Message exchange during authentication – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Security Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 318
300
Multi-Service IronWare Security Configuration Guide
53-1003035-02
How 802.1x port security works
8
By default, all controlled ports on the device are placed in the authorized state, allowing all traffic.
When authentication is activated on an 802.1x-enabled interface, the controlled port on the
interface is placed initially in the unauthorized state. When a client connected to the port is
successfully authenticated, the controlled port is then placed in the authorized state until the client
logs off. Refer to
“Enabling 802.1x port security”
for more information.
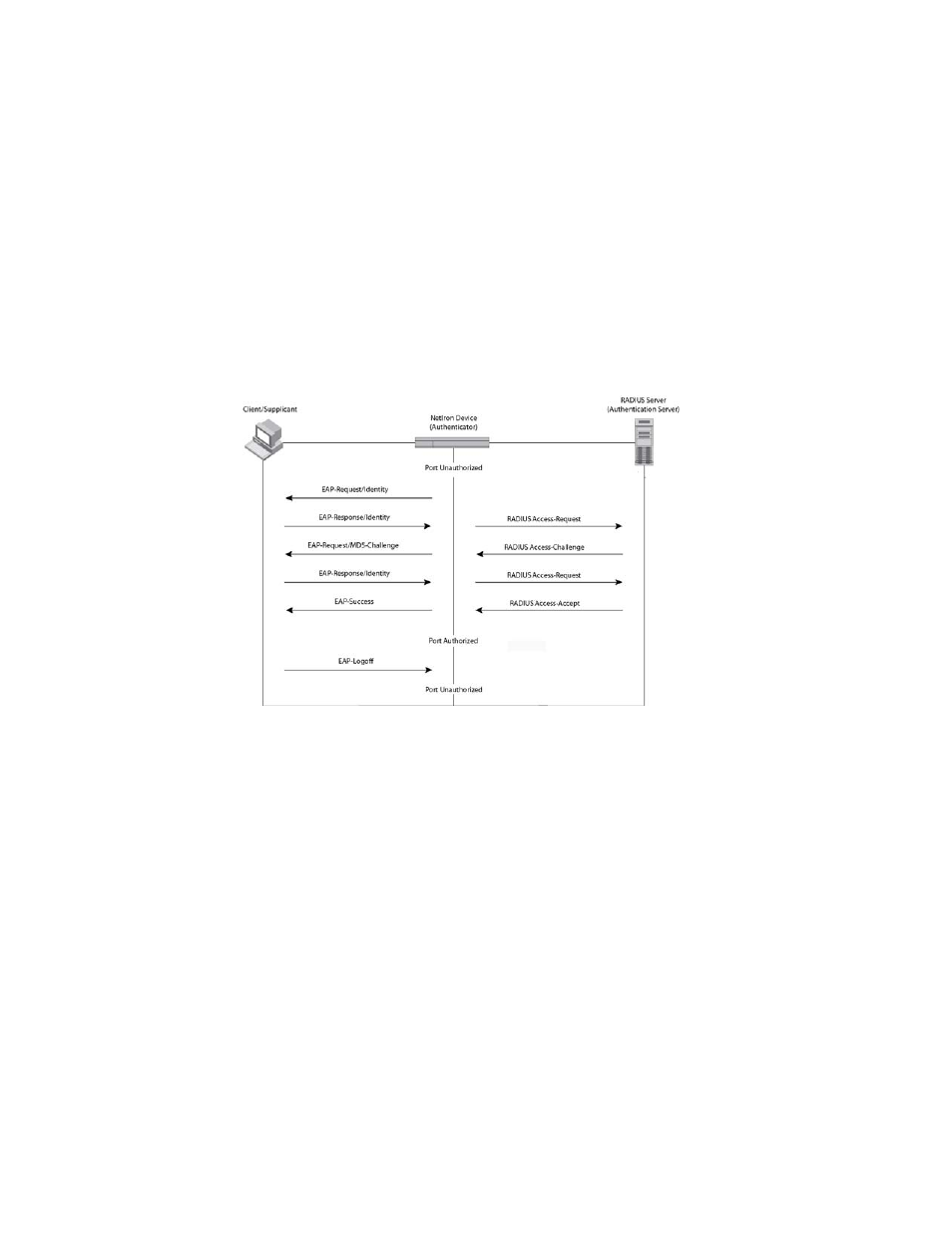
Message exchange during authentication
illustrates a sample exchange of messages between an 802.1x-enabled client, a device
acting as Authenticator, and a RADIUS server acting as an Authentication Server.
FIGURE 5
Message exchange during authentication
In this example, the Authenticator (the device) initiates communication with an 802.1x-enabled
client. When the client responds, it is prompted for a user name (255 characters maximum) and
password. The Authenticator passes this information to the Authentication Server, which
determines whether the client can access services provided by the Authenticator. When the client
is successfully authenticated by the RADIUS server, the port is authorized. When the client logs off,
the port becomes unauthorized again.
Brocade’s 802.1x implementation supports dynamic VLAN assignment. If one of the attributes in
the Access-Accept message sent by the RADIUS server specifies a VLAN identifier, and this VLAN is
available on the device, the client’s port is moved from its default VLAN to the specified VLAN.
When the client disconnects from the network, the port is placed back in its default VLAN. Refer to
“Configuring dynamic VLAN assignment for 802.1x ports”
for more information.
Brocade’s 802.1x implementation supports dynamically applying an IP ACL or MAC address filter to
a port, based on information received from the Authentication Server.
