9 input balance, 1 introduction to input balance, Input balance – Barco CLM HD8 R9050130 User Manual
Page 82: Introduction to input balance
9. Image menu
9.3.9
Input balance
Overview
•
•
9.3.9.1
Introduction to Input Balance
Introduction: Unbalanced color signals
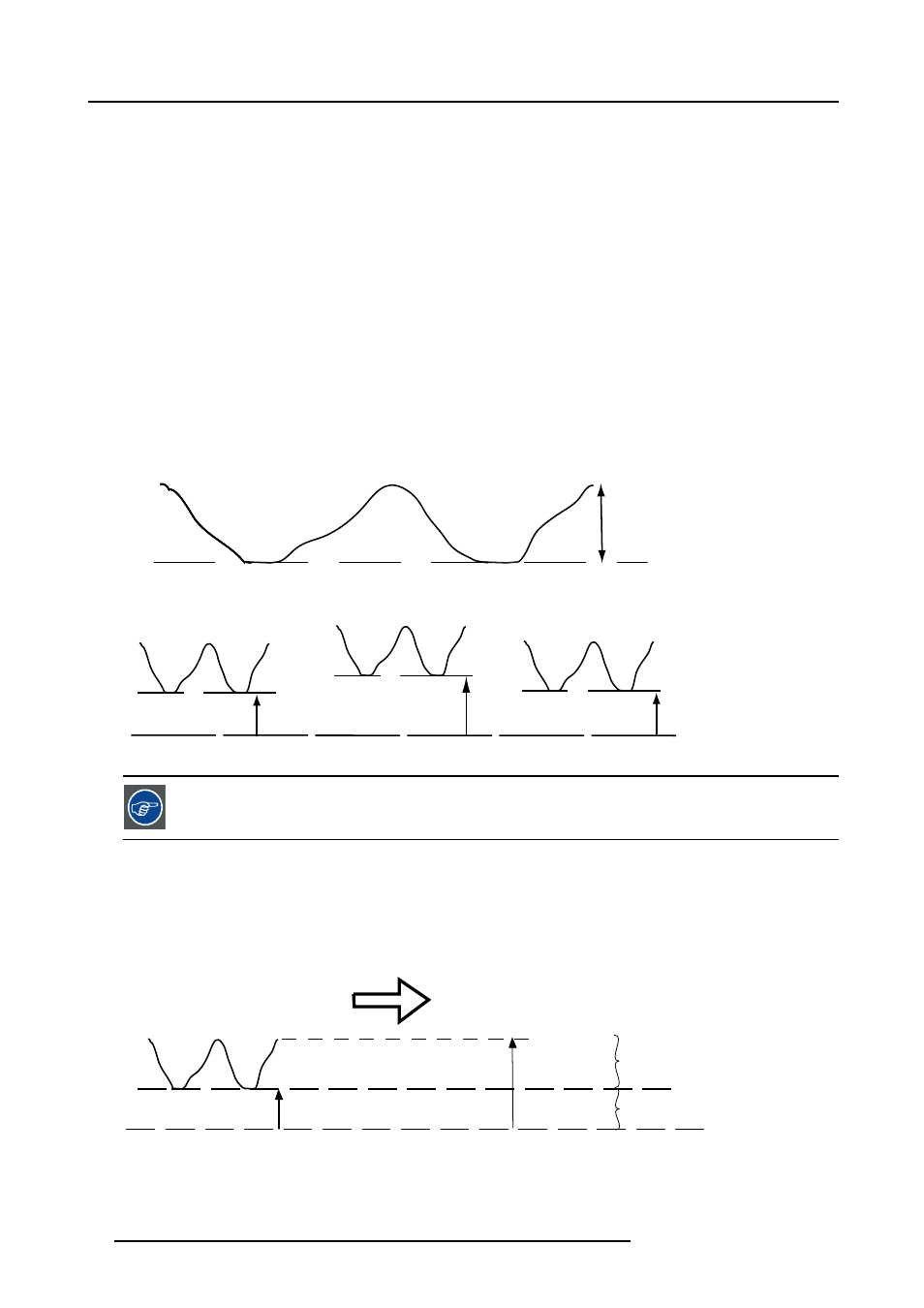
When transporting signals, there is always a risk of deterioration of the information contained in the signals.
In case of information contained in the amplitude of the signals which is the case of data color signals (R, G, B),image 9-41 , we are
quite sure that the amplitude of these color signals is subject to alterations.
An example of alteration may be a DC component added to the signal, in the form of a DC offset repositioning the black level, since
this black level (“brightness”) will become crucial later on (clamping circuit) it will result in “black not being black”.
Another value that is subject to alteration is the amplitude of the signal, resulting in an altered “Gain” of the signal (“white level” or
contrast).
The alterations of the three color signals will happen independently i.e. the colors will end to be unbalanced, image 9-42
B
Black level
0.7V
Image 9-41
Black level
Δ
G
ΔΒ
Δ
R
R
G
B
Image 9-42
One can conclude here that a good color tracking can only be met by using three previously (input) balanced
color signals
Analog Digital Conversion
The analog color signals must pass through an Analog/Digital conversion circuit prior to any digital processing in the PMP.
A typical ADC transforms the analog value into an 8 bit coded digital signal.
The graphic shows that when converting a signal containing a DC offset component the range of the converter is not optimally used.
Black level
Δ
R
ADC
0
255
i1 : superfluous information
i2 : video information
Image 9-43
78
R59770057 CLM HD8 15/03/2010
