Parity group configuration, Overview of volume initialize function, Overview of make volume function – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 161
also divide a logical volume into smaller ones for a command device, which efficiently exploits the
disk's capacity.
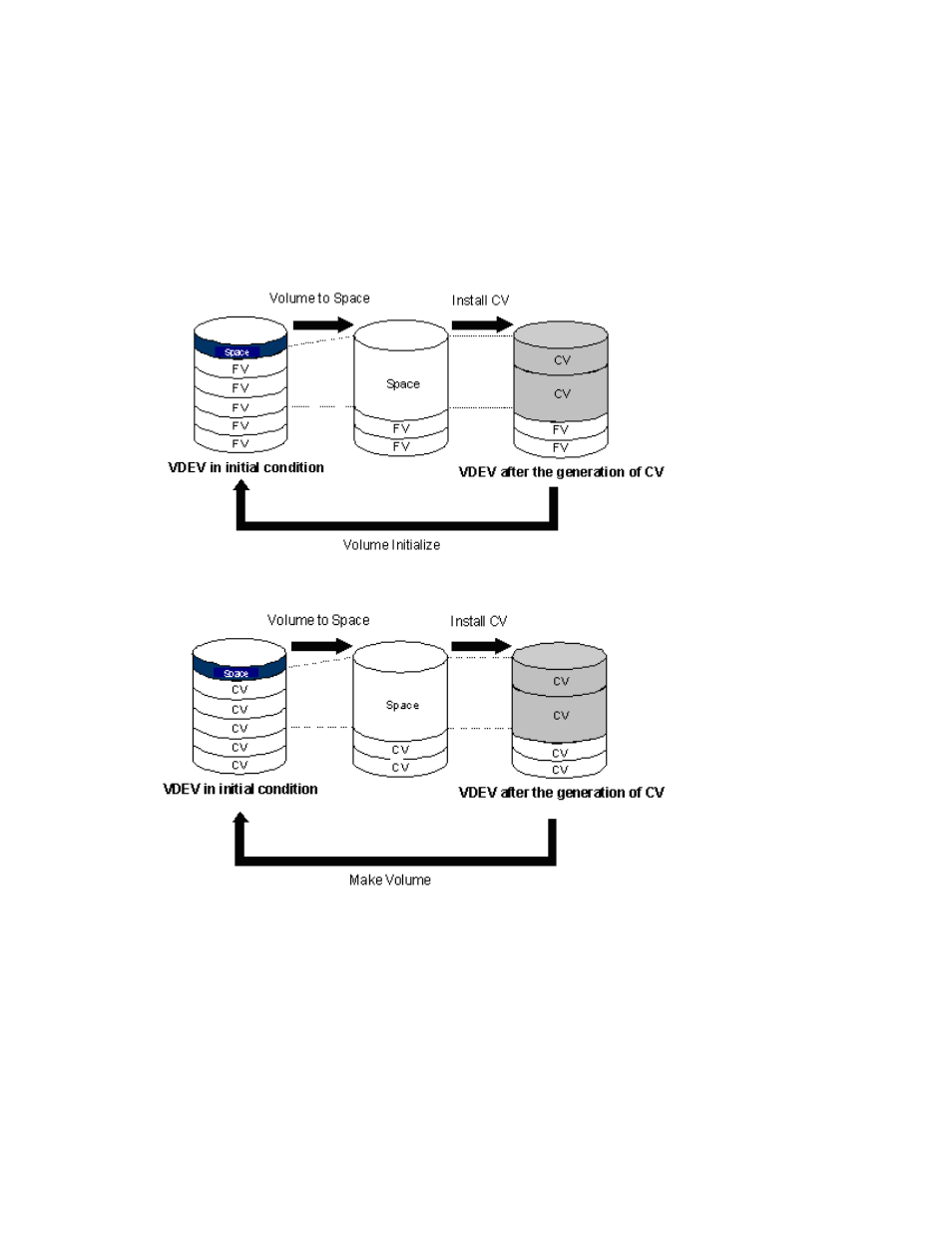
CVS operations include: Volume to Space, Install CV, Volume Initialize, and Make Volume. The
Volume to Space function formats one or more LDEVs on a selected Virtual Device (VDEV) into free
space. That free space can either be used to install one or more variable-sized volumes (CVs) using
the Install CV function, or left as free space for future use. The Volume Initialize function de-installs all
variable sized volumes (CVs) under a CVS volume, and reformats the CVS volume as a normal volume
(VDEV). The Make Volume function clears all variable-sized volumes (CVs) under a CVS volume and
creates an initial volume (VDEV) consisting of the new user-defined CVs.
For an overview of how the Volume Initialize function works, see
. For an overview of how
the Make Volume function works, see
.
Figure 77 Overview of Volume Initialize function
.
Figure 78 Overview of Make Volume function
.
Parity group configuration
One parity group consists of a maximum of 16 VDEVs. For RAID-5 (7D + 1P) or RAID-6 (6D + 2P)
levels, a maximum of 512 fixed-size volumes (FVs) and a certain amount of free space are available
in one VDEV. For other RAID levels, a maximum of 256 FVs and a certain amount of space are
available in one VDEV. Each VDEV in a parity group has the same configuration, and is assigned
the same FVs of the same size and RAID level.
XP LUN Configuration and Security Manager User Guide
161
