Lontalk protocol support for routers, Message buffers – Echelon LonWorks Router User Manual
Page 24
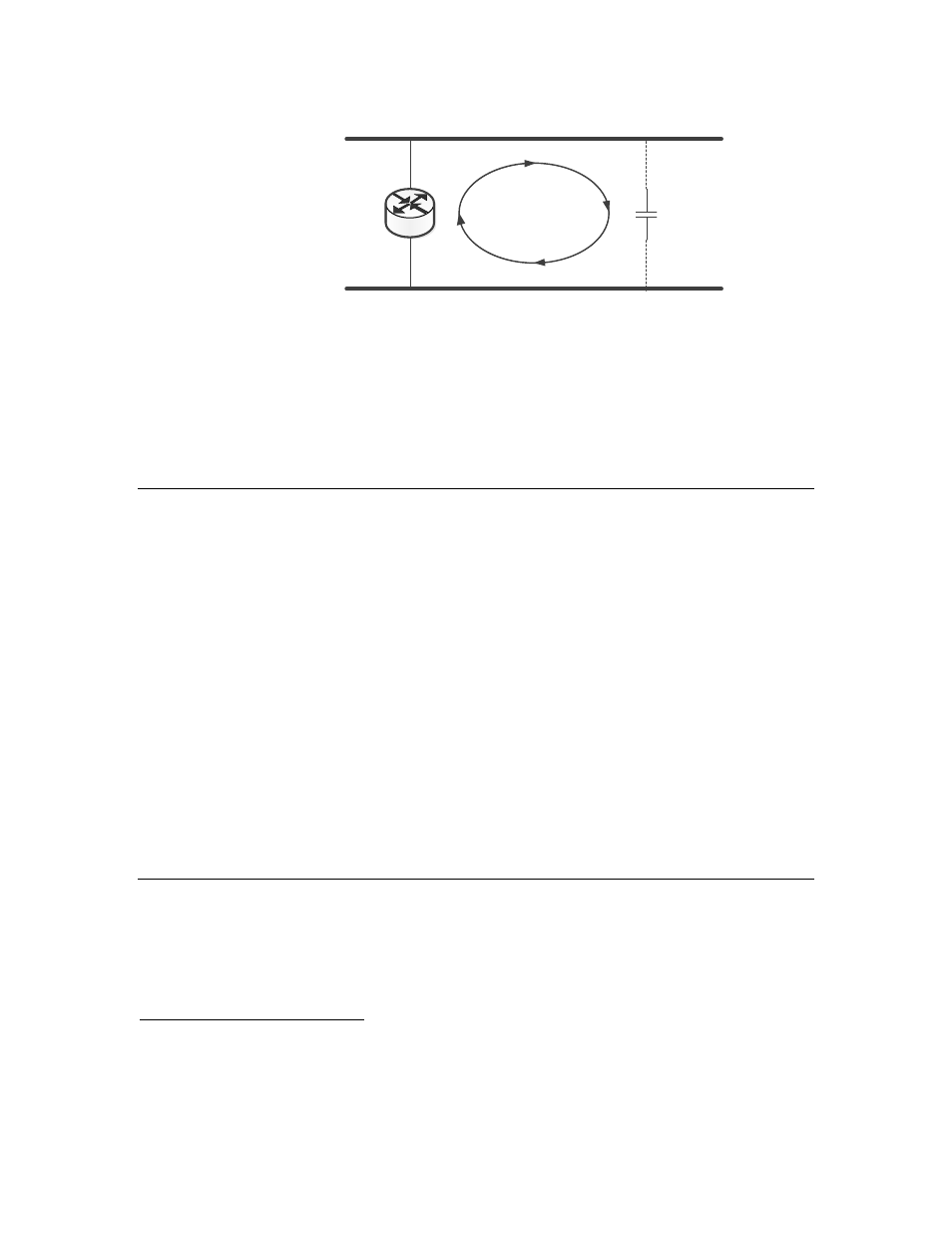
PL Phase A
Power Line
Router
Passive
Coupling
PL Phase B
Figure 7. A Looping Topology with One Router
Routers can be used between power line channels only if the two channels are
fully isolated. Such isolation is generally not the case between two phases on the
same circuit, but can be the case between phases on different distribution
transformers. Use an Echelon PLCA-22 Power Line Communication Analyzer to
confirm isolation between power line channels before installing power-line-to-
power-line routers.
LonTalk Protocol Support for Routers
The LonTalk protocol
is designed to provide transparent routing of messages
between devices that communicate through routers. To increase the efficiency of
routers, the LonTalk protocol defines a hierarchical form of addressing using
domain, subnet, and device (node) addresses. An intelligent router operates at
the subnet level. The router determines which subnets lie on each of its two
sides, and forwards packets accordingly.
Subnets do not span intelligent routers, which allow intelligent routers to make
routing decisions based on the subnet component of a device’s logical address. To
further facilitate the addressing of multiple dispersed devices, the LonTalk
protocol defines another class of addresses using domain and group addresses.
Intelligent routers also can be configured to make routing decisions based on the
group addressing component of a message.
In general, a network management tool, such as OpenLNS CT, is responsible for
domain, subnet, node, and group address assignments.
See the ISO/IEC 14908 Control Network Protocol specification for detailed
information about the LonTalk protocol.
Message Buffers
As messages are received by a router, they are placed in an input buffer queue. By
default, this queue is limited to two message buffers to ensure that priority
messages are never enqueued behind more than one non-priority message. When
forwarded to the transmitting side of the router, priority messages have their own
1
Echelon’s implementation of the ISO/IEC 14908 Control Network Protocol is called the
LonTalk protocol. Echelon has implementations of the LonTalk protocol in several product
offerings, including the Neuron firmware, OpenLNS
®
Server, SmartServers, and various
network interfaces. This document refers to the ISO/IEC 14908-1 Control Network Protocol
as the “LonTalk protocol,” although other interoperable implementations exist.
14
Introduction to LONWORKS Routers
