Communication between the devices – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Security Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 316
298
Multi-Service IronWare Security Configuration Guide
53-1003035-02
How 802.1x port security works
8
Authentication server – The device that validates the client and specifies whether or not the client
may access services on the device. The device supports Authentication Servers running RADIUS.
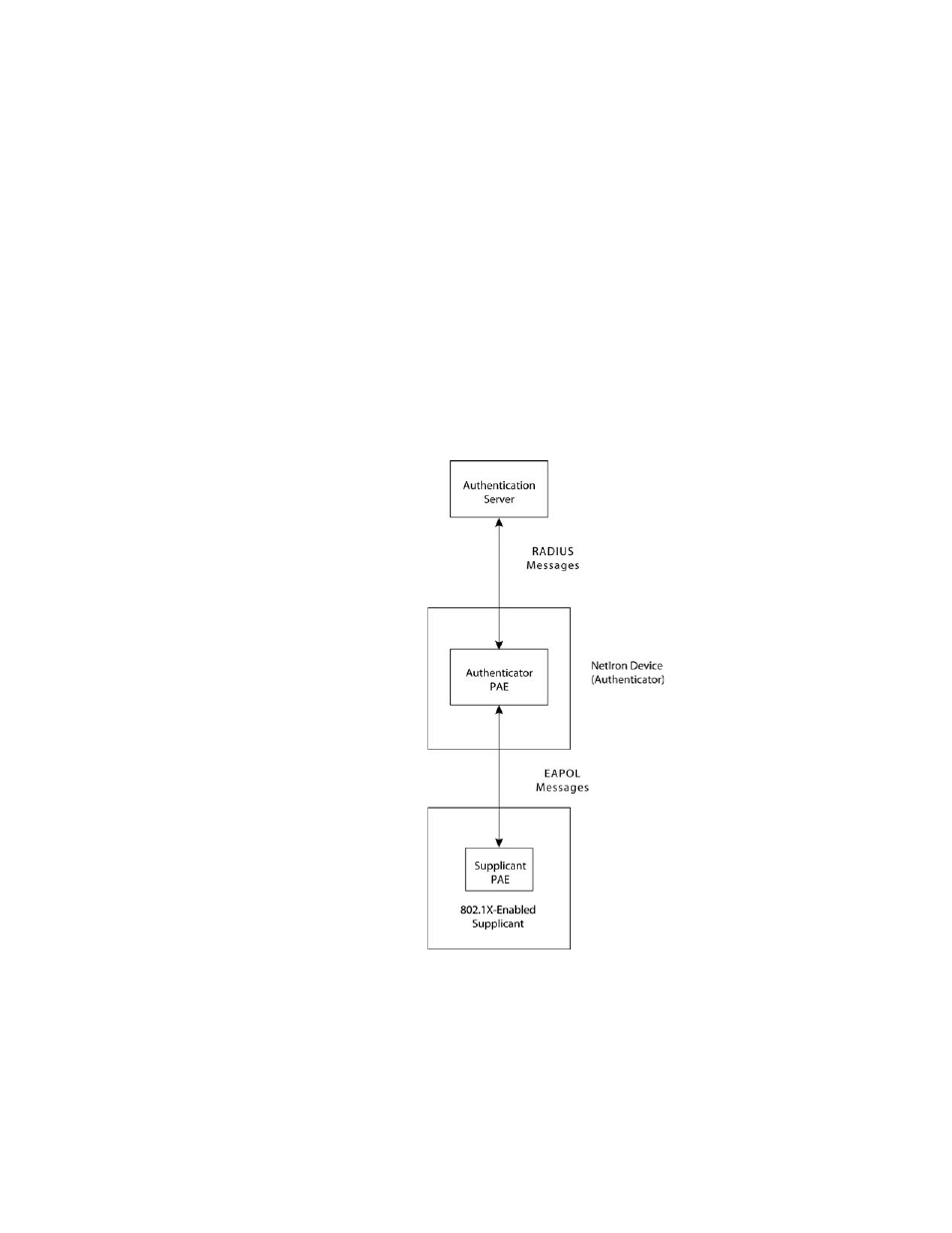
Communication between the devices
For communication between the devices, 802.1x port security uses the Extensible Authentication
Protocol (EAP), defined in RFC 2284. The 802.1x standard specifies a method for encapsulating
EAP messages so that they can be carried over a LAN. This encapsulated form of EAP is known as
EAP over LAN (EAPOL). The standard also specifies a means of transferring the EAPOL information
between the client or Supplicant, Authenticator, and Authentication Server.
EAPOL messages are passed between the Port Access Entity (PAE) on the Supplicant and the
Authenticator.
shows the relationship between the Authenticator PAE and the Supplicant
PAE.
FIGURE 3
Authenticator PAE and supplicant PAE
Authenticator PAE – The Authenticator PAE communicates with the Supplicant PAE, receiving
identifying information from the Supplicant. Acting as a RADIUS client, the Authenticator PAE
passes the Supplicant’s information to the Authentication Server, which decides whether the
Supplicant can gain access to the port. If the Supplicant passes authentication, the Authenticator
PAE grants it access to the port.
