4 type of service (tos), 5 tos (type of service) and wmm qos, 1 diffserv 7.3.4.2 dscp and per-hop behavior – ZyXEL Communications NWA3550 User Manual
Page 95: Figure 50 diffserv: differentiated service field
Chapter 7 Wireless Configuration
NWA3550 User’s Guide
95
7.3.4 Type Of Service (ToS)
Network traffic can be classified by setting the ToS (Type Of Service) values at the data source
(for example, at the ZyXEL Device) so a server can decide the best method of delivery, that is
the least cost, fastest route and so on.
7.3.4.1 DiffServ
DiffServ is a class of service (CoS) model that marks packets so that they receive specific per-
hop treatment at DiffServ-compliant network devices along the route based on the application
types and traffic flow. Packets are marked with DiffServ Code Points (DSCPs) indicating the
level of service desired. This allows the intermediary DiffServ-compliant network devices to
handle the packets differently depending on the code points without the need to negotiate paths
or remember state information for every flow. In addition, applications do not have to request
a particular service or give advanced notice of where the traffic is going.
7.3.4.2 DSCP and Per-Hop Behavior
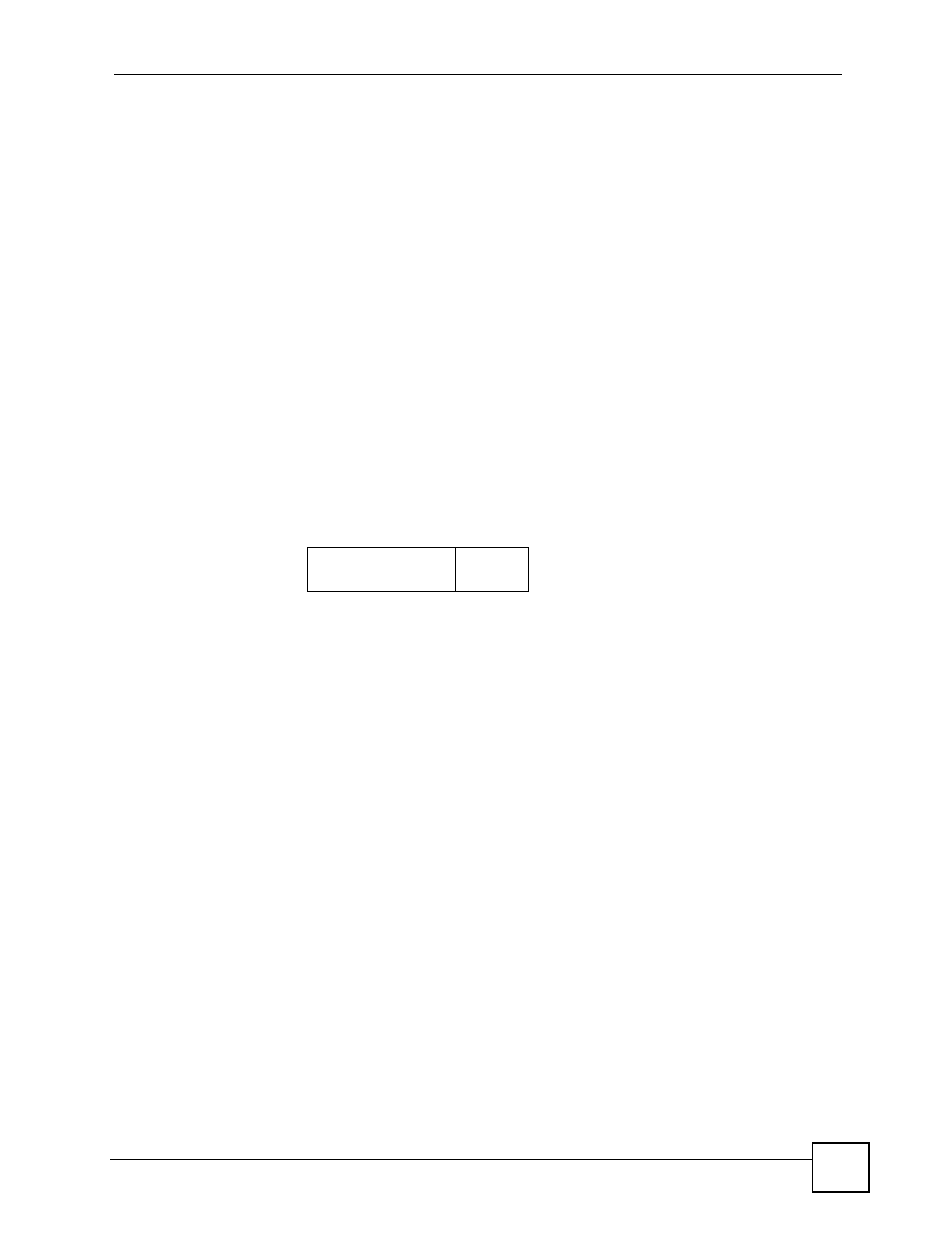
DiffServ defines a new DS (Differentiated Services) field to replace the Type of Service (TOS)
field in the IP header. The DS field contains a 2-bit unused field and a 6-bit DSCP field which
can define up to 64 service levels. The following figure illustrates the DS field.
Figure 50 DiffServ: Differentiated Service Field
DSCP is backward compatible with the three precedence bits in the ToS octet so that non-
DiffServ compliant, ToS-enabled network device will not conflict with the DSCP mapping.
The DSCP value determines the forwarding behavior, the PHB (Per-Hop Behavior), that each
packet gets across the DiffServ network. Based on the marking rule, different kinds of traffic
can be marked for different priorities of forwarding. Resources can then be allocated
according to the DSCP values and the configured policies.
7.3.5 ToS (Type of Service) and WMM QoS
The DSCP value of outgoing packets is between 0 and 255. 0 is the default priority. WMM
QoS checks the DSCP value in the header of data packets. It gives the traffic a priority
according to this number.
In order to control which priority level is given to traffic, the device sending the traffic must
set the DSCP value in the header. If the DSCP value is not specified, then the traffic is treated
as best-effort. This means the wireless clients and the devices with which they are
communicating must both set the DSCP value in order to make the best use of WMM QoS. A
Voice over IP (VoIP) device for example may allow you to define the DSCP value.
DSCP
(6-bit)
Unused
(2-bit)
