Configuring a logical digital voice interface, Configuring r2 signaling – H3C Technologies H3C MSR 5600 User Manual
Page 44
34
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2.
Enter E1 or T1 interface
view.
controller { e1 | t1 } number N/A
3.
Create a timeslot set and
enable R2 signaling for it.
timeslot-set ts-set-number
timeslot-list timeslots-list signal r2
By default, no timeslot set is created.
Configuring a logical digital voice interface
The system automatically creates a logical voice interface in the form of E1/T1 interface number:timeslot
set number for a timeslot set.
The description, shutdown, receive gain, transmit gain, and cng-on commands for a logical digital voice
interface have the same functions as those for analog voice interfaces. For more information about those
commands, see related sections in "Configuring analog voice interfaces."
To configure a logical digital voice interface:
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2.
Enter logical digital voice
interface view.
subscriber-line
number:ts-set-number
N/A
3.
Configure a companding law
for PCM.
pcm { a-law | μ-law }
The default is a-law for logical
digital voice interfaces of E1
interfaces and μ-law for logical
digital voice interfaces of T1
interfaces.
Configuring R2 signaling
ITU-T recommendations Q.400 through Q.490 define the R2 signaling standards. However, the R2
signaling standards implemented in different countries and regions are ITU variants.
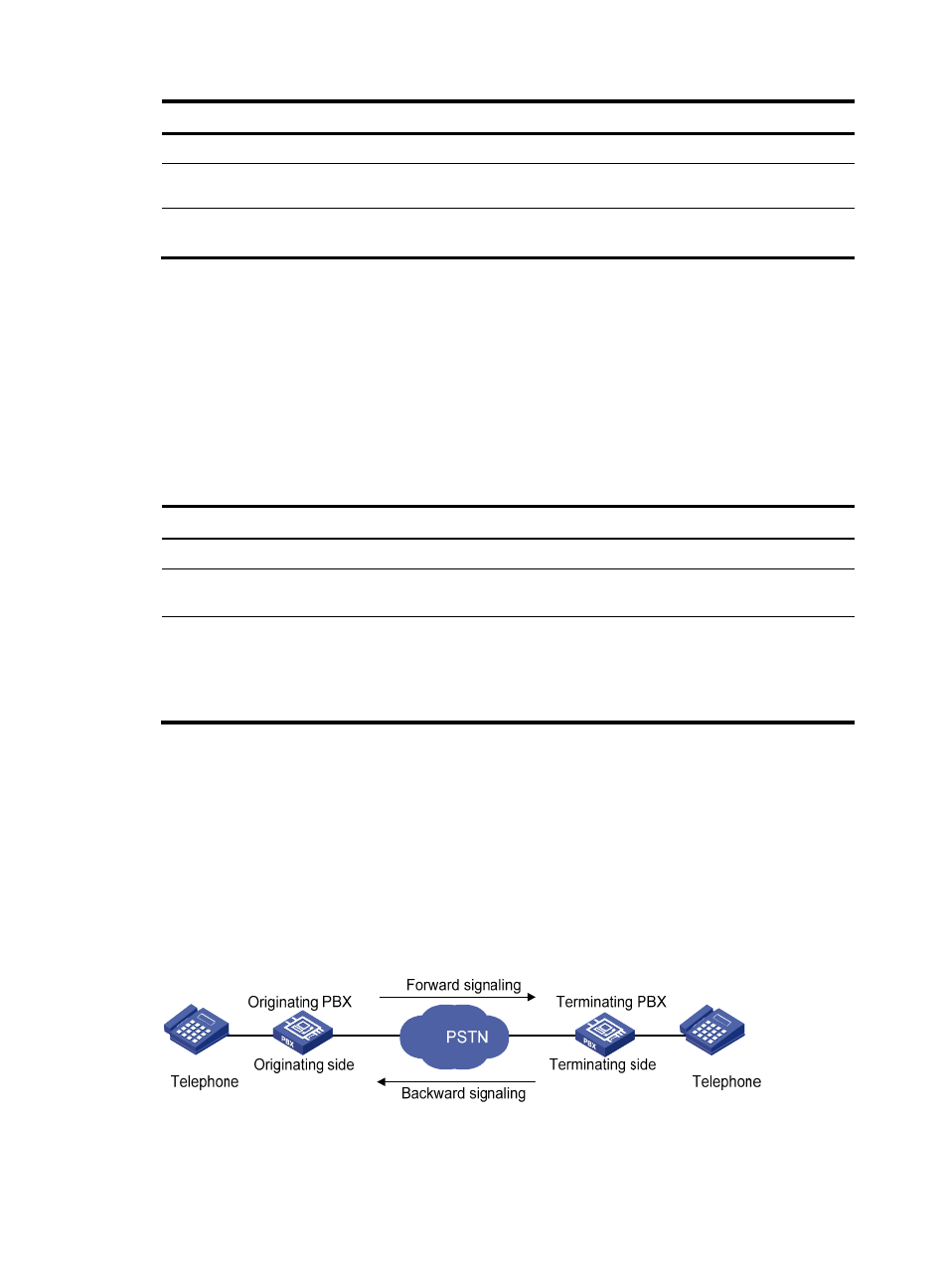
In R2 signaling, the calling side serves as the originating PBX, and the called side serves as the
terminating PBX. Signaling sent by the originating PBX is called forward signaling, and signaling sent by
the terminating PBX is called backward signaling, as shown in
.
Figure 15 R2 signaling elements
