Introduction to raid, Raid benefits – Toshiba Magnia 560S User Manual
Page 27
Introduction to RAID
Introduction to RAID
9
Introduction to RAID
RAID is an array of multiple independent hard disk drives that provide high
performance and fault tolerance. A RAID disk subsystem improves I/O performance
over a computer using only a single drive. The RAID array appears to the host computer
as a single storage unit or as multiple logical units. I/O is expedited because several
disks can be accessed simultaneously. RAID systems improve data storage reliability
and fault tolerance compared to single-drive computers. Data loss because of a disk
drive failure can be recovered by reconstructing missing data from the remaining data
and parity drives.
RAID Benefits
RAID has gained popularity because it improves I/O performance and increases storage
subsystem reliability. RAID provides data security through fault tolerance and
redundant data storage. The RAID Controller Kit-G management software configures
and monitors RAID disk arrays.
Improved I/O
Although disk drive capabilities have improved drastically, actual performance has
been improved only three to four times in the last decade. Computing performance has
been improved over 50 times during the same time period.
Increased Reliability
The electro-mechanical components of a disk subsystem operate more slowly, require
more power, and generate more noise and vibration than electronic devices. These
factors reduce the reliability of data stored on disks.
In This Chapter
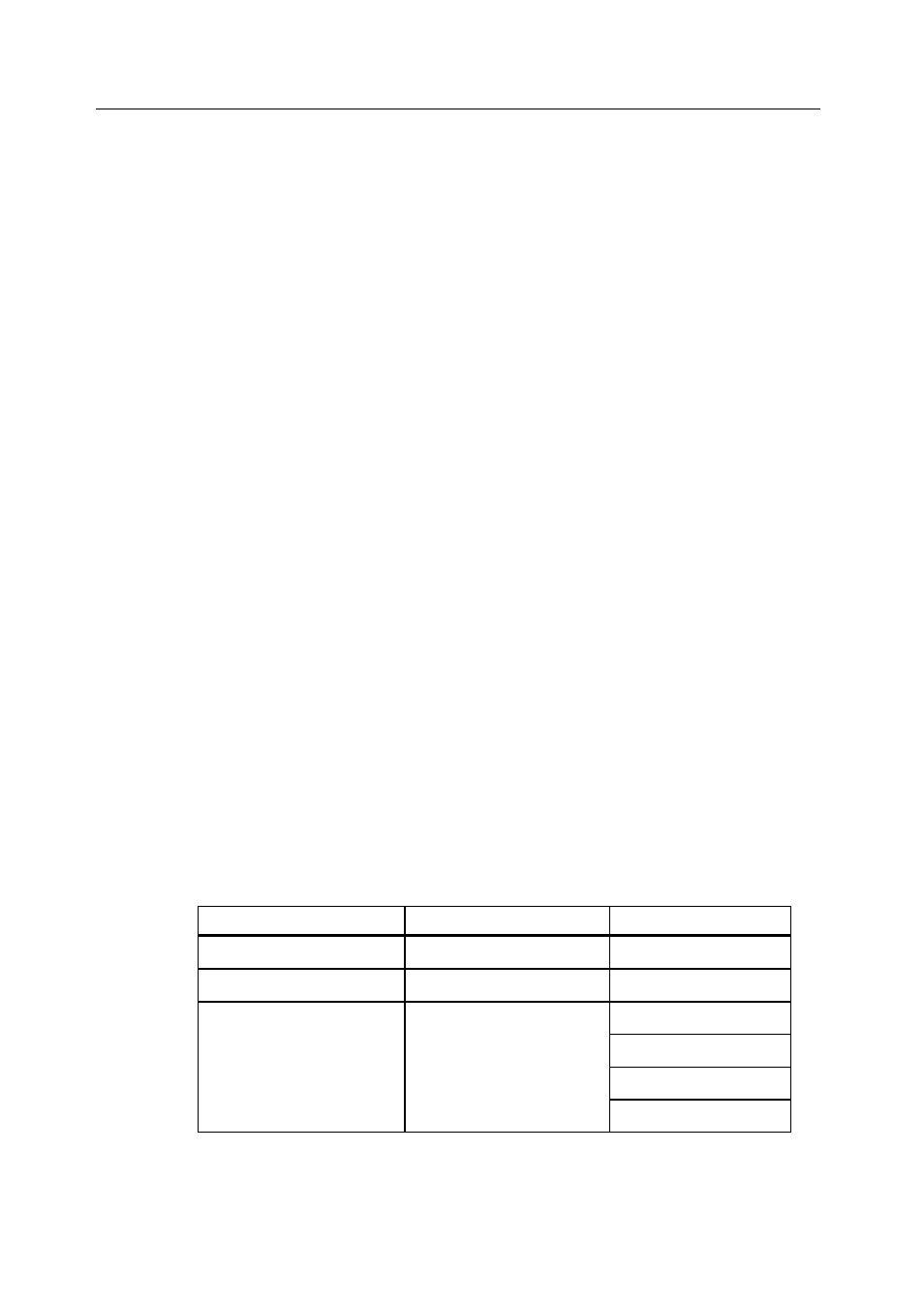
Table 2.1 lists the topics discussed in this chapter.
Table 2.1 Topics in this Chapter
Major Topic
Subtopic
Turn to
Host-based solution
page 10
RAID overview
page 11
Physical array
page 11
Logical drive
page 11
Fault tolerance
page 12
Consistency check
page 11
