2 introduction to mib, 2 introduction to mib -7 – PLANET XGS3-24042 User Manual
Page 61
4-7
Get-Bulk-Request
Set-Request
Trap
Inform-Request
NMS sends queries to the Agent with Get-Request, Get-Next-Request, Get-Bulk-Request and Set-Request
messages; and the Agent, upon receiving the requests, replies with Get-Response message. On some
special situations, like network device ports are on Up/Down status or the network topology changes, Agents
can send Trap messages to NMS to inform the abnormal events. Besides, NMS can also be set to alert to
some abnormal events by enabling RMON function. When alert events are triggered, Agents will send Trap
messages or log the event according to the settings. Inform-Request is mainly used for inter-NMS
communication in the layered network management.
USM ensures the transfer security by well-designed encryption and authentication. USM encrypts the
messages according to the user typed password. This mechanism ensures that the messages can’t be
viewed on transmission. And USM authentication ensures that the messages can’t be changed on
transmission. USM employs DES-CBC cryptography. And HMAC-MD5 and HMAC-SHA are used for
authentication.
VACM is used to classify the users’ access permission. It puts the users with the same access permission in
the same group. Users can’t conduct the operation which is not authorized.
4.4.2 Introduction to MIB
The network management information accessed by NMS is well defined and organized in a Management
Information Base (MIB). MIB is pre-defined information which can be accessed by network management
protocols. It is in layered and structured form. The pre-defined management information can be obtained from
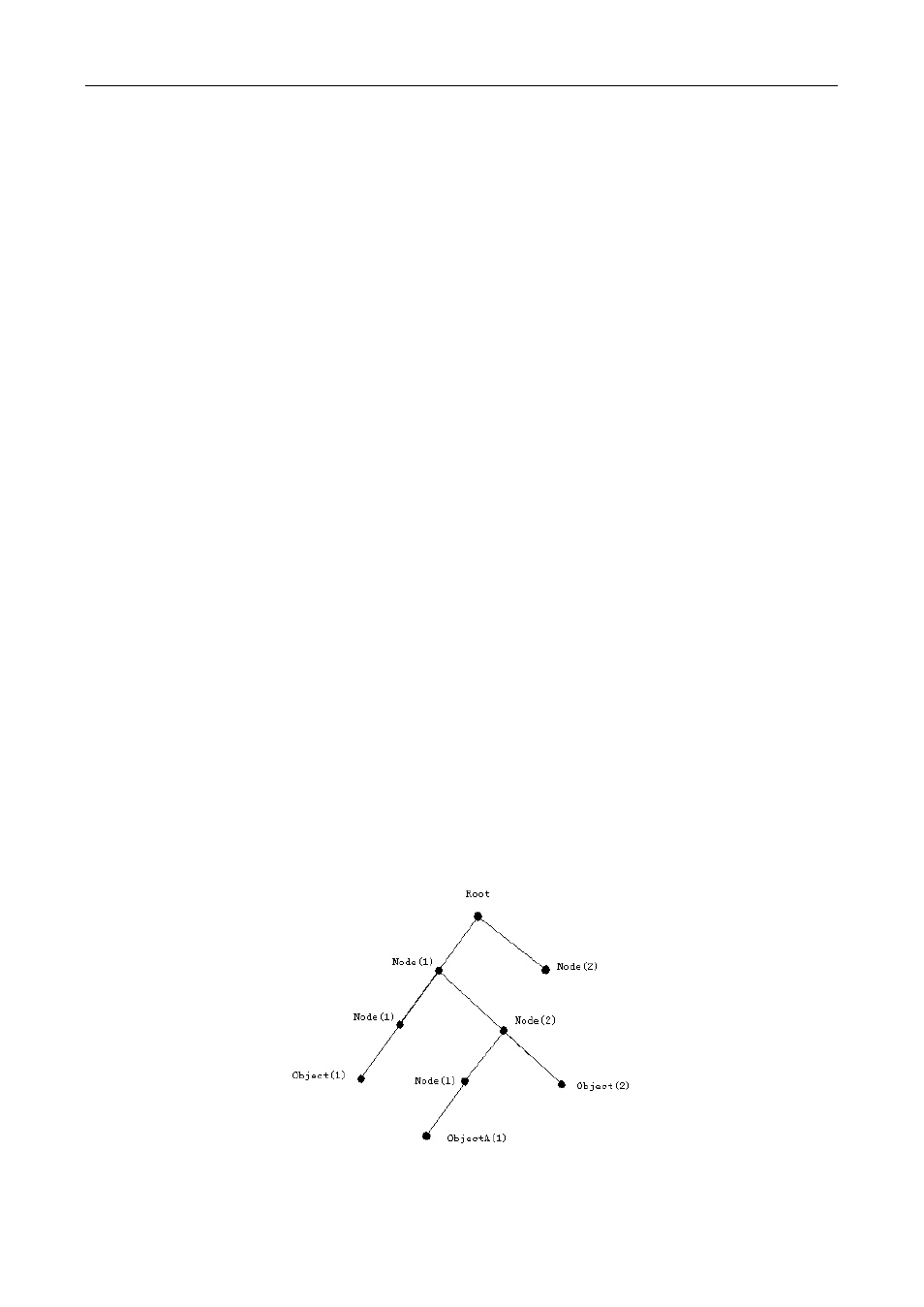
monitored network devices. ISO ASN.1 defines a tree structure for MID. Each MIB organizes all the available
information with this tree structure. And each node on this tree contains an OID (Object Identifier) and a brief
description about the node. OID is a set of integers divided by periods. It identifies the node and can be used
to locate the node in a MID tree structure, shown in the figure below:
Figure 4-1 ASN.1 Tree Instance
