Programming language, User's manual – Toshiba T2N User Manual
Page 258
User's manual
245
5. Programming Language
(A) HTOA (n) (B)
(A) ATOH (n) (B)
(A) ABS (B)
(A) +1· (A) DABS (B) +1· (B)
(A) NEG (B)
(A) +1· (A) DNEG (B) +1· (B)
(A) DW (B) +1· (B)
(A) 7 SEG (B)
(A) ASC (B)
(A) BIN (B)
(A) +1· (A) DBIN (B) +1· (B)
(A) BCD (B)
(A) +1·(A) DBCD (B) +1· (B)
(A) +1· (A) FLT (B) +1· (B)
(A) +1· (A) FIX (B) +1· (B)
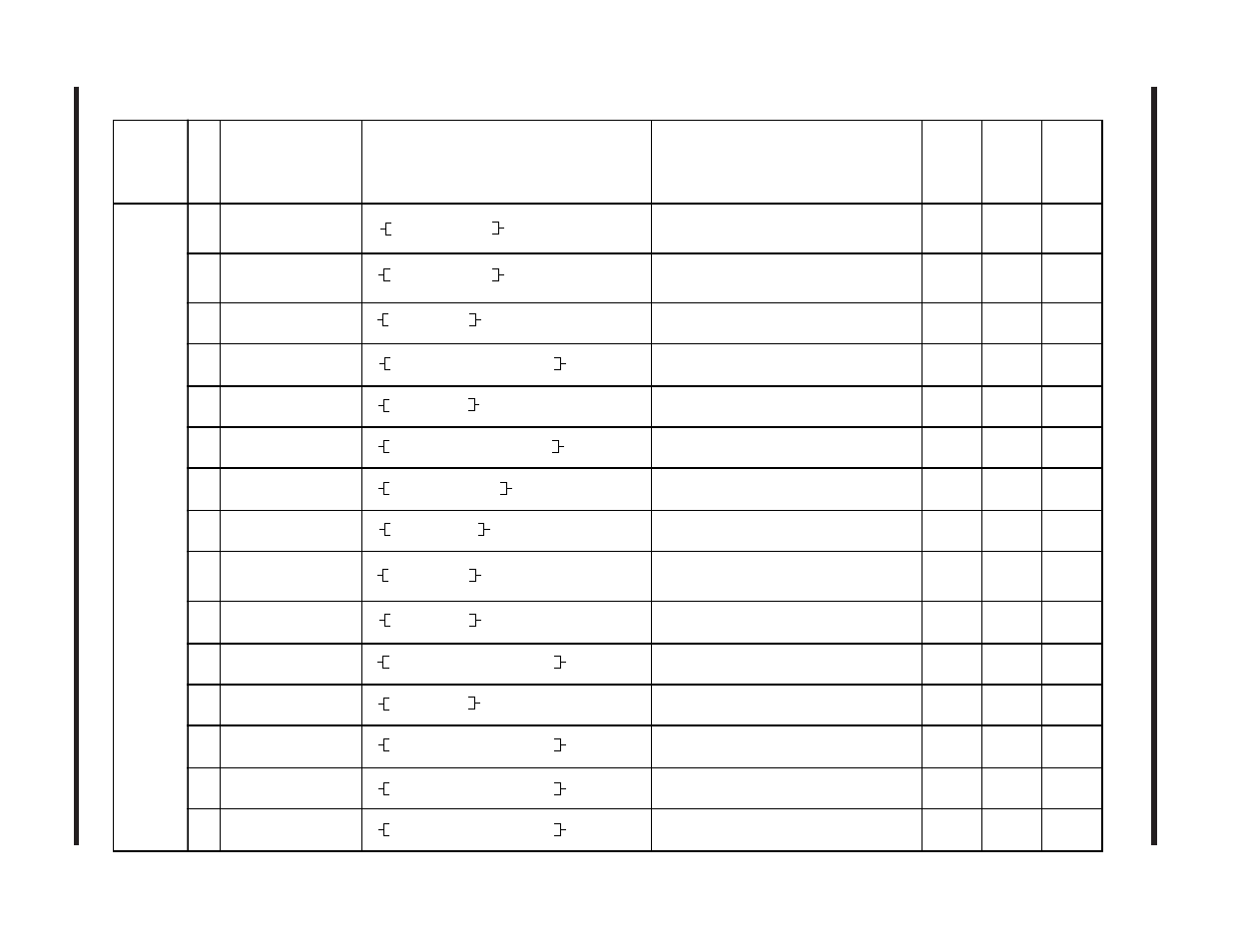
Ladder Diagram Instructions (Function Instructions)
Group
FUN
No.
Name
Representation
Summary
Number of
steps
required
Execution
time
required
(
µ
s)
Remarks
Conversion
62
HEX-ASCII conversion
Converts the HEX data in n registers headed by (A)
into ASCII data and stores them in the registers
headed by (B).
4
160+75.5n
63
ASCII-HEX conversion
Converts the ASCII data in n registers headed by (A)
into HEX data and stores them in the registers
headed by (B).
4
143+39.4n
180
Absolute value
Stores the absolute value of (A) in (B).
3~4
70
181
Double-length absolute
value
Stores the absolute value of (A)+1 and (A) in
(B)+1•(B).
3~5
103
182
2's complement
Stores the 2's complement of (A) in (B).
3~4
68
183
Double-length 2's
complement
Stores the 2's complement of (A)+1•(A) in
(A)+1• (B).
3~5
103
184
Double lenght conversion
Converts the signed data in (A) into double-length
data, and stores in (B)+1•(B).
3~4
85
185
7-segment decode
Converts the bottom 4 bits of (A) into 7-segment
code, and code stores in (B).
3~4
73
186
ASCII conversion
Takes the alphanumerics (maximum 16 characters)
indicated by (A) and converts them into ASCII code.
Stores the result in the location headed by (B).
3~10
262
188
Binary conversion
Converts the BCD data in (A) into binary data and
stores it in (B).
3~4
105
189
Double-length binary
conversion
Converts the double-length BCD data in (A)+1•(A)
into binary data and stores it in (B)+1•(B).
3~5
175
190
BCD conversion
Converts the binary data in (A) into BCD data and
stores in in (B).
3~4
101
191
Double-length BCD
conversion
Converts the binary data in (A)+1•(A) into BCD data
and stores it in (B)+1•B).
3~5
169
204
Floating point conversion
Converts the double-length integer of (A)+1•(A) into
floating point data and stores it in (B)+1•(B).
3~5
106
363
µ
s
(max)
205
Fixed point conversion
Converts the floating point data of (A)+1•(A) into
double-length integer data and stores it in (B)+1•(B).
3
96
320
µ
s
(max)
