Signal types – Grass Valley MRC v.1.2 User Manual
Page 153
143
Miranda Router Configurator
User’s Guide
If you have DVD players, it is slightly more complicated: there are several signals for each DVD
and you will need a router for each of the different signal types. Further, you might need
converters if your TVs are older models that cannot receive DVD input.
Routers (and control panels) allow you to control and route signals to and from your equipment.
Routers and control panels do not start, stop, rewind, cue, or fast-forward any device.
The Crosspoint Matrix Inside the Router
In concept, at least, a router contains an array of wires. (Physically, it might be different.)
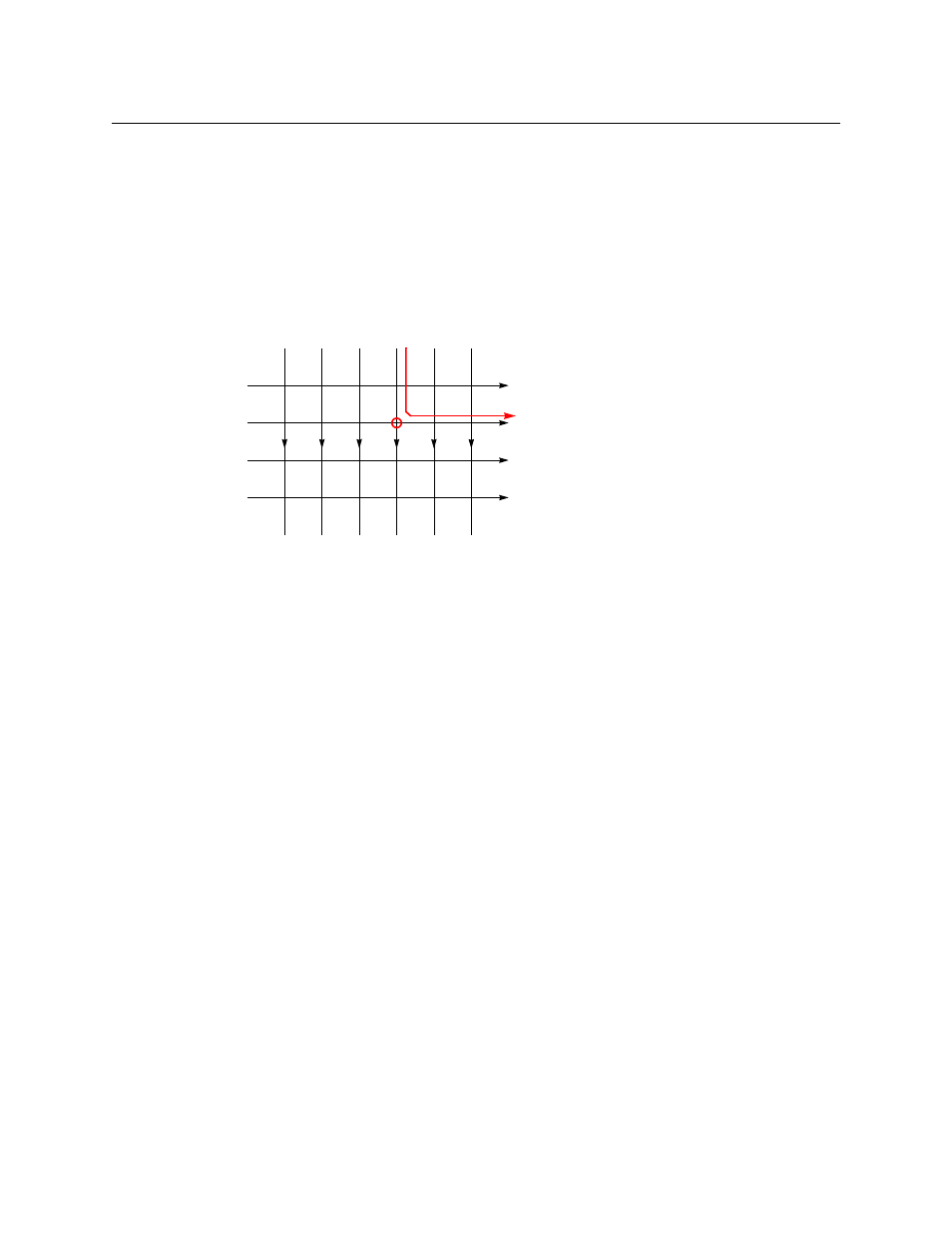
Fig. 6-1: A rudimentary switching matrix
If you had the patience and some materials, you could build a simple router. It would be nothing
more than a number of wires arranged so they cross over each other. If you pressed two wires
together where they cross, a signal could flow (given proper electrical connections) from the
input to the output. In Figure 6-1, input wire 4 and output wire 2 are connected.
The point where they cross is called a crosspoint. The pattern formed by all the points is called a
crosspoint matrix.
If a matrix has N inputs and M outputs, it has N × M crosspoints. The 6×4 matrix depicted above
has 24 crosspoints. By convention, the number at the left of the × represents inputs; the number
on the right, outputs.
In a real router, the matrix is an integrated circuit, and the connection between an input and an
output is performed electronically (by a transistor or similar circuit).
Some routers also perform signal conditioning at the inputs and outputs of the matrix.
Sources and Destinations
The signals that routers process come from, and go to, devices. “Device” is a generic name for
VCRs, DVDs, cameras, video monitors, audio monitors, mixers, video editing workstations, and
so on.
A source device is one that feeds a signal into a router. The source is where the signal originates.
A destination device is one that receives a signal from a router. The destination is where the
signal is going.
Signal Types
Video signals are classified as digital (3Gig, HD, SD) or analog. Audio signals are classified as
digital or analog and in addition, as stereo or mono. For most NVISION series routers, digital
Input wires
Output wires
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
