0 web interface, continued, 16 rf constellation page, continued, 17 constellation data interpretation – Alpha Technologies AlphaNet IDH4 for XM3-HP Series - Technical Manual User Manual
Page 42
42
746-257-B5-001, Rev. A1 (11/2013)
4.0 Web Interface, continued
4.16 RF Constellation Page, continued
Controls:
• Run — Start the sampling of data by pushing the Run button. The unit will acquire 100 samples then
stop.
• Stop — Use the Stop button to end the sampling.
Downstream Data:
• Frequency — is the downstream frequency given in Hz.
• Power — is the downstream power given in dBmV.
• SNR / (RxMER) — this is the downstream signal quality. Modulation Error Ratio (SNR).
• EVM —Error Vector Magnitude calculated from MER.
• CER Interval — Codeword Error Rate (CER) refresh rate.
• Pre FEC CER — Codeword error rate (CER) BEFORE forward error correction is applied.
• Post FEC CER — Codeword error rate (CER) AFTER forward error correction is applied.
• Updates Remaining — this is the number of sample updates remaining for this session.
4.17 Constellation Data Interpretation
The usefulness of the QAM Constellation comes in the ability to recognize common shapes and
configurations within the map. Refer to the following table for examples.
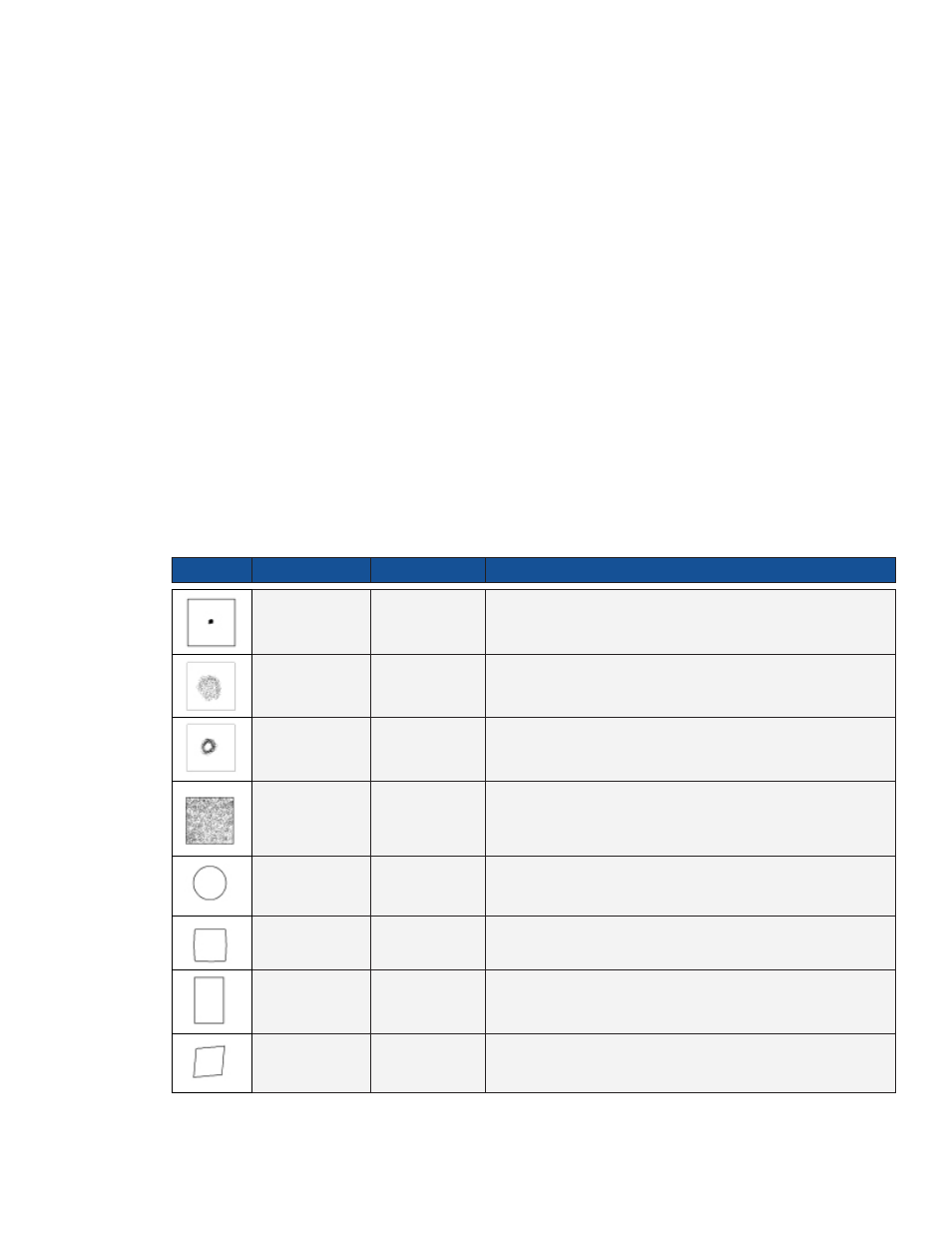
Table 4-2, Constellation Impairments
Shape
Focus
Impairment
Description
Individual cells
and entire QAM
constellation
Normal
Dots are centered in the individual QAM quadrants. The QAM
constellation has a uniform square shape.
Individual cells
Low CNR and/or
Low MER
Individual cells of QAM constellation contain a fuzzy and diffused pattern.
Individual cells
Coherent
Interference
Individual cells of QAM constellation contain diffused hollow circles or
“doughnuts”. This indicates an interfering carrier and shows the effect of
not allowing the carrier to ever reach the proper point in the target range.
Individual cells
Gaussian Noise
Individual cells contain a complete and fairly uniform smear up to all
decision boundaries, and is usually caused by improper system setup, too
many amplifiers in a cascade, damaged/overheated hardware, and/or low
power.
Entire QAM
constellation
Phase Noise
QAM constellation consists of smeared, concentric, circular patterns.
Entire QAM
constellation
Gain Compression QAM constellation looks uniformly square but the outside corners appear
to be “smashed” toward center of grid (compression in the RF plant).
Entire QAM
constellation
I-Q Imbalance in
the Modulator
Overall appearance of QAM constellation is rectangular rather than the
desired square shape (square inequality).
Entire QAM
constellation
Quadrature
Distortion
Overall appearance of QAM constellation has a twisted or skewed
parallelogram shape.
