PLANET XGS3-24042 User Manual
Page 674
81-28
route table and IFIL (Label Forwarding Information Base).
To be specific, the information in VPN instances include: LFIB, IP route table, interfaces bound with VPN
instance, and its management information (including RD, route filter policy, member interface list and etc).
VPN-IPv4 Address
The traditional BGP can’t correctly handle the VPN routes with overlapping address spaces. Assume that
VPN1 and VPN2 both use the segment of 10.110.10.0/24, and advertise separately a route reaching this
segment, BGP will only choose one of the two routes, losing the one reaching the other VPN.
PE routers use MP-BPG to advertise VPN routes between each other and solve the above problem via
VPN-IPv4 address family.
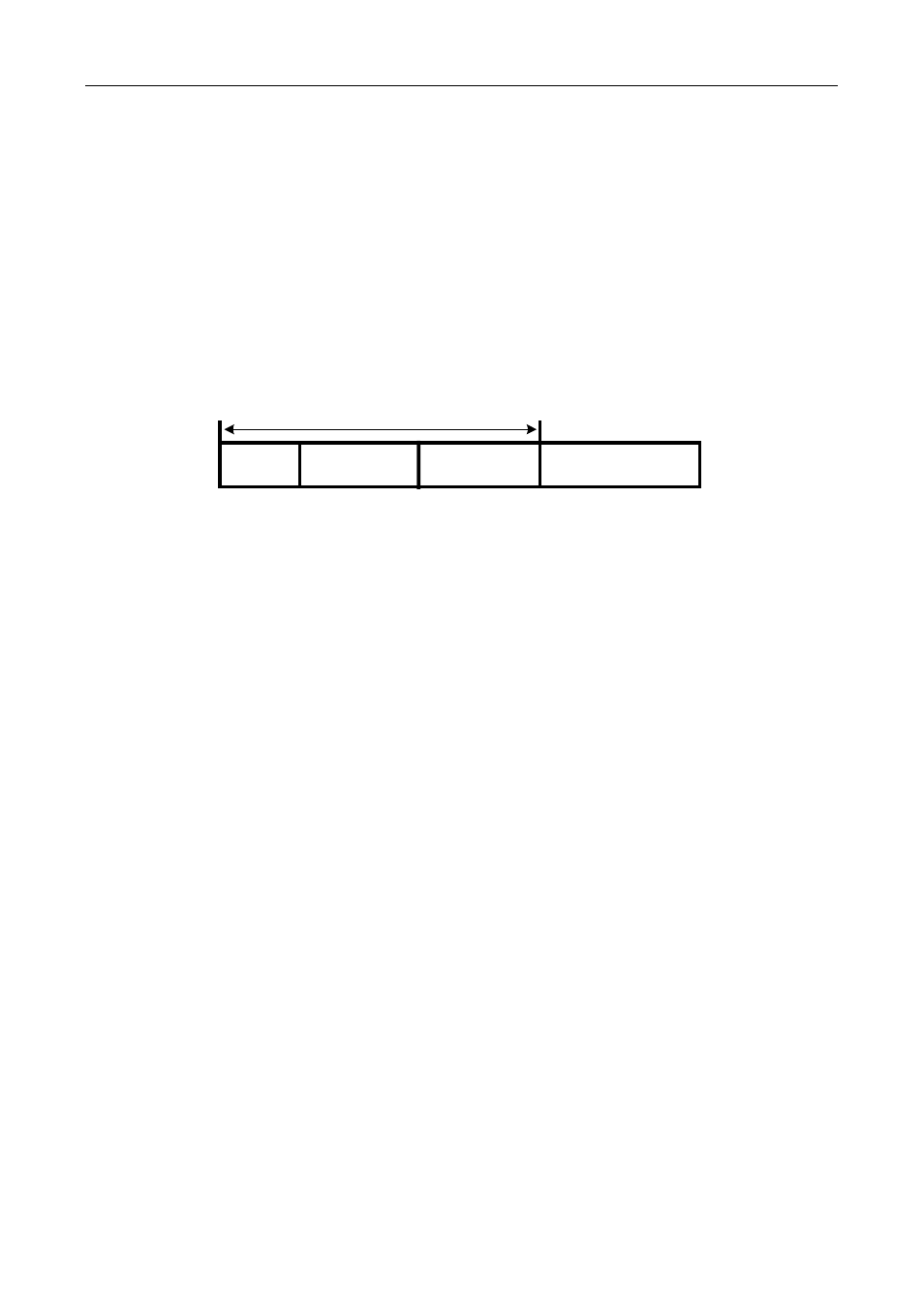
A VPN-IPv4 address consists of 12 bytes, including 8 bytes of RD (Route Distinguisher) and 4 bytes of IPv4
address prefix.
Figure 81-2 VPN-IPv4 Address Structure
After receiving the regular IPv4 routes from CE, PE should advertise these private network VPN routes to the
remote PE. The independency of the private network routes is based on the additional RD patched to them.
SP can independently distribute globally unique RD, thus, even the VPN from different SP networks use the
same IPv4 address space, the PE routers can advertise different routes to them.
It is recommended to allocate a special RD for each VPN instance on the PE to ensure all routes reaching the
same CE uses the same RD. the VPN-IPv4 address whose RD is 0 is a globally unique IPv4 address.
Adding RD is to a specific IPv4 prefix will make the latter globally unique, which is the meaning of RD.
RD may relate with ASN, in which case, it is a combination of an ASN and a random number; it may also
relate with IP address, in which case, it is a combination of an IP address and a random number.
There are two RD formats, differing with each other via 2 bytes of Type filed:
If Type is 0, the Administrator sub-field takes up 2 bytes, Assigned Number sub-field takes up 4
bytes. The format would be: 16 bits of ASN: 32 bits of user-defined number. For example: 100:1
If Type is 0, the Administrator sub-field takes up 2 bytes, Assigned Number sub-field takes up 4
bytes. The format would be: 32 bits of IPv4 address: 16 bits of user-defined number. For example:
172.1.1.1:1
To guarantee the global uniqueness of RD, please don’t set the value of Administrator sub-filed as private
ASN or private IP address.
VPN Target Attribute
BGP/MPLS VPN uses a 32 bit BGP extended community attribute – VPN Target (also called Route Target) to
control the advertisement of VPN route information.
There are two types of VPN Target attribute used by VPN instances on PE routers:
Export Target attribute: the local PE sets the Export Target attribute for the VPN-IPv4 routes it learns
from the sites directly connected to it, before advertising the routes to other PE.
Subfield
Type Field
( 2-Byte )
IPv4 Address Prefix
( 4-Byte )
Administrator
Assigned
Number Subfield
Route Distinguisher ( 8-Byte )
