6 liquid combustion heat, Calculations, C= specific combustion heat – Liquid Controls SP4000 User Manual
Page 21
SP4000 Flow Computer
18
3.6 Liquid Combustion Heat
Measurements:
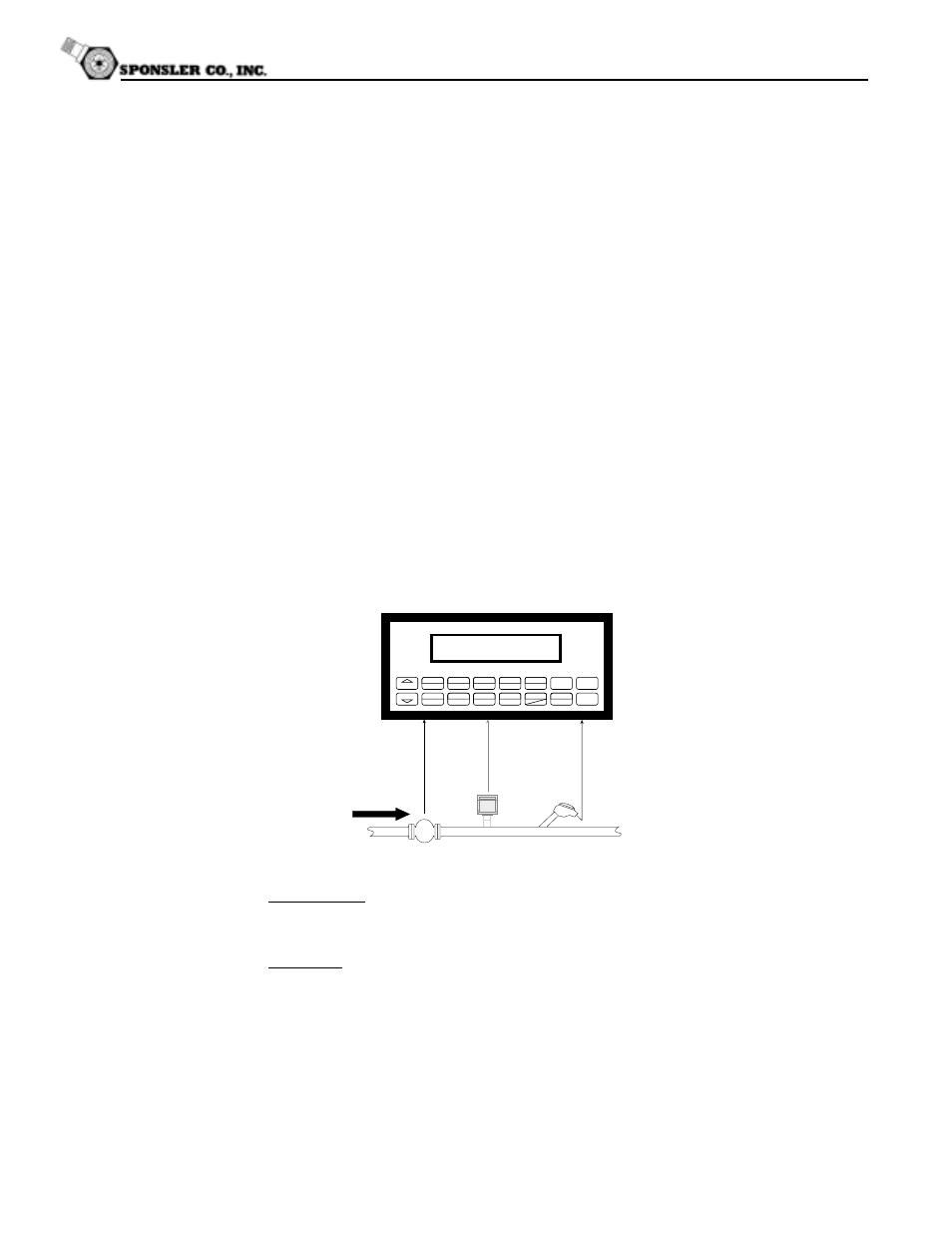
Actual volume flow is measured by the flowmeter. Temperature is measured by the
temperature transmitter. A pressure transmitter can be used to monitor pressure. Pressure
measurement does not affect the calculation.
Calculations:
• The density, mass flow and combustion heat are calculated using the fluid
characteristics stored in the flow computer. (see "FLUID DATA" submenu)
Output Results:
• Display Results
Combustion Heat, Mass or Volume Flow Rate, Resettable Total, Non-Resettable
Total, Temperature, Pressure, Density (optional: peak demand, demand last
hour, time/date stamp)
• Analog Output
Combustion Heat, Mass or Volume Flow Rate, Temperature, Pressure, Density,
Peak Demand, Demand Last Hour
• Pulse Output
Combustion Heat, Mass or Volume Total
• Relay Outputs
Combustion Heat, Mass or Volume Flow Rate, Total, Temperature, Pressure
Alarms, Peak Demand, Demand Last Hour
Applications:
Calculate the energy released by combustion of liquid fuels
LIQUID COMBUSTION
HEAT
Liquid Combustion
Heat Illustration
Volume Flow
As calculated in section 3.4
Heat Flow
Heat Flow = C • volume flow • (1-
α
• (T
1
-T
ref
))
2
• ref. density
α
= Thermal expansion coefficient • 10
-6
C
= Specific combustion heat
Calculations
Flowmeter
Temperature
Transmitter
5
0
–
TIME
CLEAR
•
MENU
ENTER
HELP
TEMP
4
PRE 1
3
RATE
2
TOTAL
1
GRAND
6
SCROLL
7
PRE 2
8
DENS
9
Optional
Pressure
Transmitter
T
1
