Table 17. spi input and output pins, Table 18. spi interface control registers, Spi example: enabling master mode – Maxim Integrated MAXQ Family Users Guide: MAXQ2000 Supplement User Manual
Page 52: Maxq family user’s guide: maxq2000 supplement
MAXQ Family User’s Guide:
MAXQ2000 Supplement
ADDENDUM TO SECTION 11: SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI)
The MAXQ2000 provides a Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) module, which operates as described in the MAXQ Family User’s Guide.
Table 17 shows the associated pins and Table 18 shows the associated registers for this interface.
SPI Example: Enabling Master Mode
move SPICN, #03h
; Enable SPI for master mode communication
move SPICF, #00h
; Rising clock, active edge sample, 8-bit character
move SPICK, #010h
; Divide by 16 clock
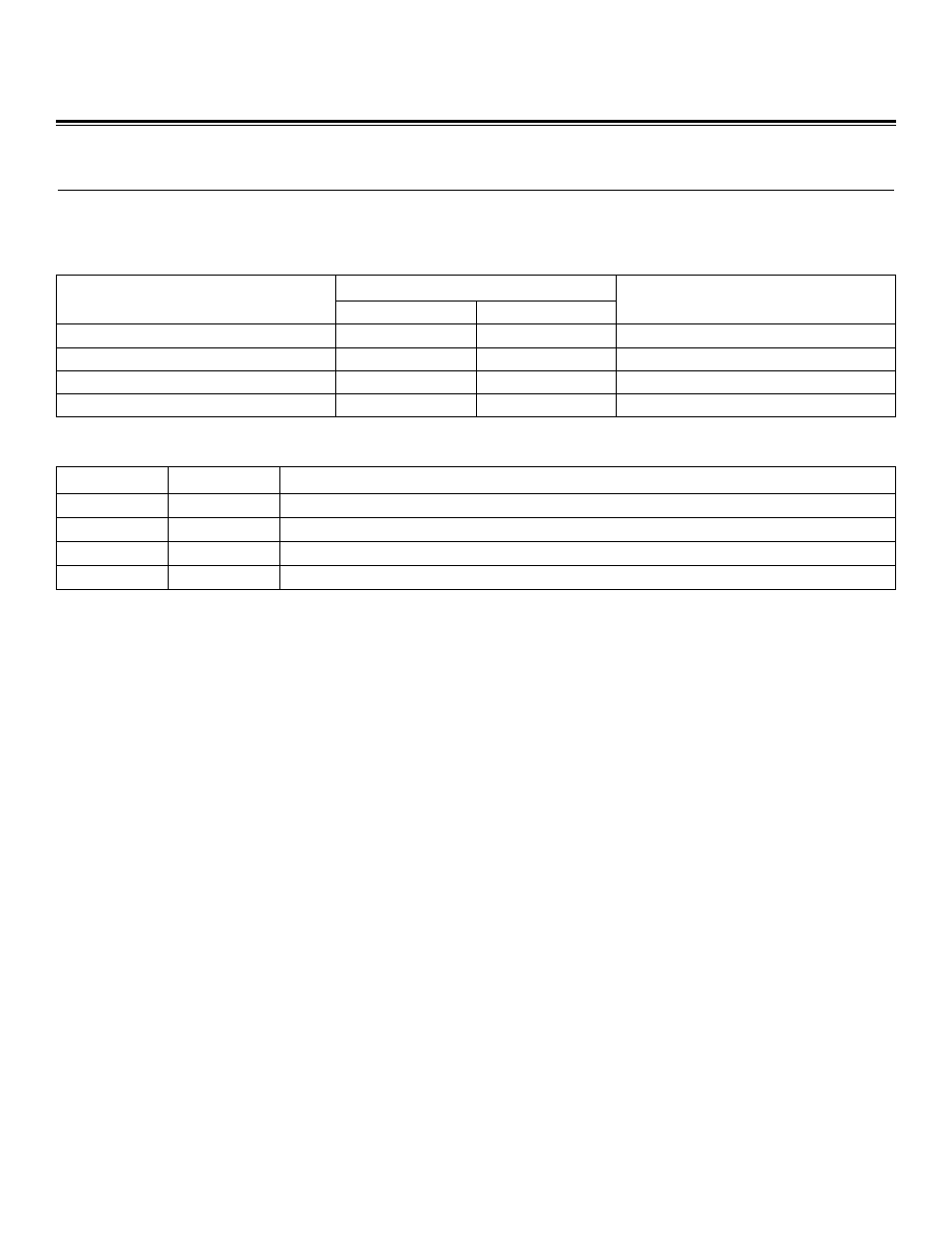
PIN NUMBER
SPI INTERFACE FUNCTION
68-PIN
56-PIN
MULTIPLEXED WITH PORT PIN
Slave Select—SSEL
38
—
P5.4
Slave Clock—SCLK
40
—
P5.6
Master Out-Slave In—MOSI
39
—
P5.5
Master In-Slave Out—MISO
41
—
P5.7
Table 17. SPI Input and Output Pins
REGISTER
ADDRESS
FUNCTION
SPICN
M3[15h]
SPI Control Register. Enable, master/slave mode select, status, and interrupt flags.
SPICF
M3[16h]
SPI Configuration Register. Clock polarity/phase, character length, interrupt enable.
SPICK
M3[17h]
SPI Clock Register. Master baud rate = 0.5 x sysClock / (SPICK + 1)
SPIB
M3[05h]
SPI Data Buffer. Writes go to SPI write buffer; reads come from SPI read buffer.
Table 18. SPI Interface Control Registers
Maxim Integrated
52
