SkyTrak 6036 Service Manual User Manual
Page 216
Section 10.
Electrical System
10-22
Model 6036 S/N 9B0499 and Before
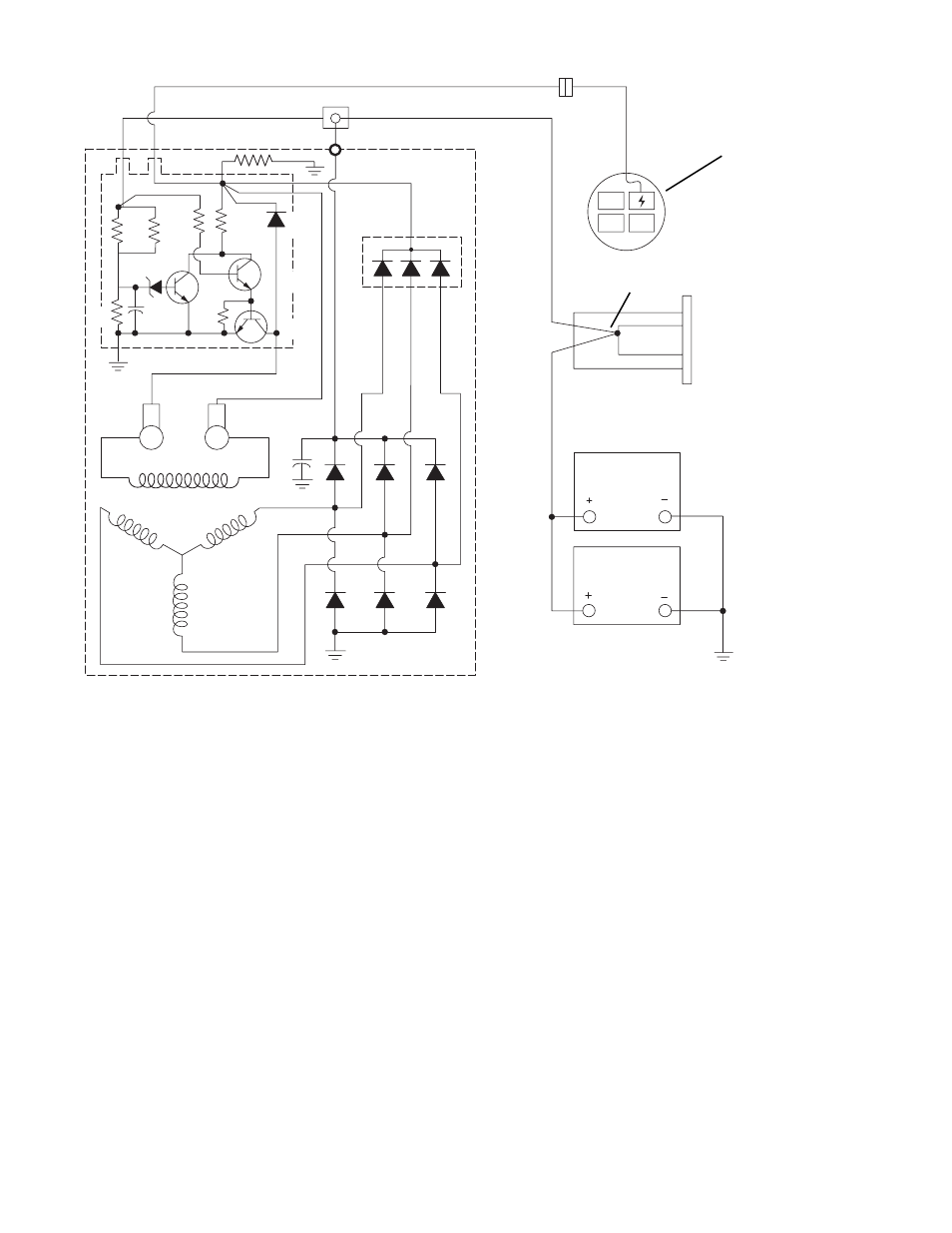
Capacitor C1 smooths out the voltage across R3,
resistor R4 prevents excessive current through
TR1 at high temperatures, and diode D2 prevents
high-induced-voltages in the field windings when
TR1 turns off. Resistor R2 is a thermistor which
causes the regulated voltage to vary with the
temperature, thus providing optimum voltage for
charging the battery.
b. Troubleshooting Procedures
Close adherence to the following procedures in
the order presented will lead to the location and
correction of charging system defects in the
shortest possible time. Only a portion of these
procedures need to be performed. It will never be
necessary to perform all the procedures in order to
locate the trouble.
Either of two methods may be used to trou-
bleshoot the charging system. One method uses
alternator tester Model J-26290 available from the
Kent-Moore Corporation, Tool Division, 29784
Little Mack, Roseville, MI 48066
As alternator speed increases, current is provided
for charging the battery and operating electrical
accessories. Also, with the alternator operating,
the same voltage appears at the “BAT” and No. 1
terminals, and the indicator lamp goes out to
indicate the alternator is producing voltage.
If an open should occur in the TERMINAL NO. 2
circuit, TR3 and TR1 will turn off, no field current
will flow to prevent overcharge, and indicator lamp
current will flow to a ground through R6 to indicate
a defect. Also, an open in the field circuit will
cause the indicator lamp to turn on through R6.
As the alternator speed and voltage increase, the
voltage between R2 and R3 increases to the point
where zener diode D1 conducts current. Transis-
tor TR2 then turns on and TR3 and TR1 turn off.
With TR1 off, the field current and system voltage
decrease, and D1 then blocks current flow,
causing TR3 and TR1 to turn back on. The field
current and system voltage increase, and this
cycle then repeats many times per second to limit
the alternator voltage to a preset value.
Fig. 10.26 Charging Circuit Showing Internal Circuits of a Typical 12-SI Alternator
ALTERNATOR
NOT CHARGING
WARNING LIGHT
STARTER SOLENOID
TERMINAL
BATTERIES
DIODE TRIO
REGULATOR
FIELD (ROTOR)
RECTIFIER BRIDGE
BAT.
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
2
1
TR2
C1
STATOR
TR1
IGNITION SWITCH
D2
D1
TR3
MA1092
