Calculating worst-case remote i/o scan time, Optimizing remote i/o scan time – Rockwell Automation 1785-Lxxx Enhanced and Ethernet PLC-5 Programmable Controllers User Manual
Page 295
Publication 1785-UM012D-EN-P - July 2005
Maximizing System Performance C-9
Calculating Worst-Case Remote I/O Scan Time
Since it is impossible to predict within which remote I/O scan a block-transfer
will occur, you only can calculate the worst-case remote I/O scan time. To
calculate the worst case time:
1. Determine the normal I/O time (without block-transfers)
2. Add the time of the longest block-transfer to each entry in the scan list.
(The controller can only perform one block-transfer per entry in the
scan list per I/O scan.)
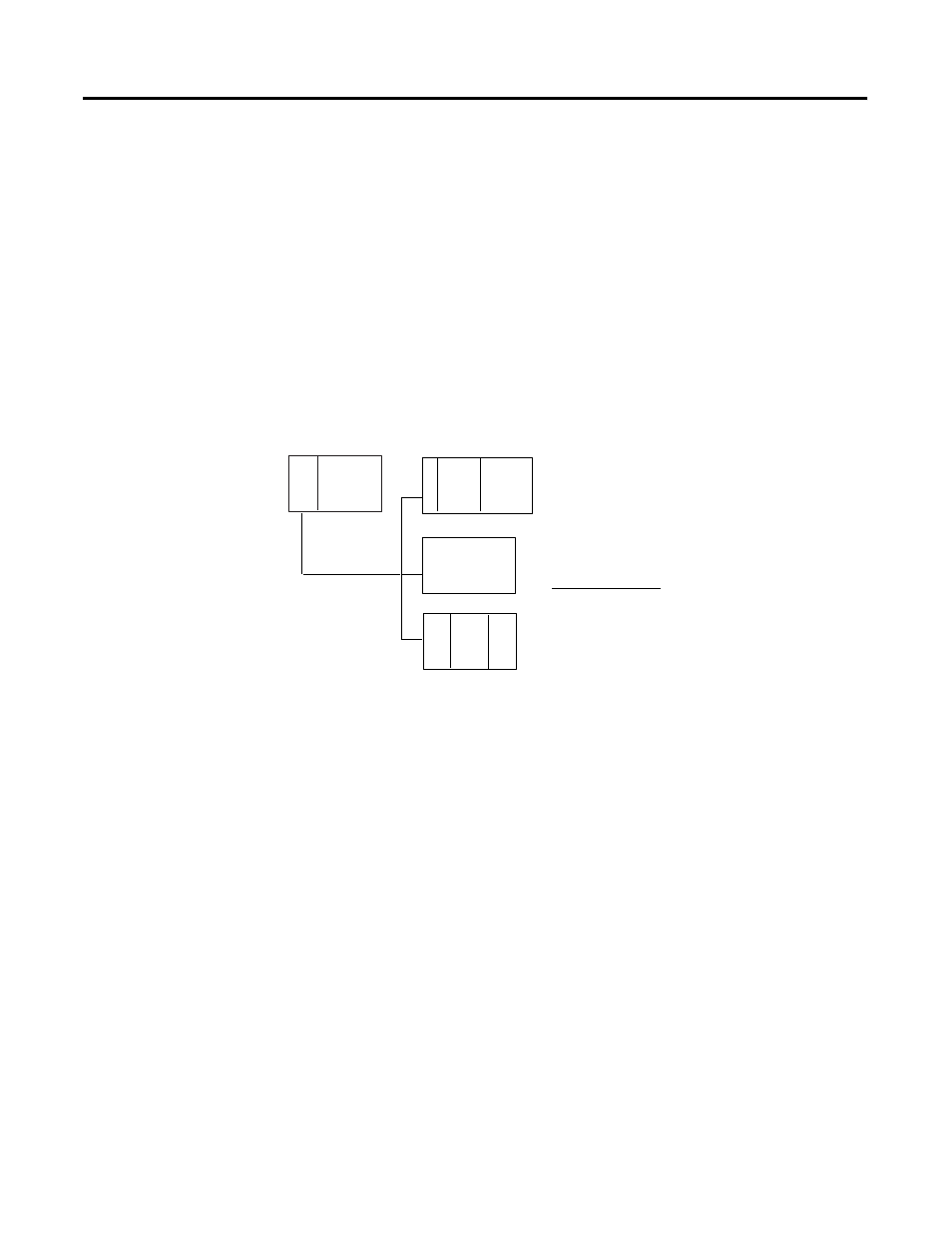
For example, if your system is:
Optimizing Remote I/O Scan Time
The best way to optimize your scan time is to place your most time-critical
I/O on a separate channel from non-critical I/O. If you have only one
channel available for I/O, however, you can still optimize the scanning by
using the controller’s configurable scan list.
In a normal 4-rack system, the scan list would be:
rack 1
rack 2
rack 3
rack 4
If you are using 57.6 kbps, the normal I/O scan is 4 racks x 10 ms = 40 ms.
Each entry is of equal priority, so each rack is scanned every 40 ms.
PLC
115.2 kbps
Rack 1
Rack 2
Rack 3
No BTs
BT
30
words
BT
10
words
BT
20
words
Worst-case I/O scan:
(3 x 6)
+ (20 x .14) + 2.5
+ 0
+ (30 x .14) + 2.5
3 racks at 115.2 kbps*normal I/O scan
longest BT in rack 1
no BTs in rack 2
longest BT in rack 3
18 + 5.3 + 0 + 6.7 = 30 ms
