Dhcp snooping configuration example, Network requirements – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 287
274
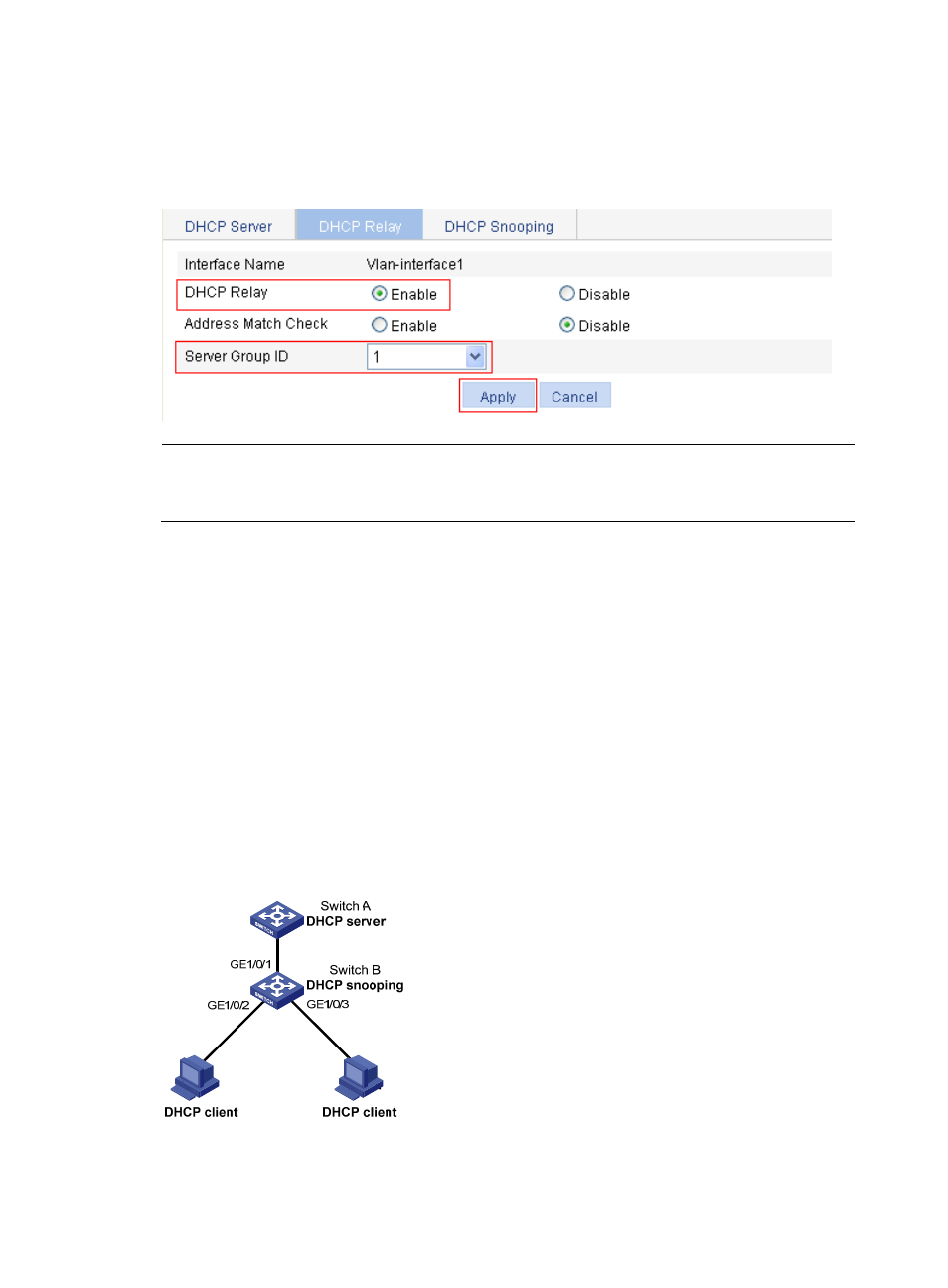
b.
Select the Enable option for DHCP Relay, and select 1 for Server Group ID, as shown in
.
c.
Click Apply.
Figure 249 Enable the DHCP relay agent on an interface and correlate it with a server group
NOTE:
Because the DHCP relay agent and server are on different subnets, you need to configure a static route or
dynamic routing protocol to make them reachable to each other.
DHCP snooping configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in
, a DHCP snooping device (Switch B) is connected to a DHCP server through
GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, and to DHCP clients through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet
1/0/3.
•
Enable DHCP snooping on Switch B and configure DHCP snooping to support Option 82.
Configure the handling strategy for DHCP requests containing Option 82 as replace.
•
Enable GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to forward DHCP server responses; disable GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 from forwarding DHCP server responses.
•
Configure Switch B to record clients’ IP-to-MAC address bindings in DHCP-REQUEST messages and
DHCP-ACK messages received from a trusted port.
Figure 250 Network diagram
