Analog filtering, Input and source impedance, Crosstalk – Measurement Computing Personal Daq rev.6.0 User Manual
Page 104: Input, Source impedance
Analog Filtering
A filter is an analog circuit element that attenuates an incoming signal according to its frequency. A low-
pass filter attenuates frequencies above the cutoff frequency. Conversely, a high-pass filter attenuates
frequencies below the cutoff. As frequency increases beyond the cutoff point, the attenuation of a single-
pole, low-pass filter increases slowly. Multi-pole filters provide greater attenuation beyond the cutoff
frequency but may introduce phase (time delay) problems that could affect some applications.
Input
and
Source Impedance
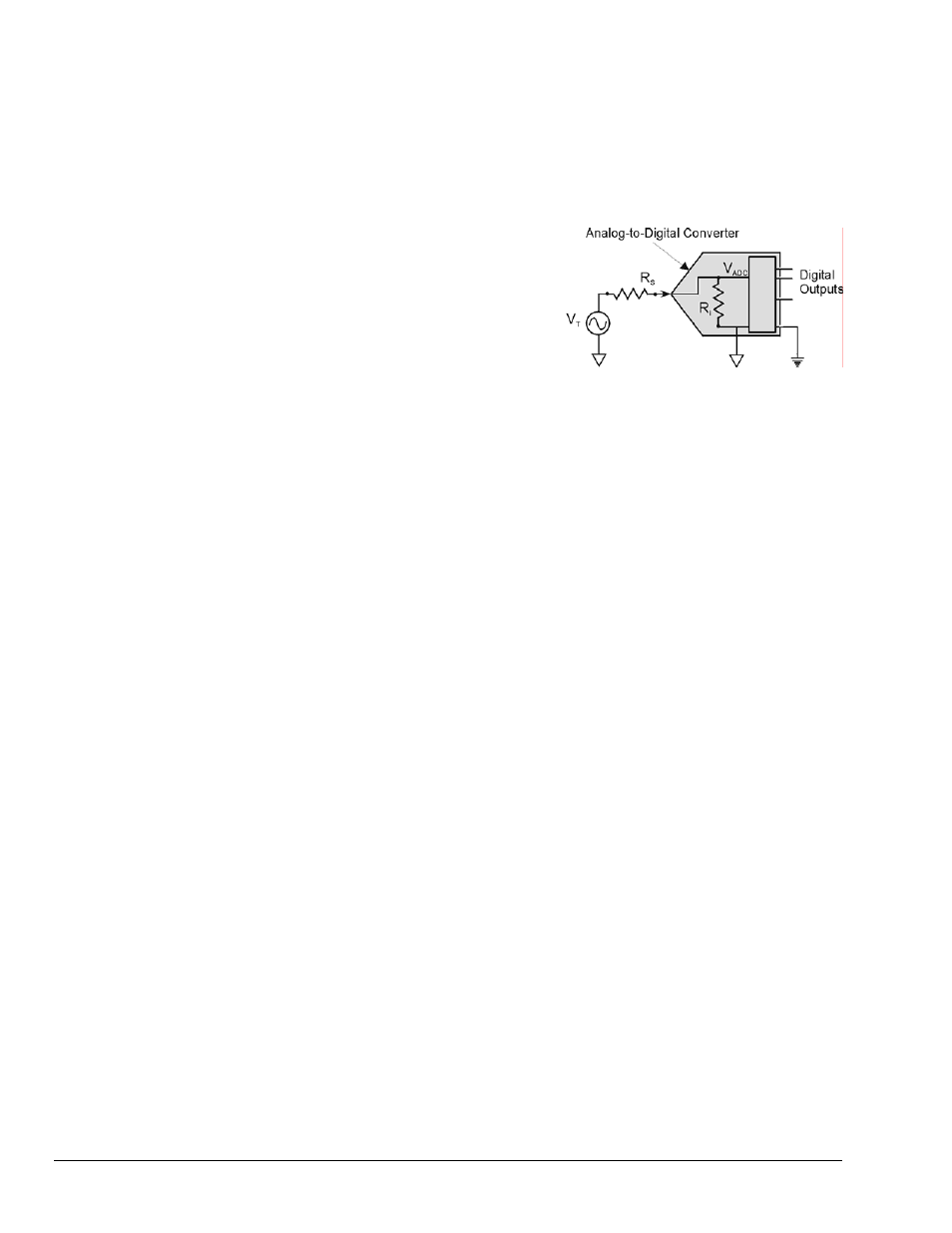
As illustrated in the figure to the right, the input impedance
(R
i
) of an analog-to-digital converter combines with the
transducer’s source impedance (R
s
) forming a voltage
divider. This divider distorts the voltage being read at the
analog-to-digital converter. The actual voltage read is
represented by the equation:
V
ADC
= V
T
× R
i
/ (R
s
+ R
i
)
The input impedance (R
i
) of most ADCs is at least 1 M
Ω; low source impedance (R
s
) usually presents no
problem. Some transducers, such as piezoelectric types, have high source impedance, and should therefore
be used with a charge-sensitive amplifier of low output impedance. As described in the following
paragraphs, multiplexing can greatly reduce the effective input impedance of an analog-to-digital
converter.
Crosstalk
Crosstalk is a type of noise related to source impedance and capacitance, in which signals from one
channel leak into an adjacent channel, resulting in interference or signal distortion. The impact of source
impedance and stray capacitance can be estimated by using the following equation.
T = RC
Where T is the time constant, R is the source impedance, and C is the stray capacitance.
High source (transducer) impedance can be a problem in multiplexed A/D systems. When using more than
1 channel, the channel input signals are multiplexed into the A/D. The multiplexer samples each signal and
then switches to the next input signal. A high-impedance input interacts with the multiplexer’s stray
capacitance and causes crosstalk and inaccuracies in the A/D sample.
A solution to high source impedance in relation to multiplexers involves the use of buffers. The term
buffer has several meanings; but in this case, buffer refers to an operational amplifier having high input
impedance but very low output impedance. Placing such a buffer on each channel (between the transducer
and the multiplexer) prevents the multiplexer’s stray capacitance from combining with the high input
impedance. This use of a buffer also stops transient signals from propagating backwards from the
multiplexer to the transducer.
5-8 Signal Management
878695
Personal Daq User’s Manual
