3 switched unregulated (nominal 12 volt), 2 voltage measurement, 1 measurement sequence – Campbell Scientific CR200/CR200X-series Dataloggers User Manual
Page 50: 2 measurement accuracy, Table 4. current sourcing limits
Section 4. Sensor Support
4.1.3 Switched Unregulated (Nominal 12 Volt)
Voltage on the SW Battery terminal will change with CR200(X) supply voltage.
The CRBASIC instruction SWBatt () controls the SW Battery terminal.
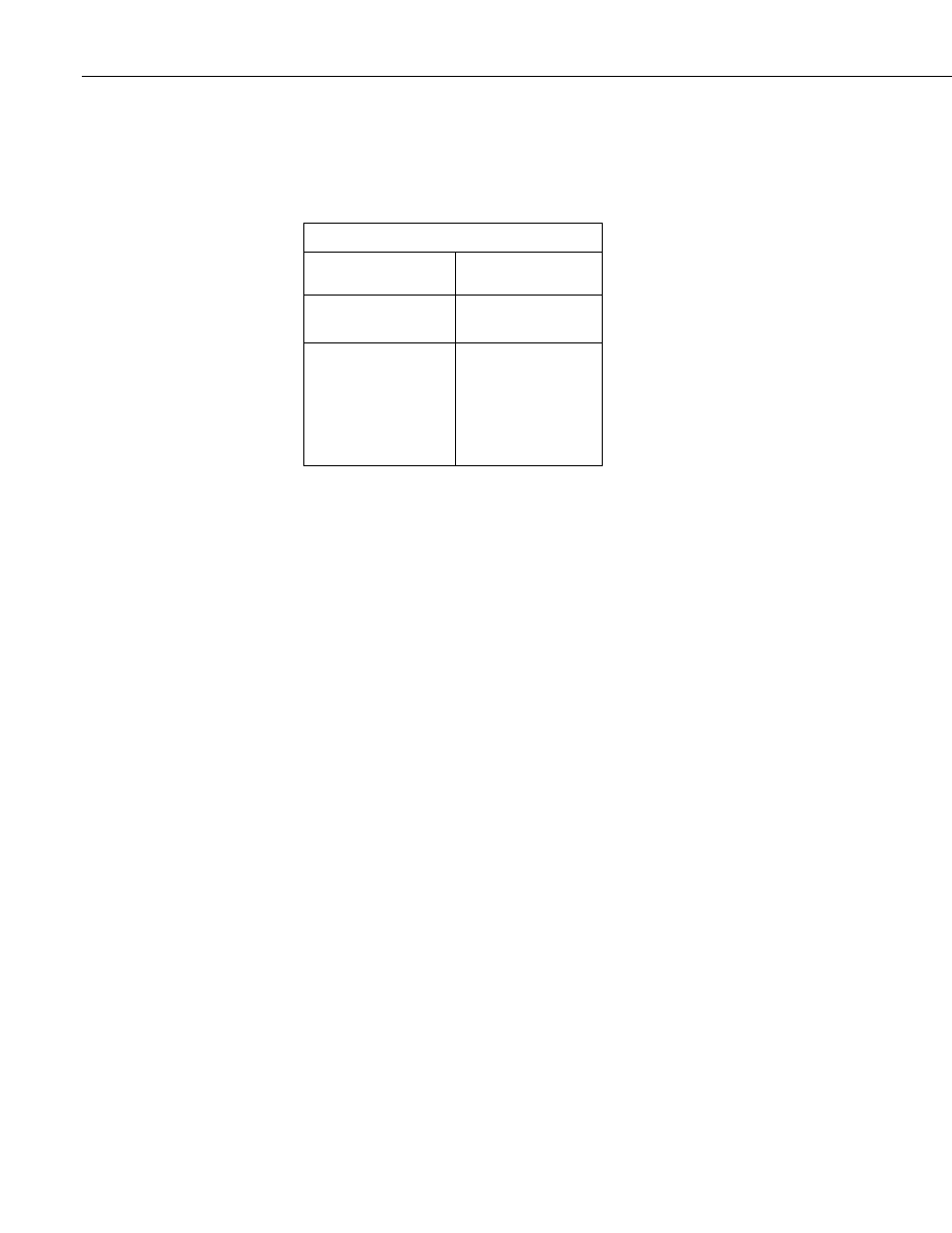
Table 4. Current Sourcing Limits
Terminal
Limit
VX1, VX2
25 mA @ 2.5V
10 mA @ 5V
SW Battery
< 900 mA @ 20°C
< 729 mA @ 40°C
< 630 mA @ 50°C
< 567 mA @ 60°C
< 400 mA @ 85°C
4.2 Voltage Measurement
4.2.1 Measurement Sequence
The first step in a voltage measurement is a calibration to measure the ground
offset. The calibration is performed once for each voltage measurement. The
CR200(X) measures analog voltages with a sample and hold analog to digital
(A/D) conversion. The A/D conversion is made with a 12-bit successive
approximation technique which resolves the signal voltage to one part in 4096
of the full scale 2.5 V range, which is 0.6 millivolts.
To reduce noise, 10 measurements are rapidly made and averaged to form the
result returned. The measurements that go into the average each take about 26
microseconds.
4.2.2 Measurement Accuracy
CR200(X) analog measurement error is calculated as
Error = Gain Error (%) + Offset Error
Gain error is expressed as ±% and is a function of input voltage and CR200(X)
temperature. It increases with component temperature and aging. Between -
40°C and +50°C, gain error is typically ±0.25% of the reading with a 1.2
millivolt offset. Worst case over that same temperature range is ±1% of the
reading with a 2.4 millivolt offset.
FIGURE. Voltage Measurement Accuracy (-40° to +50°C)
p. 40 illustrates that
as magnitude of input voltage decreases, measurement error decreases.
38
