App index examples of entering commands – Yokogawa Button Operated MV2000 User Manual
Page 47
M-4662
2-33
Using
the
Ethernet
Interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
App
Index
Examples of Entering Commands
The following are examples of commands when the MV is operating as a Modbus client
device. If the MV is operating as a Modbus master device, read the word “client” as
“master” and “server” as “slave.”
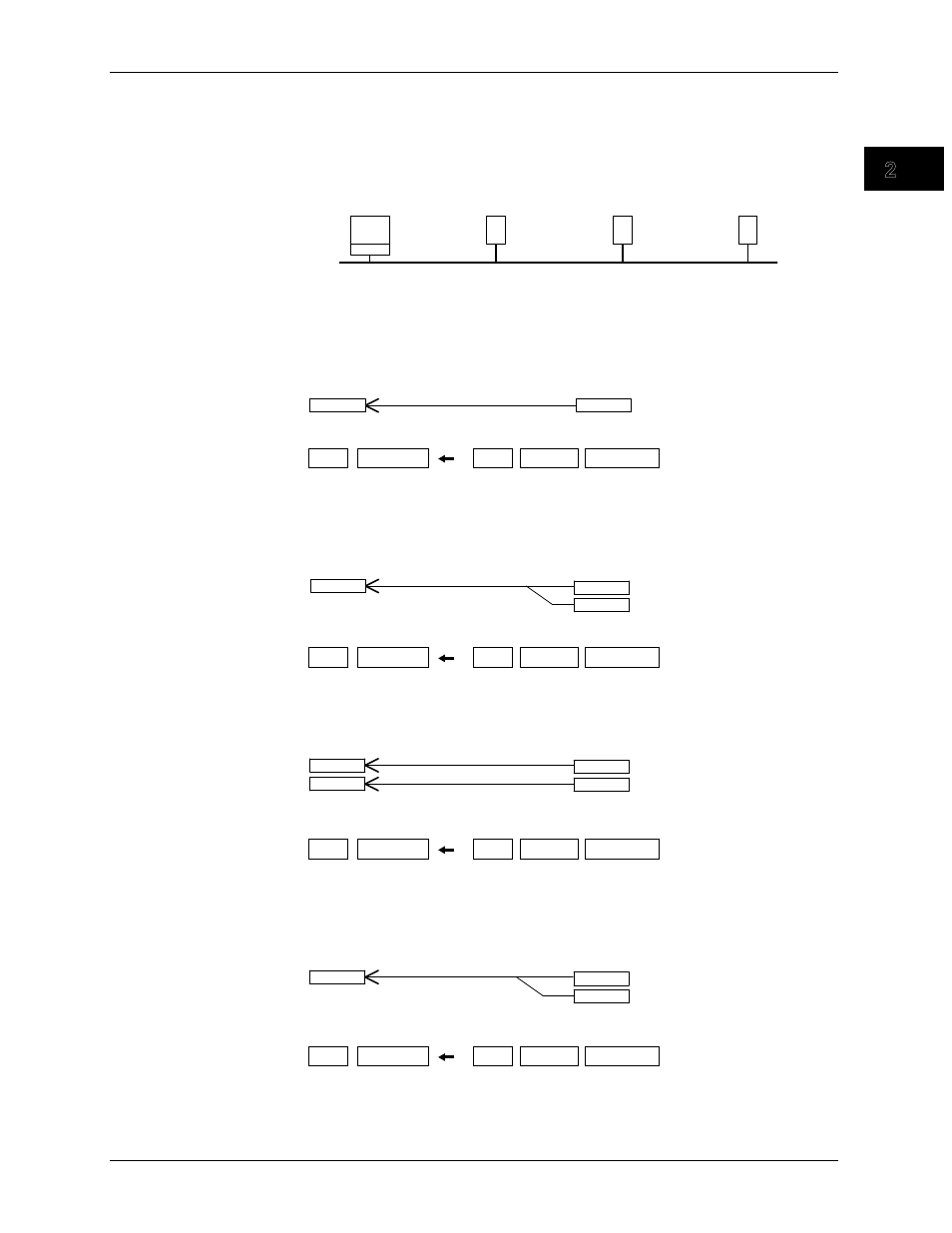
Ethernet
MVAdvanced
(Modbus client)
Instrument A
(Modbus server 1)
Instrument B
(Modbus server 2)
Instrument C
(Modbus server 3)
Connection example
Loading Data into Communication Input Channels
The MV reads the data from the server device and enters the data into communication
input channels in floating point format.
• Example 1
Read a 16-bit signed integer value from instrument A’s register 30001 into C01.
C01
30001
Communication input data
Instrument A register
16-bit signed integer
Command
R-M
C01 - C01
1
30001
INT16
• Example 2
Read a 32-bit signed integer value from instrument B’s registers 30003 and 30004
(lower bytes and higher bytes) into C03. Specify the smaller register number in the
command.
30003
Lower bytes
Higher bytes
30004
C03
32-bit signed integer
Instrument B register
Communication input data
Command
R-M
C03 - C03
2
30003
INT32_L
• Example 3
Read a 16-bit signed integer value from instrument B’s registers 30001 and 30002 into
C01 and C02. Specify the smaller register number in the command.
30001
16-bit signed integer
16-bit signed integer
30002
C01
C02
Instrument B register
Communication input data
Command
R-M
C01 - C02
2
30001
INT16
• Example 4
Read a 32-bit floating point value from instrument B’s registers 30005 and 30006
(lower bytes and higher bytes) into C04. Specify the smaller register number in the
command.
30005
Lower bytes
30006
C04
32-bit floating point
Instrument B register
Communication input data
Higher bytes
Command
R-M
C04 - C04
2
30005
FLOAT_L
2.9 Reading/Writing Data on Another Device from the MV via Modbus
