Gateway-to-gateway tunnel, Endpoint-to-gateway tunnel, Figure 14 – Dell POWEREDGE M1000E User Manual
Page 232: Protec, Figure 15, Gateway
232
Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide
53-1002745-02
Management interface security
7
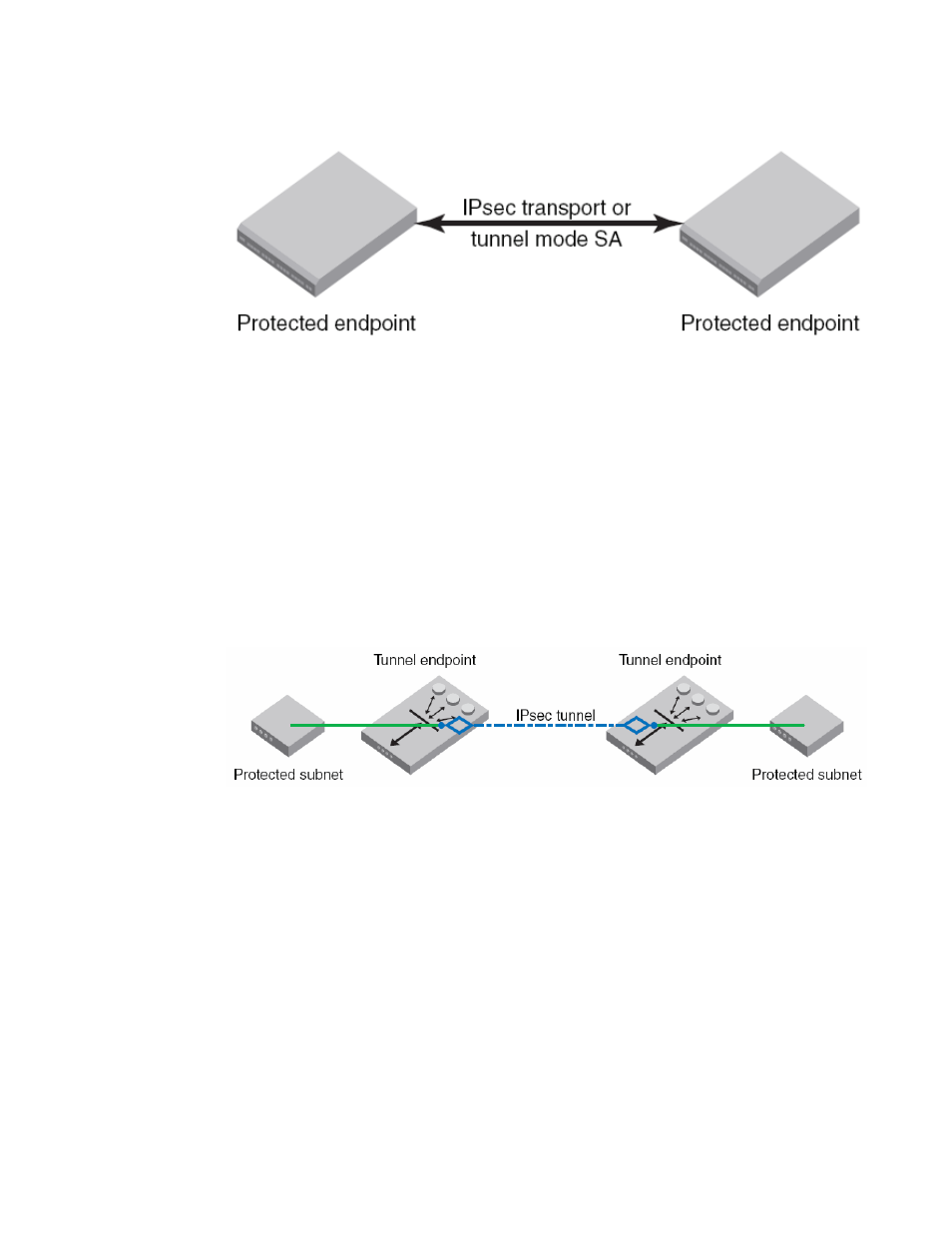
FIGURE 14
Protected endpoints configuration
A possible drawback of end-to-end security is that various applications that require the ability to
inspect or modify a transient packet will fail when end-to-end confidentiality is employed. Various
QoS solutions, traffic shaping, and firewalling applications will be unable to determine what type of
packet is being transmitted and will be unable to make the decisions that they are supposed to
make.
Gateway-to-gateway tunnel
In this scenario, neither endpoint of the IP connection implements IP sec, but the network nodes
between them protect traffic for part of the way. Protection is transparent to the endpoints, and
depends on ordinary routing to send packets through the tunnel endpoints for processing. Each
endpoint would announce the set of addresses behind it, and packets would be sent in tunnel
mode where the inner IP header would contain the IP addresses of the actual endpoints.
FIGURE 15
Gateway tunnel configuration
Endpoint-to-gateway tunnel
In this scenario, a protected endpoint (typically a portable computer) connects back to its corporate
network through an IP sec-protected tunnel. It might use this tunnel only to access information on
the corporate network, or it might tunnel all of its traffic back through the corporate network in
order to take advantage of protection provided by a corporate firewall against Internet-based
attacks. In either case, the protected endpoint will want an IP address associated with the security
gateway so that packets returned to it will go to the security gateway and be tunneled back.
