Journalgroup operations, Types of journal, Journal group operations – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 39
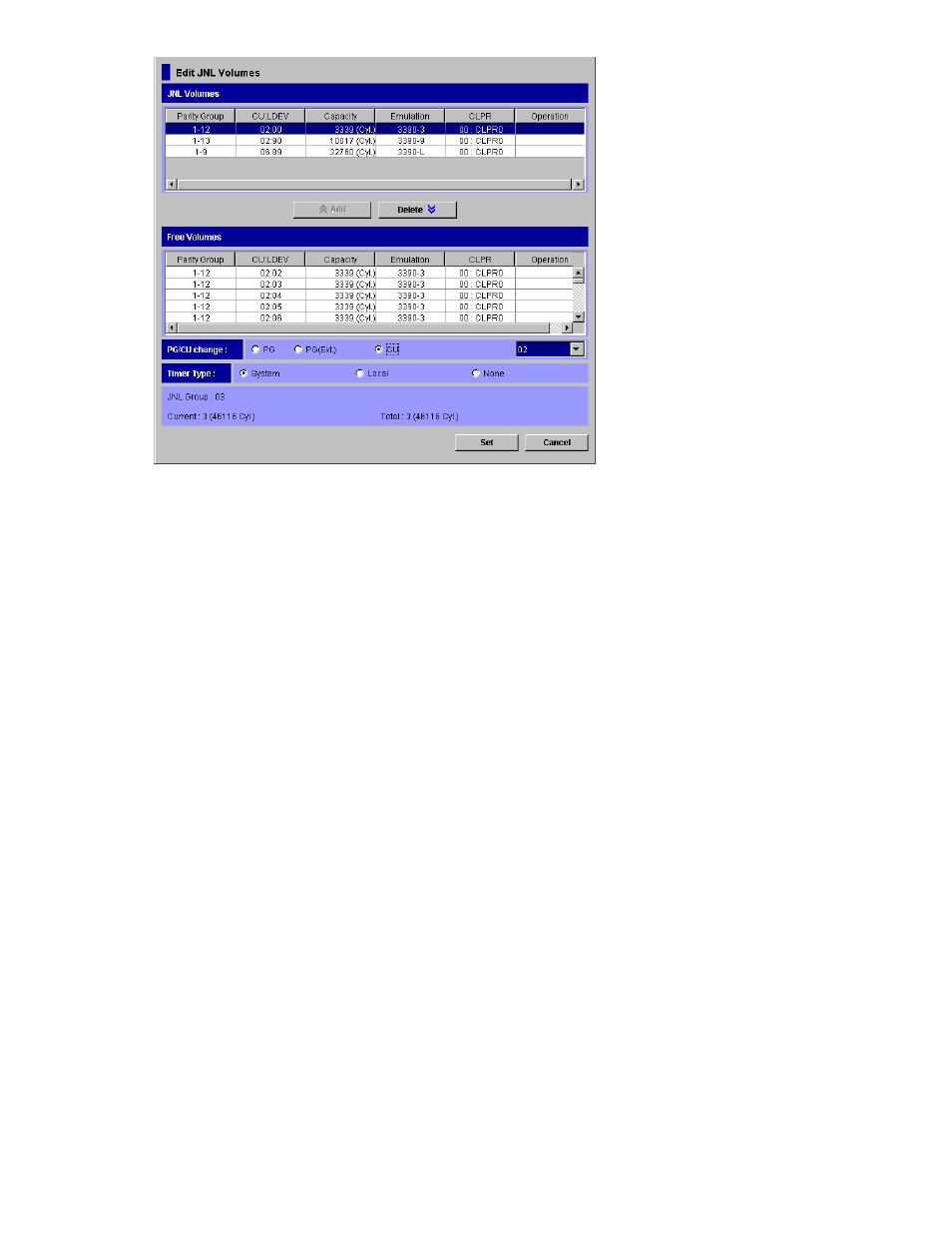
Figure 6 Selecting and Settling Journal at the Secondary Subsystem
The secondary subsystem settles and restores the journal data to the secondary data volume as follows:
•
Journal data stored in the cache
The journal data is copied to the corresponding cached track and promoted to formal data.
•
Journal data stored in the restore journal volume
The journal data is read from the restore journal volume to cache. The journal data that is read to
cache is copied to the existing cache track and promoted to formal data. After that, the space for
the restore journal volume is released.
Types of Journal
In addition to the journal data for updating, the primary subsystem sends control information to the
secondary subsystem. This control information indicates when volume pair status changes and when
a primary subsystem power-off sequence is initiated, and also maintain sequence numbers in periods
of low host activities.
Journal Group Operations
URz journal groups enable update sequence consistency to be maintained across a journal group of
volumes. The primary data volumes and secondary data volumes of the pairs in a journal group must
be located within one physical primary storage system and one physical secondary storage system
(1-to-1 requirement).
When more than one data volume is updated, the order that the data volumes are updated is managed
within the journal group that the data volumes belong to. Consistency in data updates is maintained
among paired journal groups. URz uses journal groups to maintain data consistency among data
volumes.
This section describes the following journal group operation options available in URz:
•
Timer type option
•
Journal group operations
Hitachi Universal Replicator for z/OS user guide for XP12000/XP10000 Disk Arrays and SVS 200
39
