Basic behavior – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 90
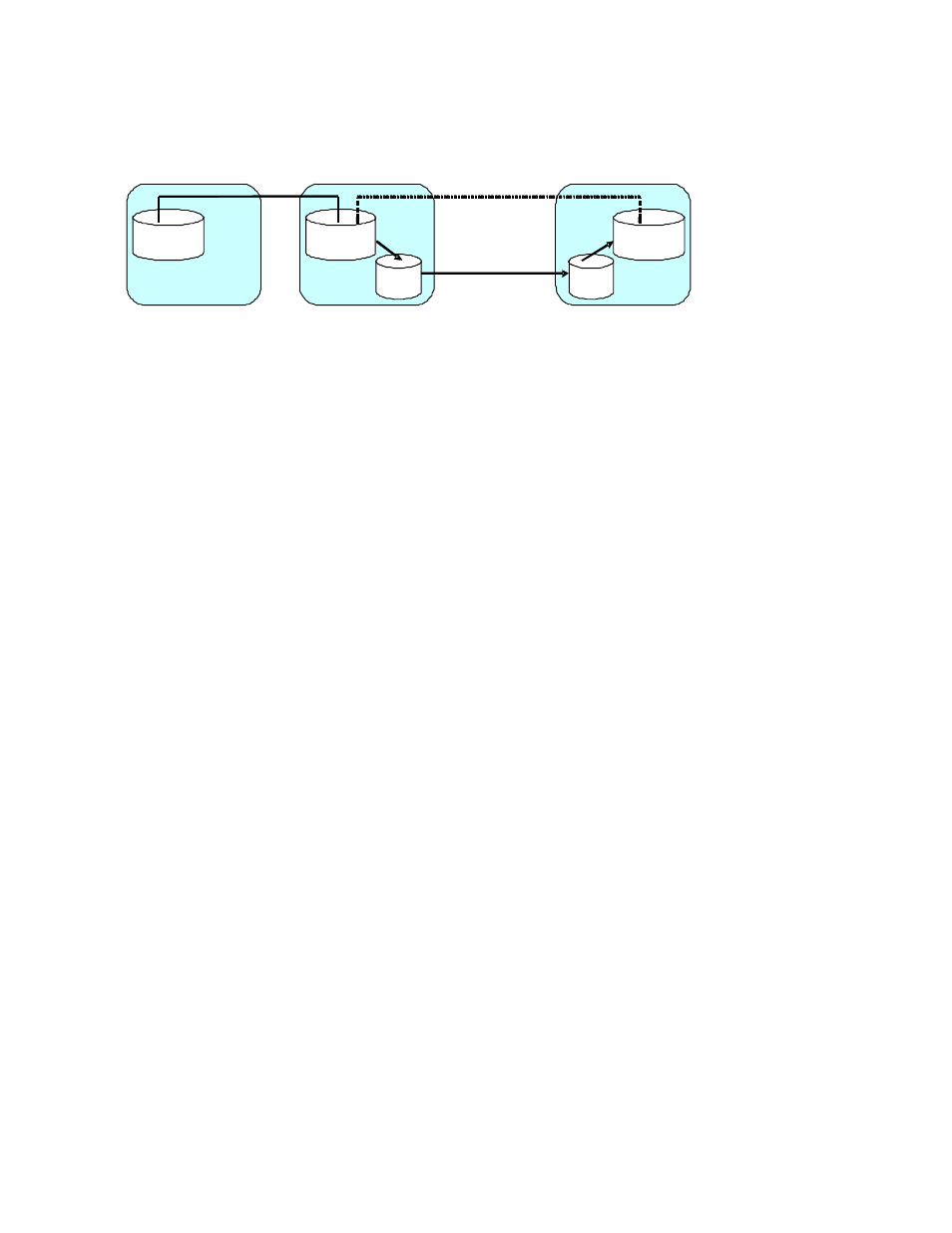
secondary data volume is the volume in the secondary site, which is within a long distance from the
intermediate site. If a host issues an I/O to the TCz Synchronous main volume in the primary site,
data will be transferred via TCz Synchronous and URz to the secondary site and will be restored to
the secondary data volume.
R-VOL/Primary
data volume
Master
JNLVOL
Restore
JNLVOL
Primary
site
Intermediate
site
Secondary
site
TCz Synchronous (Short distance)
URz (Remote distance)
M-VOL
Secondary
data VOL
Figure 35 3DC Cascading Configuration (Combining URz with TCz)
Data that is copied by TCz Synchronous is stored in the URz primary data volume. If a failure occurs
at the TCz Synchronous M-VOL, business tasks can continue by using data in the URz secondary data
volume containing data in the TCz Synchronous M-VOL. Data in the TCz Synchronous M-VOL is restored
via URz to the secondary data volume in the secondary site, with update sequence integrity ensured. If a
failure occurs at both TCz Synchronous M-VOL and secondary data volume due to a disaster or some
other reason, disaster recovery can be performed using the URz secondary data volume.
A TCz Synchronous M-VOL must be created in an XP storage system. The fence level of the TCz
Synchronous M-VOL must be Data (CRIT=Y (ALL)).
Basic Behavior
This section explains the basic behavior of a 3DC cascading configuration under the following conditions:
•
The status of the TCz Synchronous pair is Duplex. The status of the URz pair is also Duplex.
•
A host in the primary site issues an I/O request to the TCz Synchronous M-VOL
As illustrated in Figure 3.28, if a host in the primary site issues an I/O request, data will be stored into
the TCz Synchronous M-VOL. The data will also be stored into the TCz Synchronous R-VOL (i.e., the URz
primary data volume). After that, the fact that data has been stored will be reported to the primary site,
and then the fact that I/O has been finished will be reported to the host. Also, data in the URz primary
data volume (i.e., TCz Synchronous R-VOL) will be stored as journal data into the master journal volume
in the intermediate site. Sequence numbers, which indicates the order that data will be written, will be
added to these journal data. Also, journal data in the master journal volume in the intermediate site will
be transferred, independently from and asynchronously with the behavior mentioned above, to the restore
journal volume in the secondary site. Next, the journal data in the restore journal volume will be restored
to the URz secondary data volume in the secondary site; the journal data will be restored in the order
of sequence numbers that are added to journal data. These sequence numbers ensure that updates to
URz secondary data volumes in the secondary site will be made in the same order that updates to TCz
Synchronous M-VOL in the primary site are made.
As explained above, when the host in the primary site issues an I/O request to the TCz Synchronous
M-VOL, the data will be restored asynchronously to the URz secondary data volume in the secondary site
in a remote location.
90
Preparing for Universal Replicator z/OS Operations
