Dual data pointer, At8xc51snd1c – Rainbow Electronics AT89C51SND1C User Manual
Page 27
27
AT8xC51SND1C
4109E–8051–06/03
Dual Data Pointer
Description
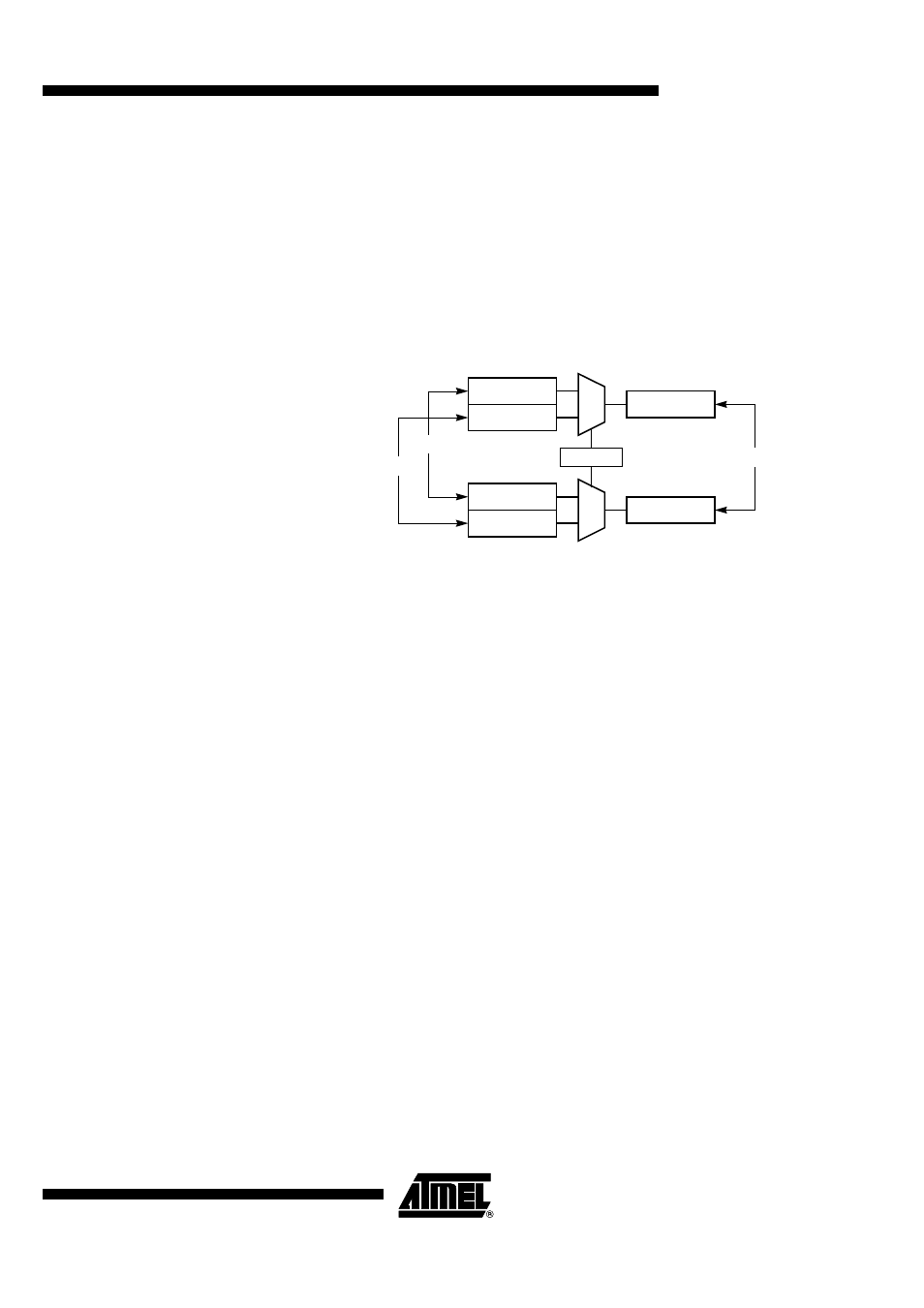
The AT8xC51SND1C implement a second data pointer for speeding up code execution
and reducing code size in case of intensive usage of external memory accesses.
DPTR0 and DPTR1 are seen by the CPU as DPTR and are accessed using the SFR
addresses 83h and 84h that are the DPH and DPL addresses. The DPS bit in AUXR1
register (see Table 21) is used to select whether DPTR is the data pointer 0 or the data
pointer 1 (see Figure 20).
Figure 20. Dual Data Pointer Implementation
Application
Software can take advantage of the additional data pointers to both increase speed and
reduce code size, for example, block operations (copy, compare, search …) are well
served by using one data pointer as a “source” pointer and the other one as a “destina-
tion” pointer.
Below is an example of block move implementation using the 2 pointers and coded in
assembler. The latest C compiler also takes advantage of this feature by providing
enhanced algorithm libraries.
The INC instruction is a short (2 Bytes) and fast (6 CPU clocks) way to manipulate the
DPS bit in the AUXR1 register. However, note that the INC instruction does not directly
force the DPS bit to a particular state, but simply toggles it. In simple routines, such as
the block move example, only the fact that DPS is toggled in the proper sequence mat-
ters, not its actual value. In other words, the block move routine works the same whether
DPS is '0' or '1' on entry.
; ASCII block move using dual data pointers
; Modifies DPTR0, DPTR1, A and PSW
; Ends when encountering NULL character
; Note: DPS exits opposite of entry state unless an extra INC AUXR1 is added
AUXR1
EQU
0A2h
move:
mov
DPTR,#SOURCE ; address of SOURCE
inc
AUXR1
; switch data pointers
mov
DPTR,#DEST
; address of DEST
mv_loop:
inc
AUXR1
; switch data pointers
movx
A,@DPTR
; get a Byte from SOURCE
inc
DPTR
; increment SOURCE address
inc
AUXR1
; switch data pointers
movx
@DPTR,A
; write the Byte to DEST
inc
DPTR
; increment DEST address
jnz
mv_loop
; check for NULL terminator
end_move:
0
1
DPH0
DPH1
DPL0
0
1
DPS
AUXR1.0
DPH
DPL
DPL1
DPTR
DPTR0
DPTR1
