1 pulse input (p_sw), Figure 30: pulse input types, 1 ms time constant filter) – Campbell Scientific CR200/CR200X-series Dataloggers User Manual
Page 56
Section 4. Sensor Support
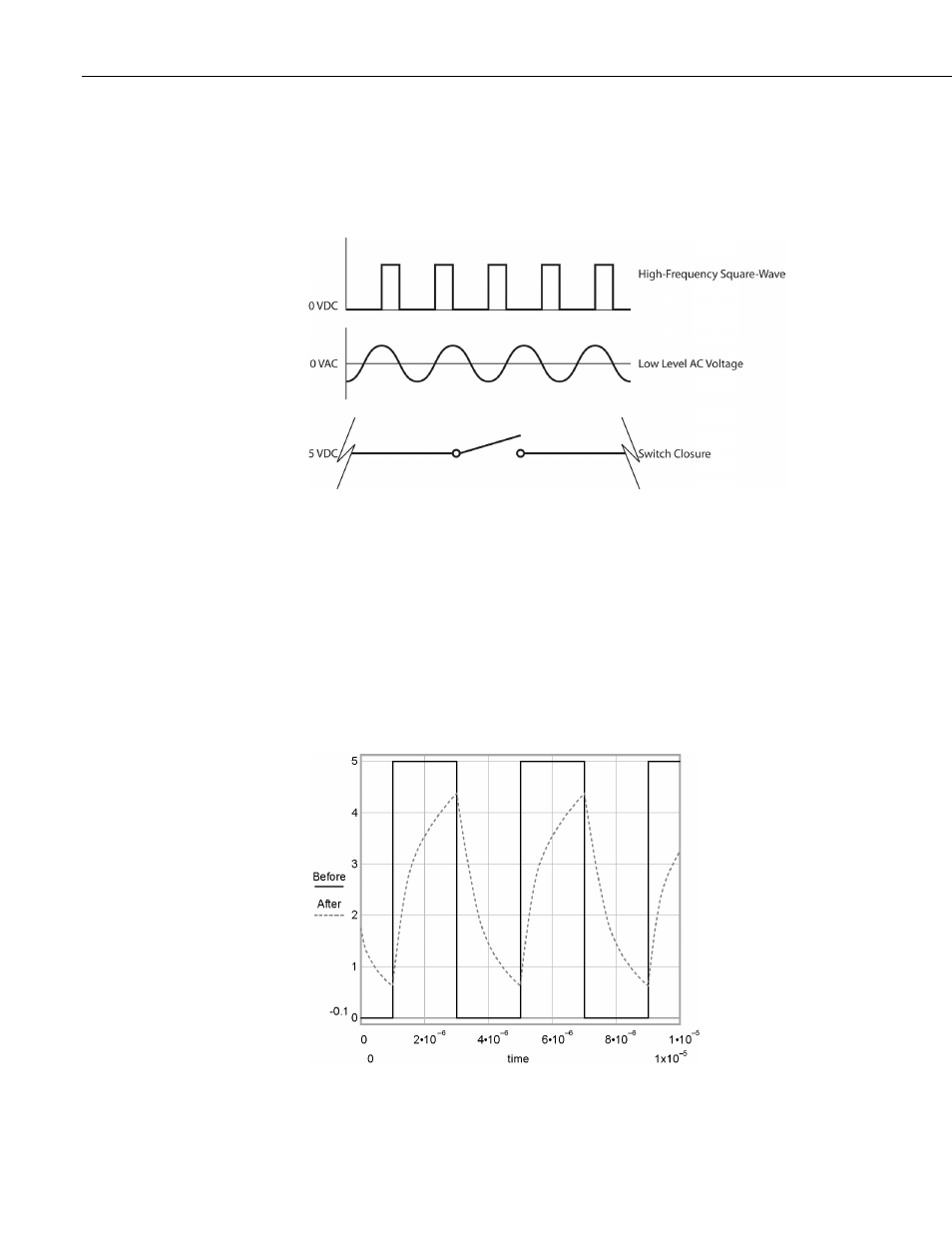
FIGURE. Pulse Input Types
(p. 7) illustrates pulse input types measured by the
CR200(X). Dedicated pulse input channel P_SW can be configured to read
high- frequency pulses or switch closure, while P_LL can be configured to read
a low-level AC signal. With a 100 kOhm pull-up resistor added to the wiring
panel P_LL, C1, or C2 can measure pulse input signals (See
Pulse Input (P_SW
Figure 30: Pulse Input Types
4.4.1.1 Pulse Input (P_SW)
Internal hardware routes high-frequency pulse to an inverting CMOS input
buffer with input hysteresis. The CMOS input buffer is guaranteed to be an
output zero level with its input ≥ 2.7 V, and guaranteed to be an output one with
its input ≤ 0.9 V. An RC input filter with approximately a 1 µs time constant
precedes the inverting CMOS input buffer, resulting in an amplitude reduction
of high frequency signals between the P_SW terminal block and the inverting
CMOS input buffer as illustrated in FIGURE. Amplitude reduction of pulse-
count waveform. For a 0 to 5 Volt square wave applied to P_SW, the maximum
frequency that can be counted in pulse input mode is approximately 1 kHz.
Figure 31: Amplitude Reduction of Pulse-Count Waveform (before and
after 1 ms time constant filter)
44
