Loop topology, D figure 5, Ee loop topology – Echelon LonWorks Router User Manual
Page 22
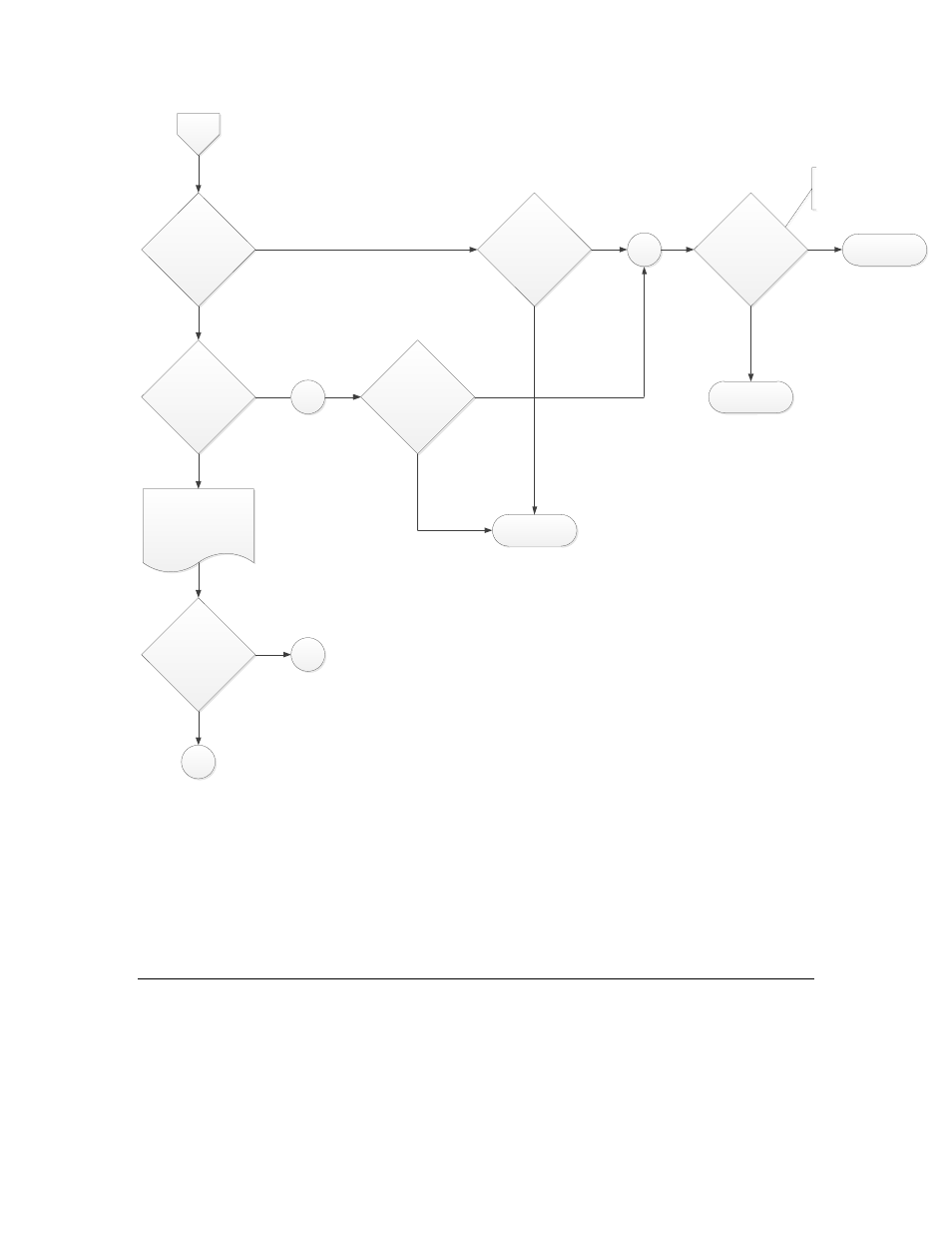
Is message addressed
to group?
Is message addressed
to subnet/node?
Message must be
addressed as broadcast or
48-bit Neuron ID
Is the group fwd flag
of the dest group set to
forward?
Drop packet
Is the subnet fwd flag
for the dest subnet set
to forward?
Is the subnet fwd flag
for the source subnet
set to forward?
Drop packet
Is message dest subnet
= zero?
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
A
Yes
A
No
B
B
Page 1
Forward packet
* Applies to
configured
router only
Figure 5. Configured and Learning Router Forwarding Rules, Part 2
As with configured routers, learning routers sometimes modify source addresses
for service-pin messages to help prevent message loops.
Learning routers, in general, are less efficient in using channel bandwidth
because they always forward all messages with group destination addresses.
Their advantage is simplified installation because the installation tool does not
need to know the network topology to configure the router.
Loop Topology
A looping topology is a network topology that has the potential for message loops.
A loop is a path through two or more routers that forwards a message from a
channel to itself. For example, Figure 6 shows a looping topology with two
channels and two routers. A message on channel A could be forwarded by router
12
Introduction to LONWORKS Routers
