Configuring a traversal server zone, Configuring the vcs as a traversal server – TANDBERG Security Camera User Manual
Page 155
155
D14049.03
MAY 2008
Grey Headline (continued)
TANDBERG
VIDEO COMMUNICATIONS SERVER
ADMINISTRATOR GUIDE
Configuring the VCS as a Traversal Server
Configuring a Traversal Server Zone
VCS Configuration > Zones
•
.
You will be taken to the
Zones
page.
Click on the name of the zone you wish to
configure.
You will be taken to the
Edit Zones
page.
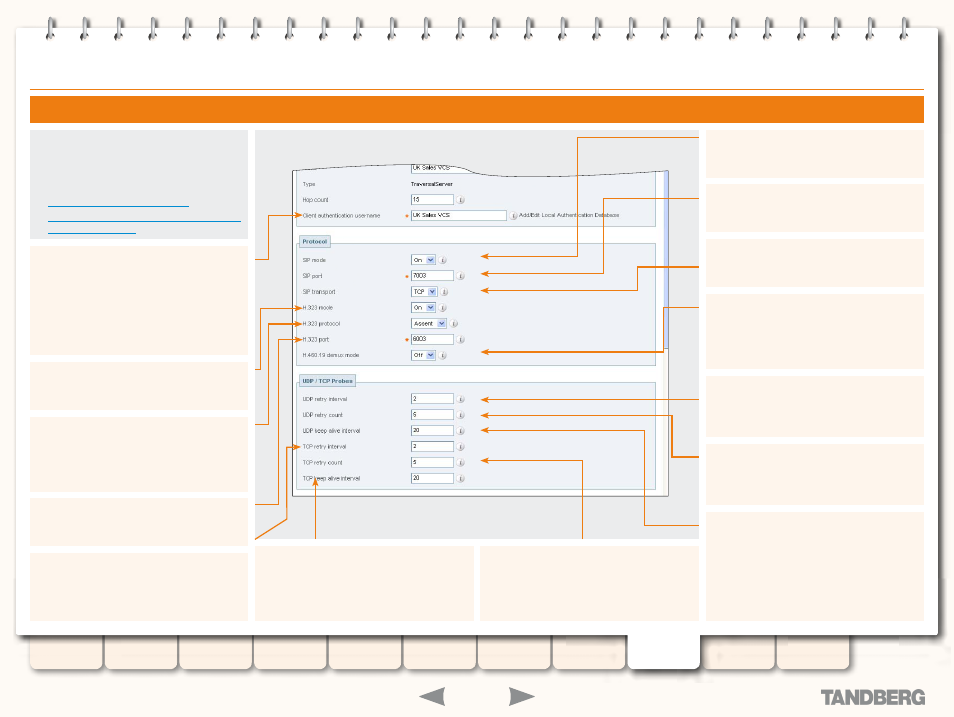
xConfiguration Zones Zone [1..200]
TraversalServer
H.323 mode
Determines whether H.323 calls will be allowed
to and from the traversal client.
H.323 port
Specifies the port on the VCS Expressway to
be used for H.323 connections from the client.
H.323 protocol
Determines which of the two firewall traversal
protocols will be used for calls through the
firewall, to and from the client. The same
protocol must be used by the client.
SIP mode
Determines whether SIP calls will be allowed to
and from the traversal client.
SIP port
Specifies the port on the VCS Expressway to
be used for SIP calls from the traversal client.
SIP transport
Determines which transport type will be used
for SIP calls to and from the traversal client.
Client authentication username
If the traversal client is a VCS, this must be the
VCS’s Authentication Username.
You must also add the client’s Authentication
username and password to the VCS’s
authentication database. To go directly to the
page where you can do this, click on the
Add/
Edit Local Authentication Database
link.
H.460.19 demux mode
On
: allows use of the same two ports for media
for all calls from the traversal client.
Off
: each call from the traversal client will use
a separate pair of ports for media.
TCP keep alive interval
Sets the interval (in seconds) with which the
traversal client will send a TCP probe to the
VCS once a call is established, in order to keep
the firewall’s NAT bindings open.
TCP retry count
Sets the number of times the traversal client
will attempt to send a TCP probe to the VCS
Expressway.
TCP retry interval
Sets the frequency (in seconds ) with which
the traversal client will send a TCP probe to the
VCS Expressway.
UDP keep alive interval
Sets the interval (in seconds) with which the
traversal client will send a UDP probe to the
VCS once a call is established, in order to keep
the firewall’s NAT bindings open.
UDP retry count
Sets the number of times the traversal client
will attempt to send a UDP probe to the VCS
Expressway.
UDP retry interval
Sets the interval (in seconds) with which the
traversal client will send a UDP probe to the
VCS Expressway.
