Basic behavior – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 73
To perform arbitration processing, the supervisor DKC must be connected with the subordinate DKCs. For
details on connections between secondary subsystems,.
Basic Behavior
This section explains the basic behavior of URz under the following conditions:
•
There are two primary subsystems and two secondary subsystems.
•
The status of all the URz pairs that use journal groups in the extended consistency group is Duplex.
•
The primary host issues write requests to URz primary data volumes.
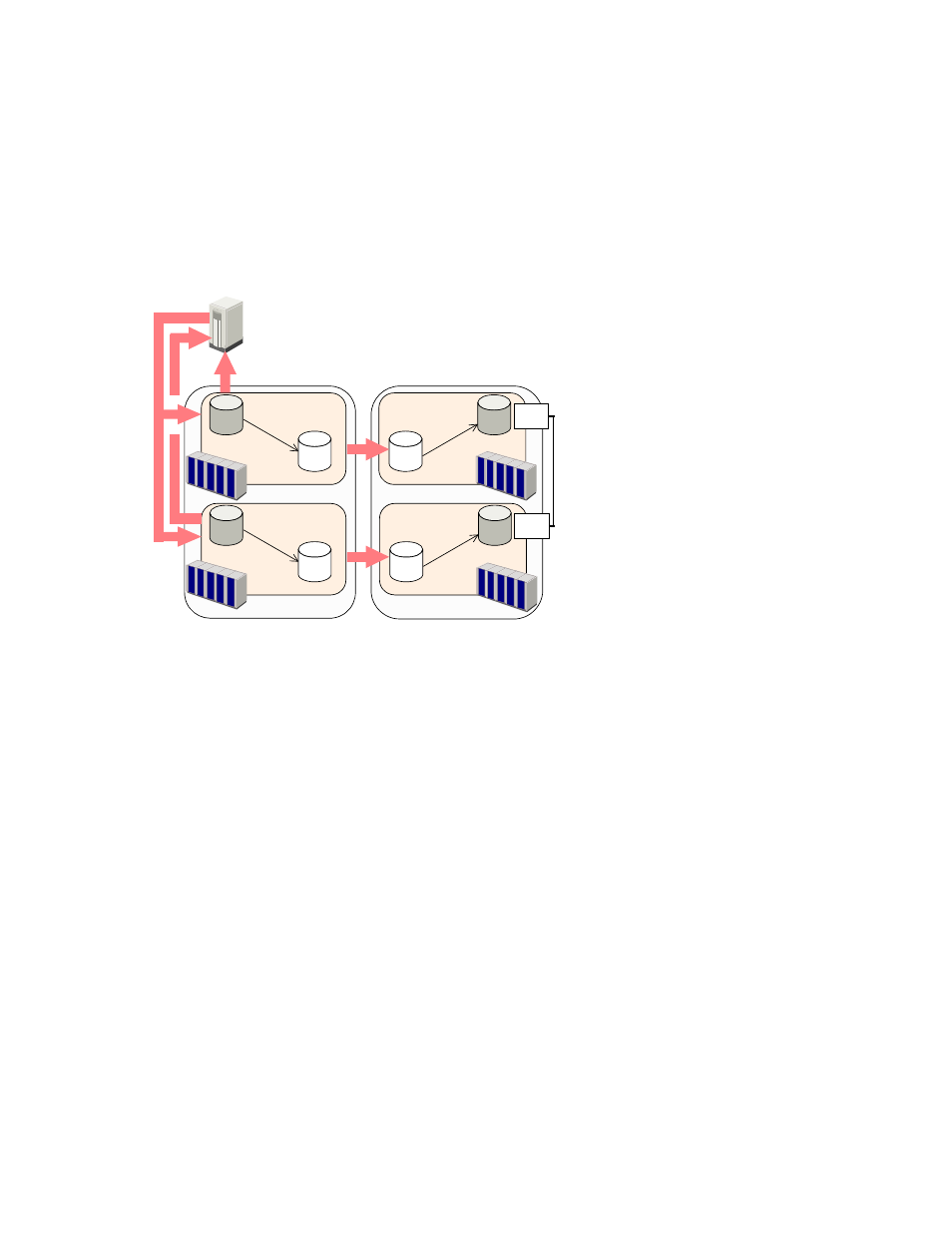
The following figure illustrates a URz operation when the above conditions are satisfied.
Primary host (can add time stamps)
Master JNL VOL
(3)
Secondary site
Primary storage system 1
Primary data
volume
Master JNL VOL
Primary data
volume
Secondary data
volume
Restore JNL VOL
Secondary storage system 1
Secondary data
volume
Restore JNL VOL
Secondary storage system 2
Target
port
External
port
Primary storage system 2
Primary site
(3)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
(4)
(4)
(5)
(5)
Figure 17 A URz Operation When Two Primary Subsystems and Two Secondary
Subsystems are Used
The numbers in the above figure indicate the order that the processing is performed, and correspond to
the numbers in the numbered procedure below:
1.
The primary host issues write requests to primary subsystems. Time stamps are added to the
data to be written.
2.
The primary subsystems receive the write requests, and then notify the primary host that primary
data volumes are updated.
3.
The URz journal obtain function stores data updated in primary data volumes to master journal
volumes as journal data. Time stamp information added by the primary host will be added to
journal data. Also, sequence numbers indicating the order of writing will be added to journal
data.
4.
The URz journal copy function copies journal data from the master journal volumes to the
corresponding restore journal volumes. This journal copy operation will be performed
asynchronously with the journal obtain operation.
5.
The secondary subsystem 1 (i.e., the supervisor DKC) performs arbitration processing. In other
words, the secondary subsystem 1 restores journal data of the secondary subsystems 1 and
2, based on the time stamps and the sequence numbers added to the journal data, so that
consistency with the primary data volume is maintained.
The flow of the arbitration processing is as follows:
1.
The supervisor DKC compares the time stamps, and then selects the oldest time stamp.
2.
The supervisor DKC requests the subordinate DKCs to restore the journal data that has the
selected time stamp.
Hitachi Universal Replicator for z/OS user guide for XP12000/XP10000 Disk Arrays and SVS 200
73
