Appendix 5. pid block, A5.1 function diagram, A5.2 functions of pid block – Yokogawa EJX930A User Manual
Page 119: A5.1, A5.2, A5-1
A5-1
IM 01C25T02-01E
Appendix 5. PID Block
A PID block performs the PID control computation based on the deviation of the measured value (PV) from the
setpoint (SV), and is generally used for constant-setpoint and cascaded-setpoint control.
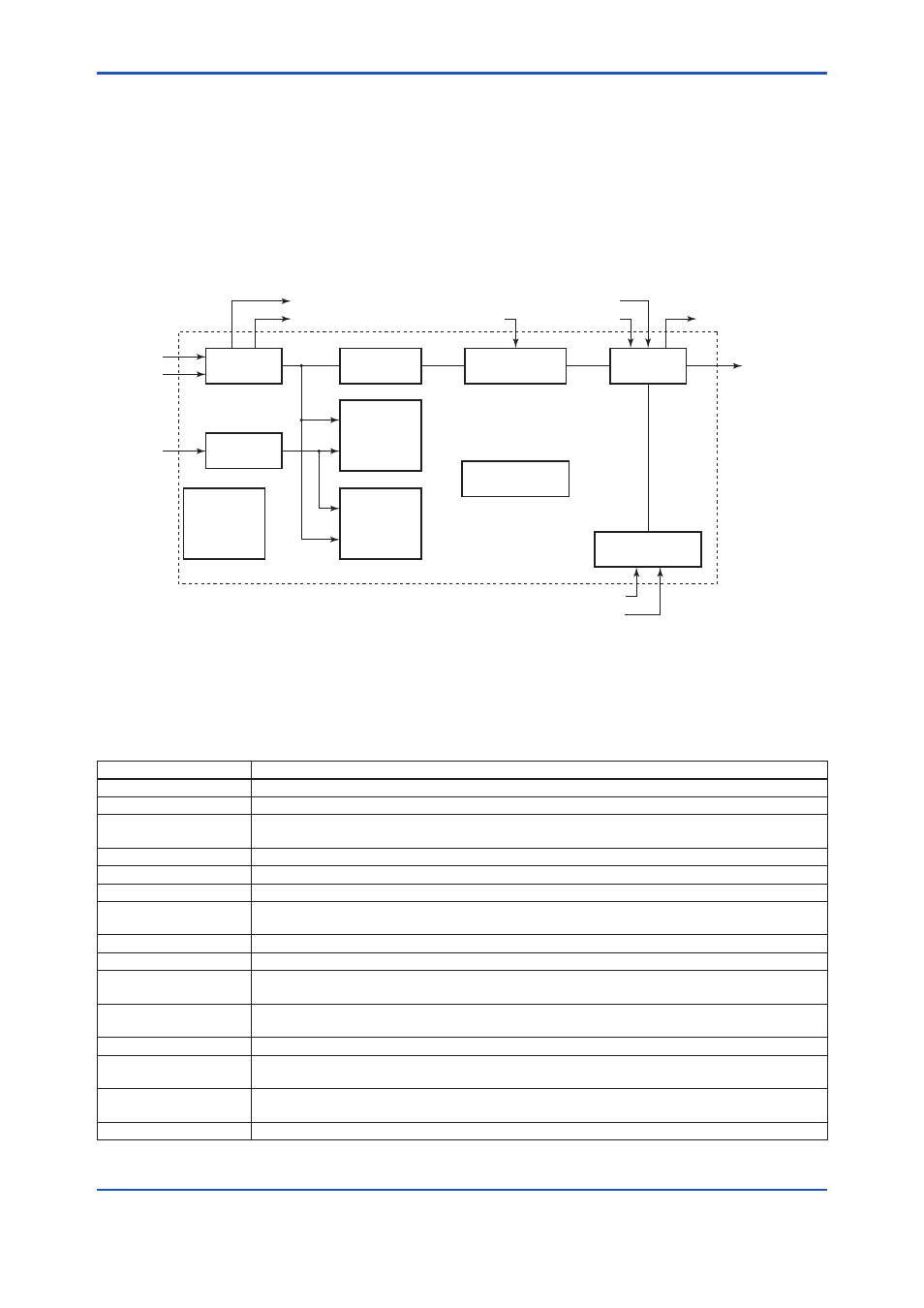
A5.1 Function Diagram
The figure below depicts the function diagram of a PID block.
Setpoint
Output
Bypass
Input Filter
PID Control
Computation
Alarm
Processing
Mode Control
Feed-forward
Data Status
Management
Output Tracking
CAS_IN
BKCAL_OUT
RCAS_OUT
BKCAL_IN
ROUT_IN
ROUT_OUT
FF_VAL
RCAS_IN
TRK_IN_D
TRK_VAL
IN
OUT
PV
SP
FA0501.ai
Figure A5.1 PID Block
A5.2 Functions of PID Block
The table below shows the functions provided in a PID block.
Function
Description
PID control computation
Computes the control output in accordance with the PID control algorithm.
Control output
Converts the change in control output ΔMV to the manipulated value MV that is to be actually output.
Switching of direction of
control action
Switches over the direction of control action between direct and reverse, i.e., the direction of changes in
the control output depending on the changes in the deviation.
Control action bypass
When the bypass is on, the value of the SP is scaled to the range of the OUT and output as the OUT.
Feed-forward
Adds the value of the FF_VAL (input to the PID block) to the output from the PID computation.
Measured-value tracking
Equalizes the setpoint SP to the measured value PV.
Setpoint limiters
Limit the value of setpoint SP within the preset upper and lower levels as well as limit the rate of change
when the PID block is in Auto mode.
External-output tracking
Performs the scaling of the value of TRK_VAL to the range of the OUT and outputs it as the OUT.
Mode change
Changes the block mode between 8 modes: O/S, IMan, LO, Man, Auto, Cas, RCas, ROut.
Bumpless transfer
Prevents a sudden change in the control output OUT at changes in block mode and at switching of the
connection from the control output OUT to the cascaded secondary function block.
Initialization and manual
fallback
Changes the block mode to IMan and suspends the control action when the specified condition is met.
Manual fallback
Changes the block mode to Man and aborts the control action.
Auto fallback
Changes the block mode to Auto when it is Cas, and continues the control action with the setpoint set by
the operator.
Mode shedding upon
computer failure
Changes the block mode in accordance with the SHED_OPT setting upon a computer failure.
Alarm processing
Generates block alarms and process alarms, and performs event updates.
