HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 77
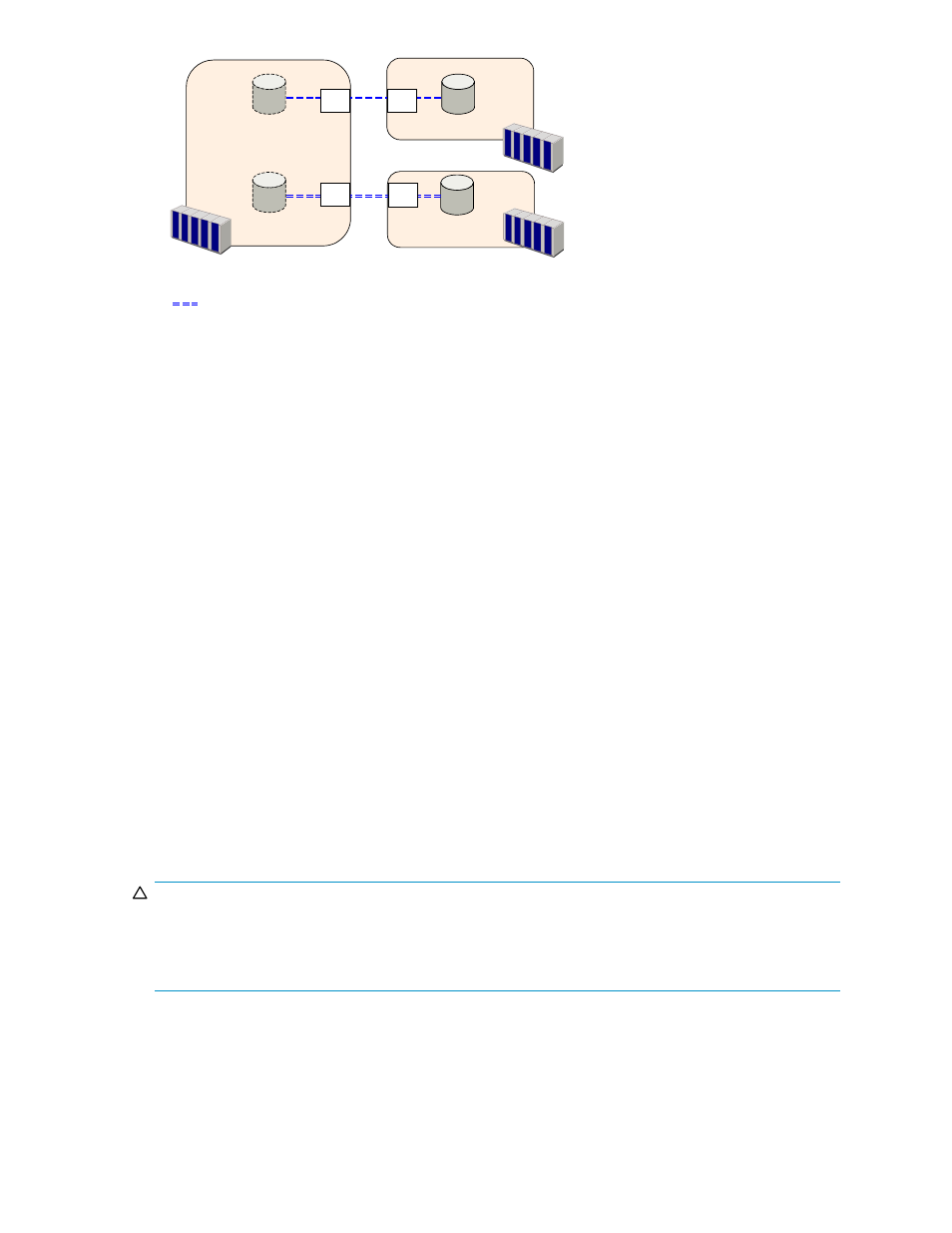
Supervisor DKC
(Secondary storage system 1)
Subordinate DKC
(Secondary storage system 2)
Remote
command device
A
A’
B
B’
Subordinate DKC
(Secondary storage system 3)
Target
port
External
port
External
port
Target
port
Command device
Command device
Remote
command device
Legend
:
mapping
Figure 19 An Example of Connections among Secondary Subsystems
Based on the example in Figure 3.12, the subsections below explain configuration of paths and ports,
and creation of remote command devices.
Configuring paths and Ports to Establish Connections among Secondary Storage Systems
To establish connections among secondary subsystems, you must configure external ports on the subsystem
that should be used as the supervisor DKC. After that, you must configure paths between these external
ports and the target ports on the subsystems that should be used as subordinate DKCs. In the example in
Figure 3.12, the secondary subsystem 1 has external ports, each of which is connected with a target port
on the secondary subsystem 2 and 3. For details on external ports, please refer to the Universal Volume
Manager User’s Guide. For details on configuring paths, please refer to the LUN Manager User’s Guide.
By using fibre channel switches, target ports can also be connected to RCU target ports on secondary
subsystems. For details on RCU target ports, see “
Initiator Ports and RCU Target Ports
” on page 28. For
details on configuring ports, see
Creating Remote Command Devices to Establish Connections among Secondary Storage
Systems
To establish connections among secondary subsystems, first you must create a command device in each
of the secondary subsystems. Next you must create mapping between command devices in the supervisor
DKC and the subordinate DKCs. Thus, the supervisor DKC will be able to use command devices in
subordinate DKCs via remote command devices.
In the example of Figure 3.12, the command devices A and B are created in the secondary subsystems 2
and 3. Also, remote command devices are created in the secondary subsystem 1 (i.e., the supervisor
DKC), and are mapped to the secondary subsystems 2 and 3 (i.e., subordinate DKCs).
The emulation type of command devices and remote command devices must be OPEN-V. For details on
remote command devices, please refer to the Universal Volume Manager User’s Guide.
CAUTION:
If maintenance operations are performed on remote command devices that are used for connections
among secondary subsystems, the pair will be suspended according to a failure. To avoid this, you must
remove all journal groups in the extended consistency group that uses the remote command devices to
be maintained.
Hitachi Universal Replicator for z/OS user guide for XP12000/XP10000 Disk Arrays and SVS 200
77
