Typical data flow sequence – Datamax-O'Neil DPL Programmer’s Manual User Manual
Page 11
Overview
3
Typical Data Flow Sequence
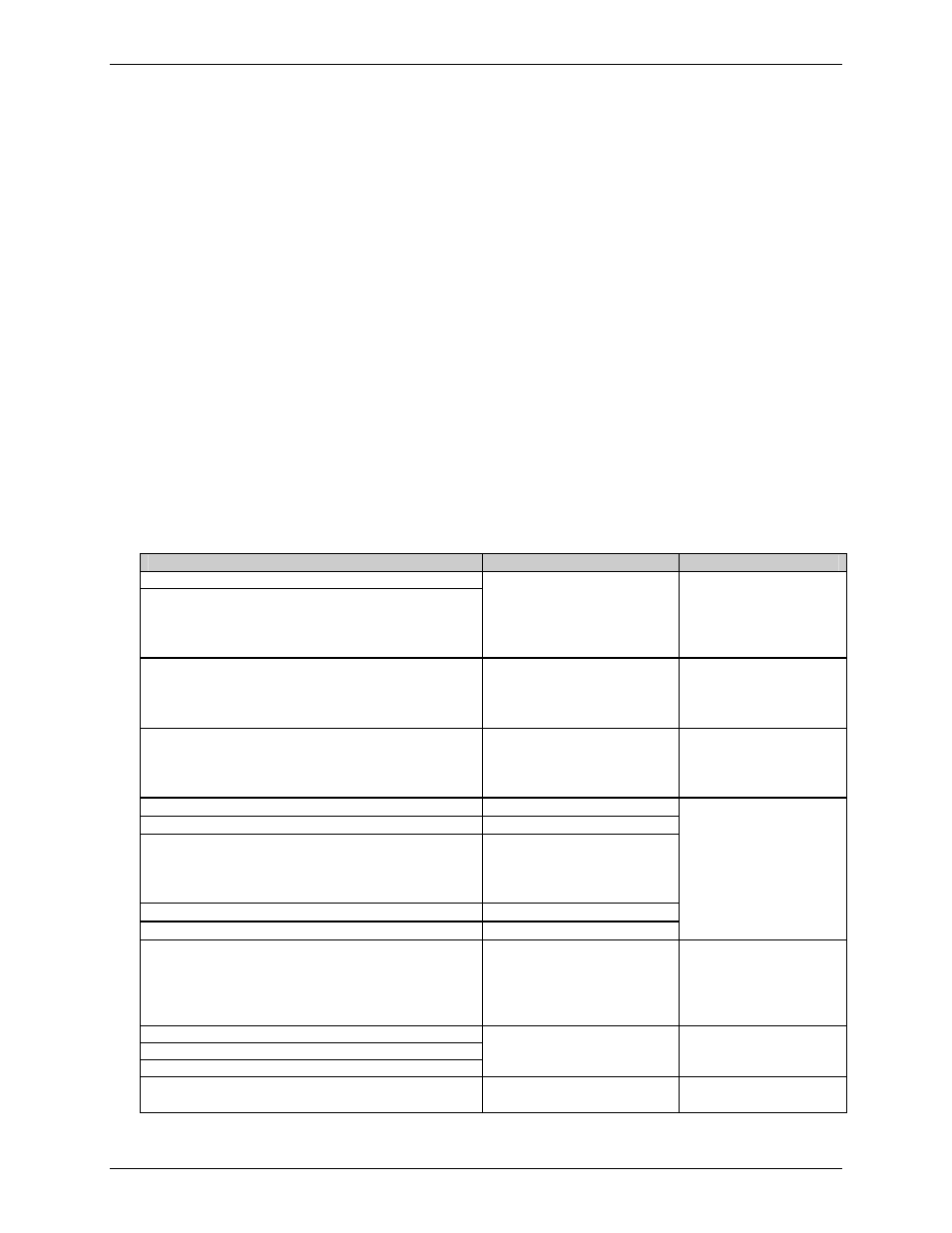
The typical data flow sequence is summarized in the following bullets and detailed in the
table below. Printer Commands data is transmitted to the printer as shown in the table from
left to right, top to bottom.
Status commands
Configuration commands
Download commands
Label format
Status commands
Label reprint commands
Memory cleanup
Typical commands used in the various stages shown above are listed in the tables that
follow.
Status Commands
Commands are available for retrieving stored label formats, updating data, and adding
new data. These techniques are used for increasing throughput; see
Command “r”, and Label Save Command “s”.
Printer Commands
Description
Notes
“Status” commands: Get
Status, Request Memory
Module Storage
Information…
Optional,
bidirectional
communication
required for these
commands.
“Configuration”
commands, download
image…
See
reduce configuration
commands
transferred
“Download” commands,
image, fonts…
RAM (temporary) or
Flash (semi-
permanent)
memory.
Begin label
Existing label
formats may be
recalled. Label
header records are
not required.
D11
Label Header record
131100000500050Typical text field 01
Label Formatting Data
record –
Object type, orientation,
position, data
Q0001
Label Quantity
E
Label Terminate record
Status command
Optional,
bidirectional
communication
required for these
commands.
Reprint with New Data
Records
Used for fast
reprints.
Memory cleanup
Typically used for
temporary storage.
