Metrohm 794 Basic Titrino User Manual
Page 29
2.6 Selection of the mode, key
794 Basic Titrino
25
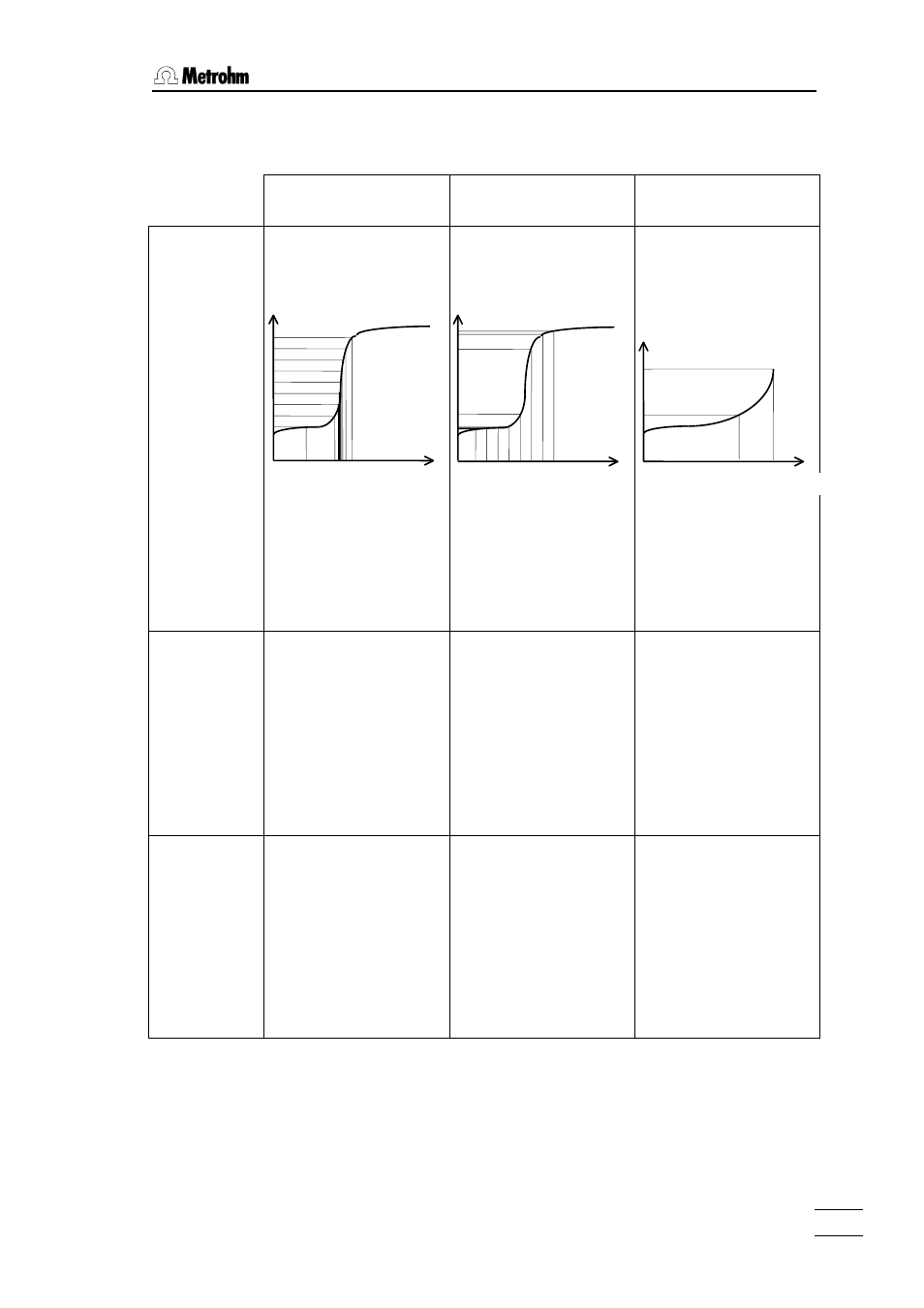
Overview of the titration modes
DET
Dynamic Equivalence
point Titration
MET
Monotonic Equivalence
point Titration
SET, KFT
Endpoint Titration
Titration
Reagent feeding:
Variable volume increments,
depending on the slope of
the curve.
Acquisition of measured
values:
Drift controlled ("equilibrium
titration")
and/or
after a fixed equilibration
time.
Reagent feeding:
Constant volume incre-
ments, independent of the
slope of the curve.
Acquisition of measured
values:
Drift controlled ("equilibrium
titration")
and/or
after a fixed equilibration
time.
Titration to preset end-point.
Acquisition of measured
values:
Continuously
Evaluation
The evaluation of EP' s is
based on the zero crossing
of the second derivative with
a Metrohm correction for the
distortion of the curve from
superimposed jumps. Can
be combined with selectable
recognition criteria.
Recognition criteria:
as for MET
The evaluation of EP's is
based on the Fortuin inter-
polation.
Recognition criteria:
all EP's
only the last EP
only the greatest EP
EP windows
Volume that has been dis-
pensed up to the endpoint
(EPX in mL).
Applications
Suitable titration mode for
most problems. Specially
recommended if jumps lie
very close together and for
very flat jumps.
Note: The reagent feeding
algorithm is based on meas-
ured data. The curve should
therefore not deviate
markedly from S-shape.
For
•
slow titration reactions
(diazotations, coupling
reactions)
•
sluggish electrode
response.
•
For rapid, quantitative
determinations in ana-
lytical chemistry. Re-
quirement: EP of the ti-
tration reaction is
known and does not
change during a de-
termination series.
•
If an excess of titrant
must be avoided.
V/mL
U/mV
V/mL
U/mV
V/mL
U/mV
Control
range
EP
