Toshiba Magnia 560S User Manual
Page 42
RAID Levels
24
RAID Levels
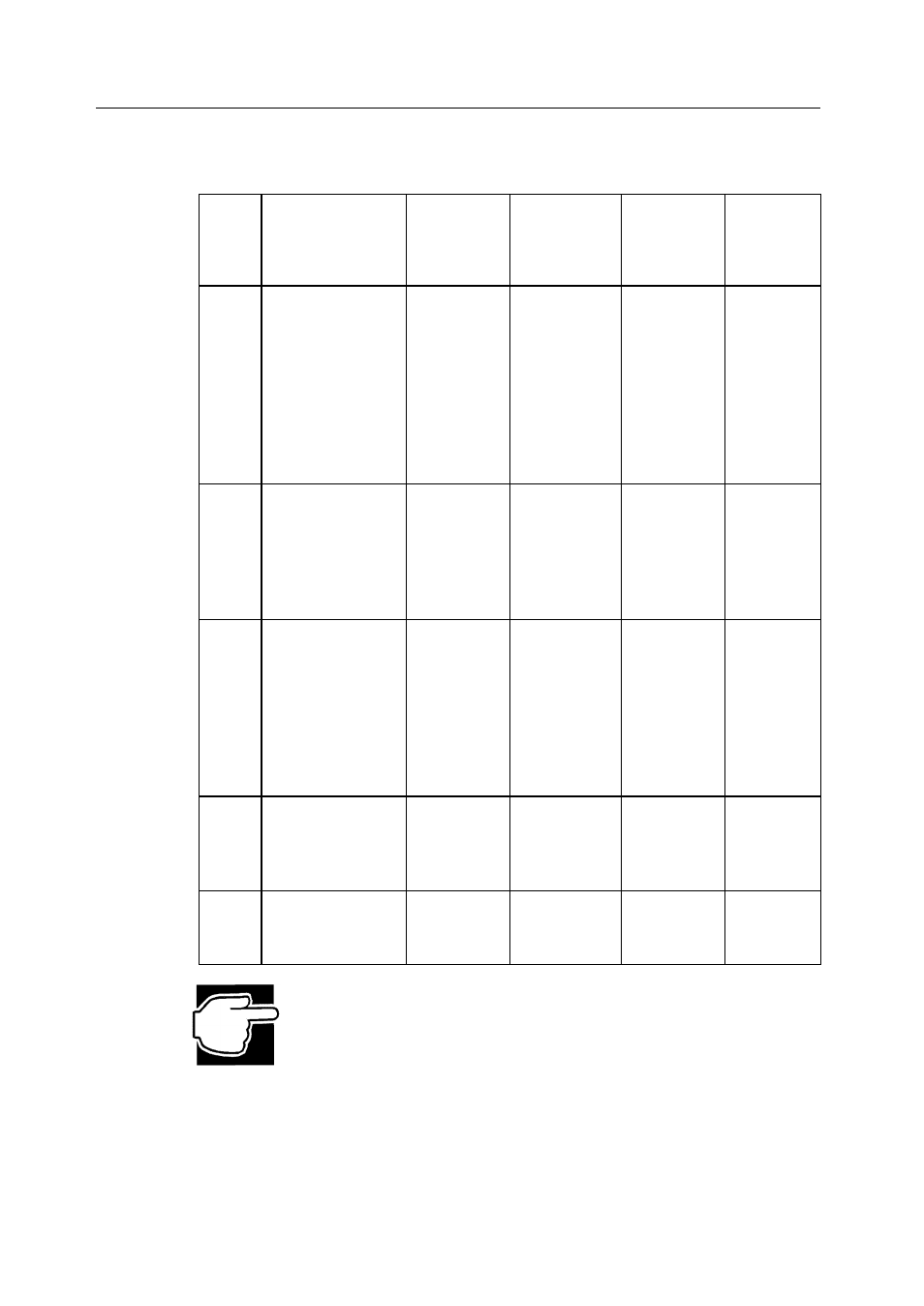
Table 3.2 describes the factors you need to consider when selecting a RAID level.
Table 3.2 Factors for Selecting RAID Levels
Level
Description and
Use
Pros
Cons
Maximum
Number of
Physical
Drives
Fault
Tolerant
0
Data divided in
blocks and
distributed
sequentially
(pure striping).
Use for non-
critical data that
requires high
performance.
High data
throughput
for large
files
No fault
tolerance.
All data lost
if any drive
fails.
One to 15
No
1
Data duplicated
on another disk
(mirroring). Use
for read-
intensive fault-
tolerant systems.
100% data
redundancy
Doubles
disk space.
Reduced
performance
during
rebuilds.
Two
Yes
5
Disk striping and
parity data across
all drives. Use for
high read volume
but low write
volume, such as
transaction
processing.
Achieves
data
redundancy
at low cost
Performance
not as good
as RAID 1
Three to 15
Yes
10
Data striping and
mirrored drives.
High data
transfers,
complete
redundancy
More
complicated
Four to 14
(must be a
multiple of
two)
Yes
50
Disk striping and
parity data across
all drives.
High data
transfers,
redundancy
More
complicated
Six to 15
Yes
NOTE: The maximum number of physical drives supported by the SCSI
320-1 controller is 15.
