2 crbasic instructions - modbus, 3 addressing (modbusaddr), 4 supported function codes (function) – Campbell Scientific CR200/CR200X-series Dataloggers User Manual
Page 153
Section 15. Alternate Telecoms Resource Library
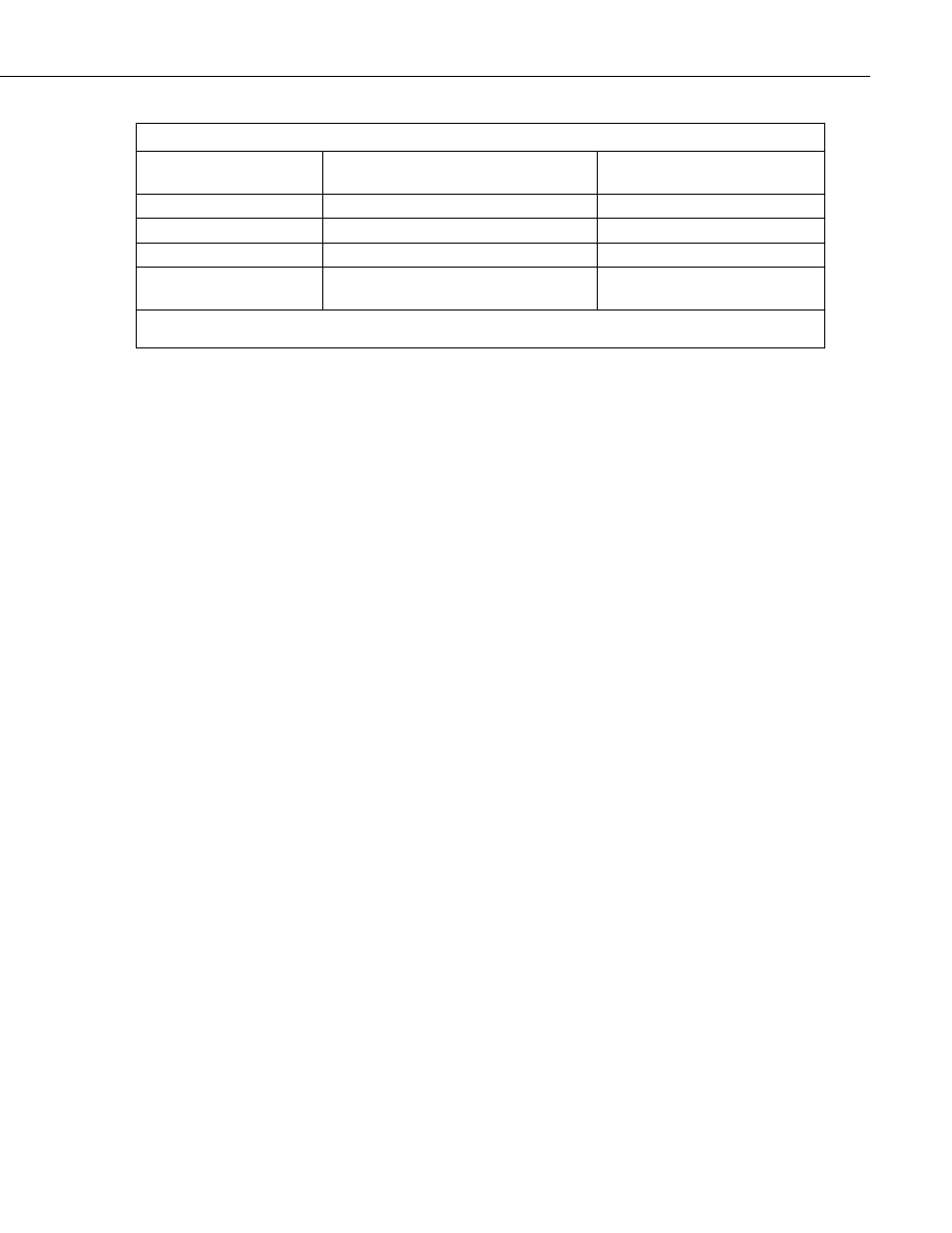
Table 20. CRBASIC Ports, Flags, Variables and Modbus Registers
CR200(X) Feature
Example CRBASIC
Declaration
Equivalent Example
Modbus Register
Control Port (Port)
Public Port(8)
00001 to 00009
Flag
Public Flag(17)
00001 to 00018
Boolean Variable
Public ArrayB(56) as Boolean
00001 to 00057
Variable
Public ArrayV(20)*
40001 to 40041*
or
30001 to 30041*
*Because of byte number differences, each CR200(X) domain variable translates to two Modbus domain input / holding
registers.
15.1.3.2 CRBASIC Instructions - Modbus
Complete descriptions and options of commands are available in CRBASIC
Editor Help.
ModbusMaster ()
Sets up a CR200(X) as a Modbus master to send or retrieve data from a Modbus
slave.
Syntax
ModbusMaster (ResultCode, ComPort, BaudRate,
ModbusAddr, Function, Variable, Start, Length,
Tries, TimeOut)
ModbusSlave ()
Sets up a CR200(X) as a Modbus slave device.
Syntax
ModbusSlave (ComPort, BaudRate, ModbusAddr,
DataVariable, BooleanVariable)
15.1.3.3 Addressing (ModbusAddr)
Modbus devices have a unique address in each network. Addresses range from 1
to 247. Address 0 is reserved for universal broadcasts. When using the NL100,
use the same number as the Modbus and PakBus® address.
15.1.3.4 Supported Function Codes (Function)
Modbus protocol has many function codes. CR200(X) commands support the
following.
•
01 Read Coil Status
•
02 Read Input Status
•
03 Read Holding Registers
•
04 Read Input Registers
141
