Address map and data format, Data format, 1 data format – Dwyer UXF3 User Manual
Page 27: 1 transmission data format, 2 handling of decimal point
- 23 -
7. ADDRESS MAP AND DATA FORMAT
7.1 Data
Format
7.1.1 Transmission
data
format
The MODBUS protocol used in this product is RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) mode.
The transmitted data is “numerical value”, but ASCII code data is partly included.
7.1.2
Handling of decimal point
Numerical value data includes integer data, decimal point position fixed data and floating data. Handling of data
containing a decimal point is described below.
(1) Data with determined decimal point position (int type, long type)
No decimal point is added in the transmission data. Execute decimal point position alignment processing
(elimination of decimal point at the time of transmission, addition of decimal point at the time of reception)
on data with decimal point.
Example: Case of damping data
Read-out data: 03 E8
H
= 1000
Decimal point position: 1 digit
Value:
100.0sec
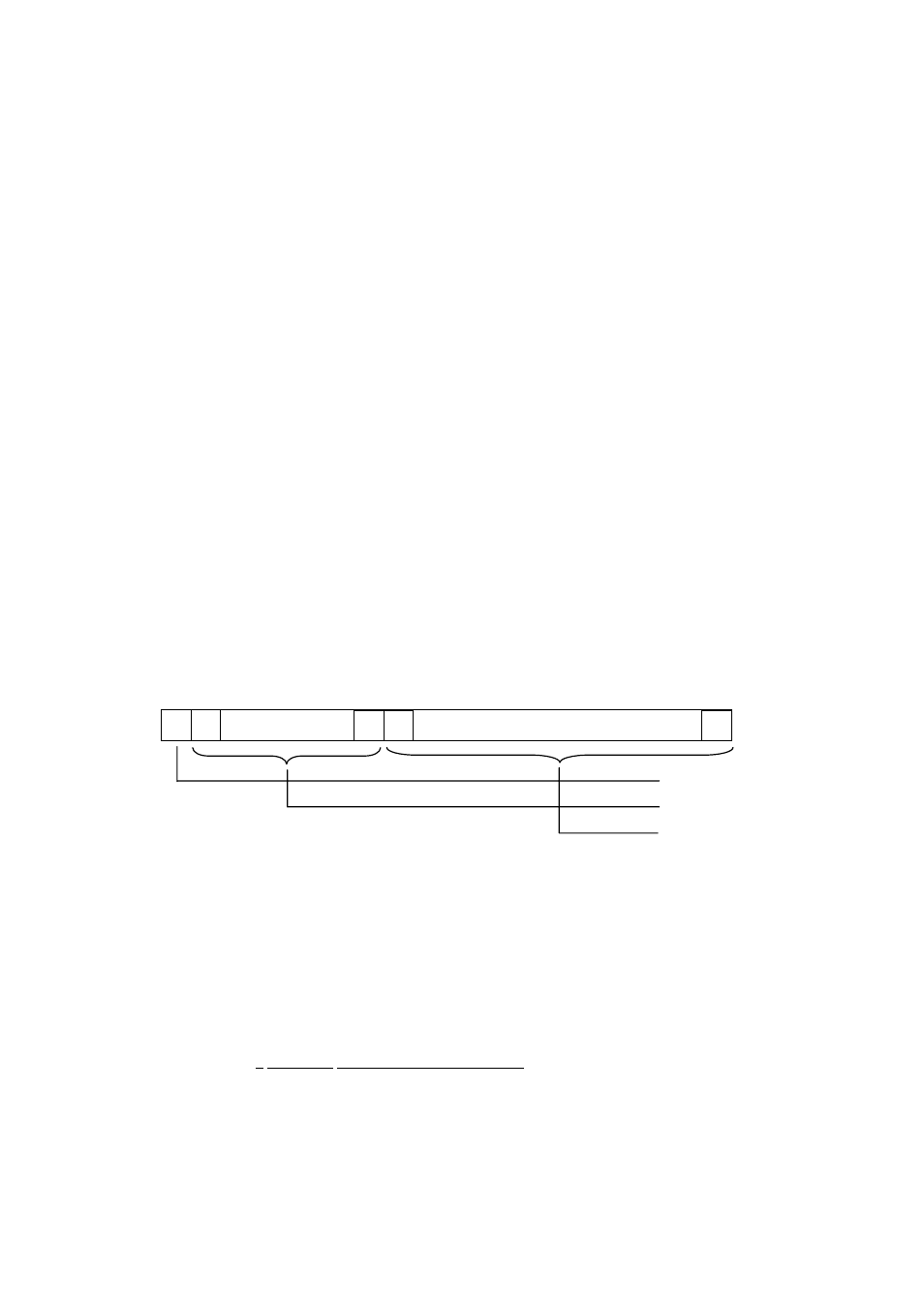
(2) 32-bit floating data (float type)
Instantaneous values or the like are expressed by 32-bit single precision float type.
The meaning of each bit is as follows (standard format specified in IEEE).
1) Sign part
Indicates the sign of the floating decimal point. “0” represents “positive”, and “1” represents “negative”.
2) Exponent part
Indicates the exponent of the floating decimal point by a power of 2. The value obtained by subtracting
127 from this value is the actual exponent.
3) Significand part
This is the data that corresponds to the significant figure of the floating decimal point. The actual
numerical value is interpreted by adding 1 to the top.
Example: 1 10000000 11000000000000000000000
Sign
:
Minus
Exponent
:
10000000
(2)
127 = 1
Significand
:
1.11
(2)
= 1 + 1/2 + 1/4 = 1.75
Value
:
1.75 u (1st power of 2) = 3.5
31 30
23 22
0
Sign part
Exponent part (8 bits)
Significand part (23 bits)
Bulletin F-107-UXF3-S
