reliability, high request rates, and high data transfer and medium to
large capacity.
Strong Points
RAID 50 provides high data throughput, data redundancy, and very
good performance.
Weak Points
Requires 2 to 4 times as many parity drives as RAID 5.
Drives
Six to 15
The initiator takes one ID per channel. This leaves 15 IDs available
for one channel.
