Raid 5 – Toshiba Magnia 560S User Manual
Page 45
RAID Levels
RAID Levels
27
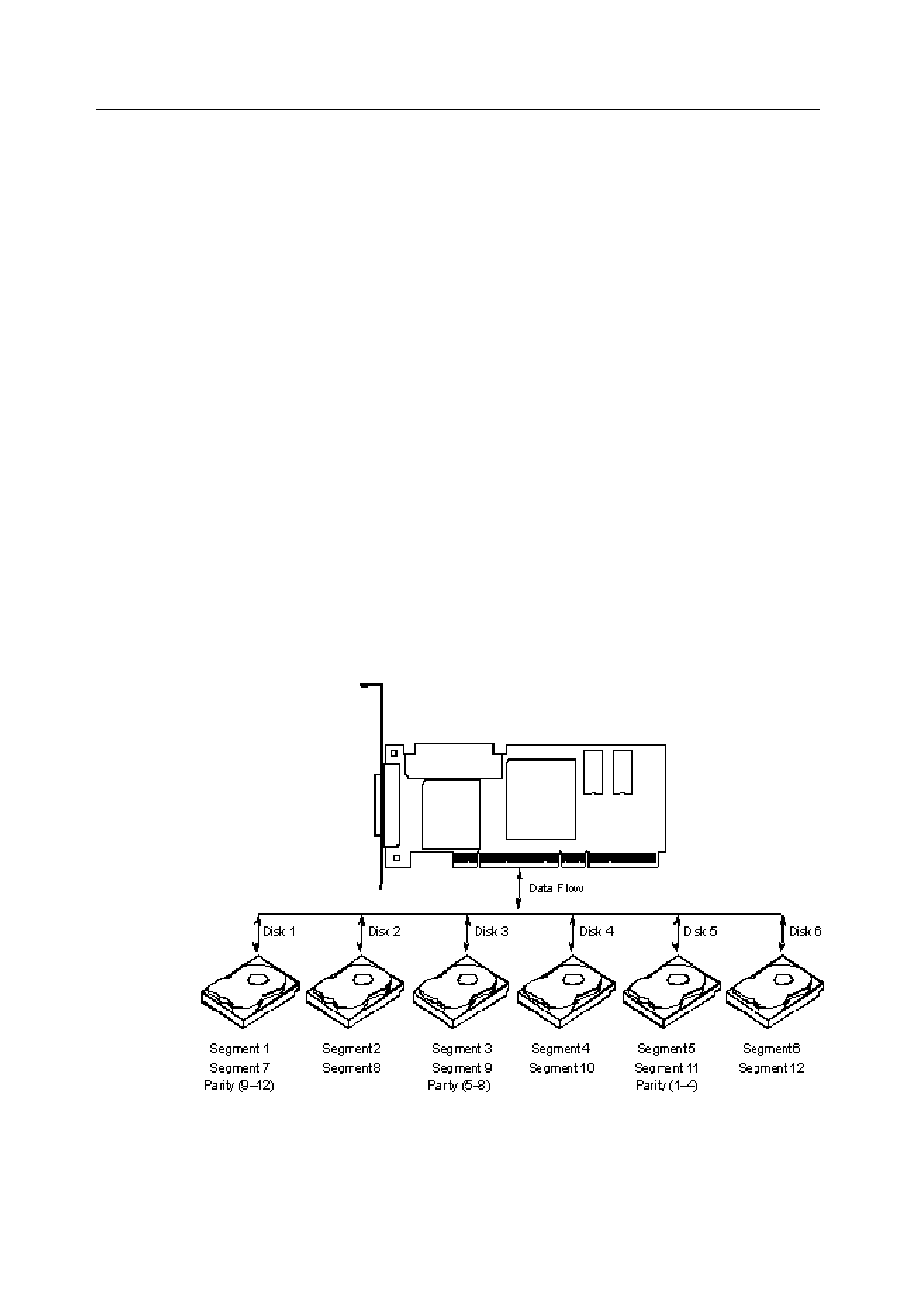
RAID 5
RAID 5 includes disk striping at the byte level and parity. In RAID 5, the parity
information is written to several drives. RAID 5 is best suited for networks that perform
a lot of small I/O transactions simultaneously.
RAID 5 addresses the bottleneck issue for random I/O operations. Since each drive
contains both data and parity numerous writes can take place concurrently. In addition,
robust caching algorithms and hardware based exclusive-or assist make RAID 5
performance exceptional in many different environments.
Uses
RAID 5 provides high data throughput, especially for large files. Use
RAID 5 for transaction processing applications because each drive
can read and write independently. If a drive fails, RAID Controller
Kit-G uses the parity drive to recreate all missing information. Use
also for office automation and online customer service that requires
fault tolerance. Use for any application that has high read request
rates ,but low write request rates.
Strong Points
Provides data redundancy and good performance in most
environments.
Weak Points
Disk drive performance will be reduced if a drive is being rebuilt.
Environments with few processes do not perform as well because the
RAID overhead is not offset by the performance gains in handling
simultaneous processes.
Drives
Three to 15.
