3 identifier example, 4 sequence of data transfer, Identifier example – NORD Drivesystems BU0060 User Manual
Page 50: Sequence of data transfer, Table 11: identifier example
CANopen – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
50
BU 0060 GB-4112
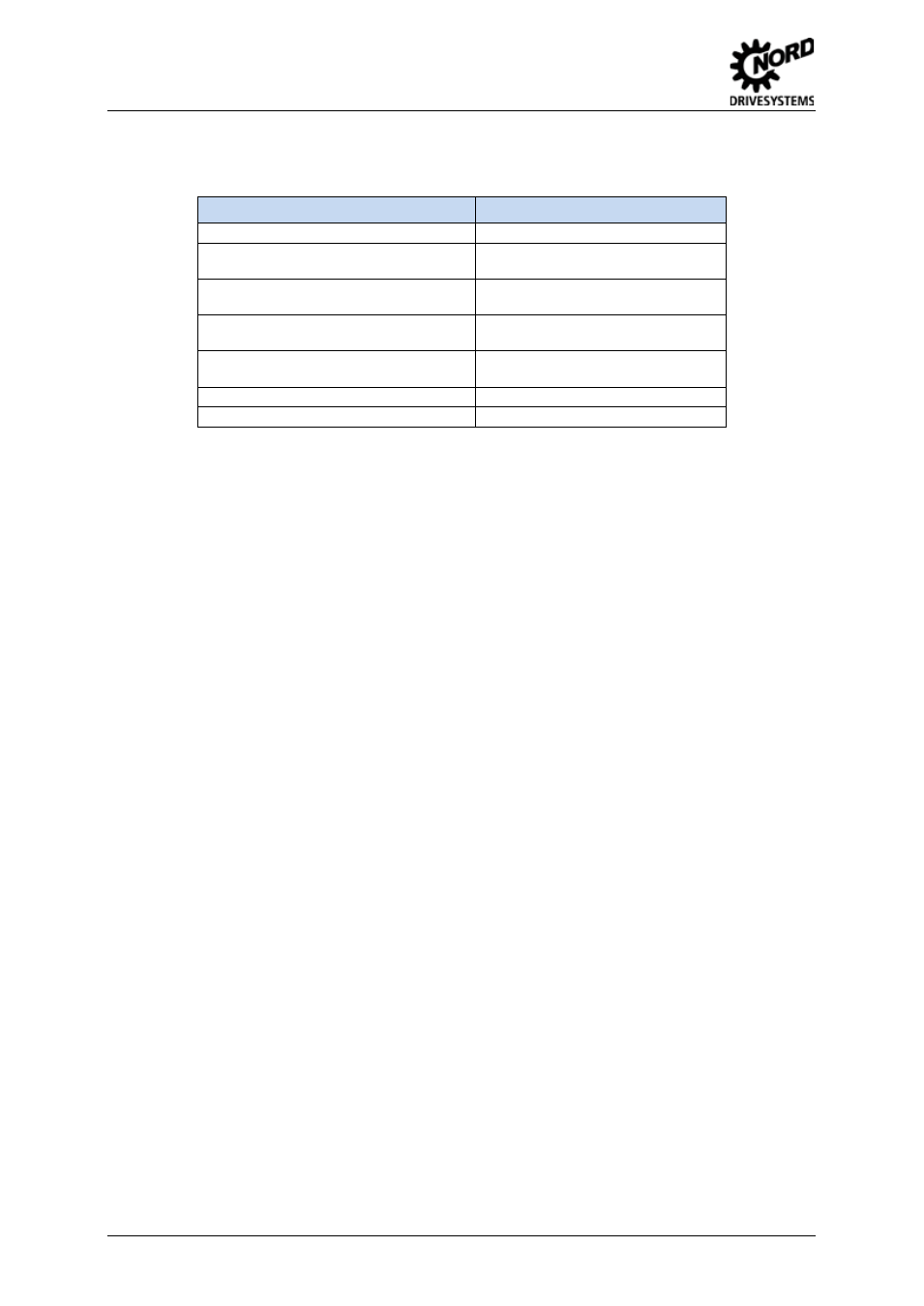
4.2.3 Identifier example
In the frequency inverter, the CANnord address (P515) is set to the value 100.
This results in the following identifier:
Message objects
Identifier
CAN bus address
100
dez
Process data Master
à Frequency
inverter
200
dez
Process data frequency inverter
à
Master
201
dez
Parameter order Master
à Frequency
inverter
712
dez
Parameter response frequency inverter
à
Master
713
dez
Broadcast identifier No. 4
1027
dez
Broadcast identifier No. 9 (all)
1032
dez
Table 11: Identifier example
Based on the above example, the master transmits its process data to the frequency inverter with the
identifier 200. As a response, it receives the actual values with the identifier 201. A parameter is sent
with the identifier 712 to the frequency inverter, the response of the frequency inverter is sent with the
identifier 713.
If P509 is set to 11, the broadcast identifiers 1027 and 1032 are also valid.
Pos : 79 /Anl eitungen/ Elektroni k/ Bus s yst eme/4. Kommuni kati on und Prot okoll + Proz ess datentr ans fer /CAN open [ BU 0060]/D as C ANnord Pr ot okoll /Ablauf der Datenübertrag ung [CAN ] @ 1\ mod_1342085421991_388.doc x @ 32000 @ 3 @ 1
4.2.4 Sequence of data transfer
If the user sends process data to the frequency inverter, it responds via the appropriate message
channel. It acts in the same way with parameter orders.
The following delays occur between transmitting and receiving:
- Process data
(t
PZD
)
approx 1 to 3 ms
- Parameter data (t
PKW
)
approx. 5 to 10 ms
If an error occurs in the frequency inverter, it immediately transmits its status word and actual value
via the PZD channel. The error state is indicated by the error bit in the status word. The current error
number can then be read out via the PKW channel.
