3 smbus write block to any address, 4 i2c(tm) block write, 3 smbus write block to any address 14.5.3.4 i – Rainbow Electronics LM93 User Manual
Page 21: Block write, 0 smbus interface
14.0 SMBus Interface
(Continued)
14.5.3.3 SMBus Write Block to Any Address
The start address for a block write is embedded in this transaction. In this operation the master sends a block of data to the slave
as follows:
1.
The master device asserts a START condition.
2.
The master sends the 7-bit slave address followed by the write bit (low).
3.
The addressed slave device asserts ACK.
4.
The master sends a command code that tells the slave device to expect a block write. The LM93 command code for a block
write is F0h.
5.
The slave asserts ACK.
6.
The master sends a byte that tells the slave device how many data bytes it will send (N). The SMBus specification allows a
maximum of 32 data bytes to be sent in a block write.
7.
The slave asserts ACK.
8.
The master sends data byte 1, the starting address of the block write.
9.
The slave asserts ACK after each data byte.
10. The master sends data byte 2.
11. The slave asserts ACK.
12. The master continues to send data bytes and the slave asserts ACK for each byte.
13. The master asserts a STOP condition to end the transaction.
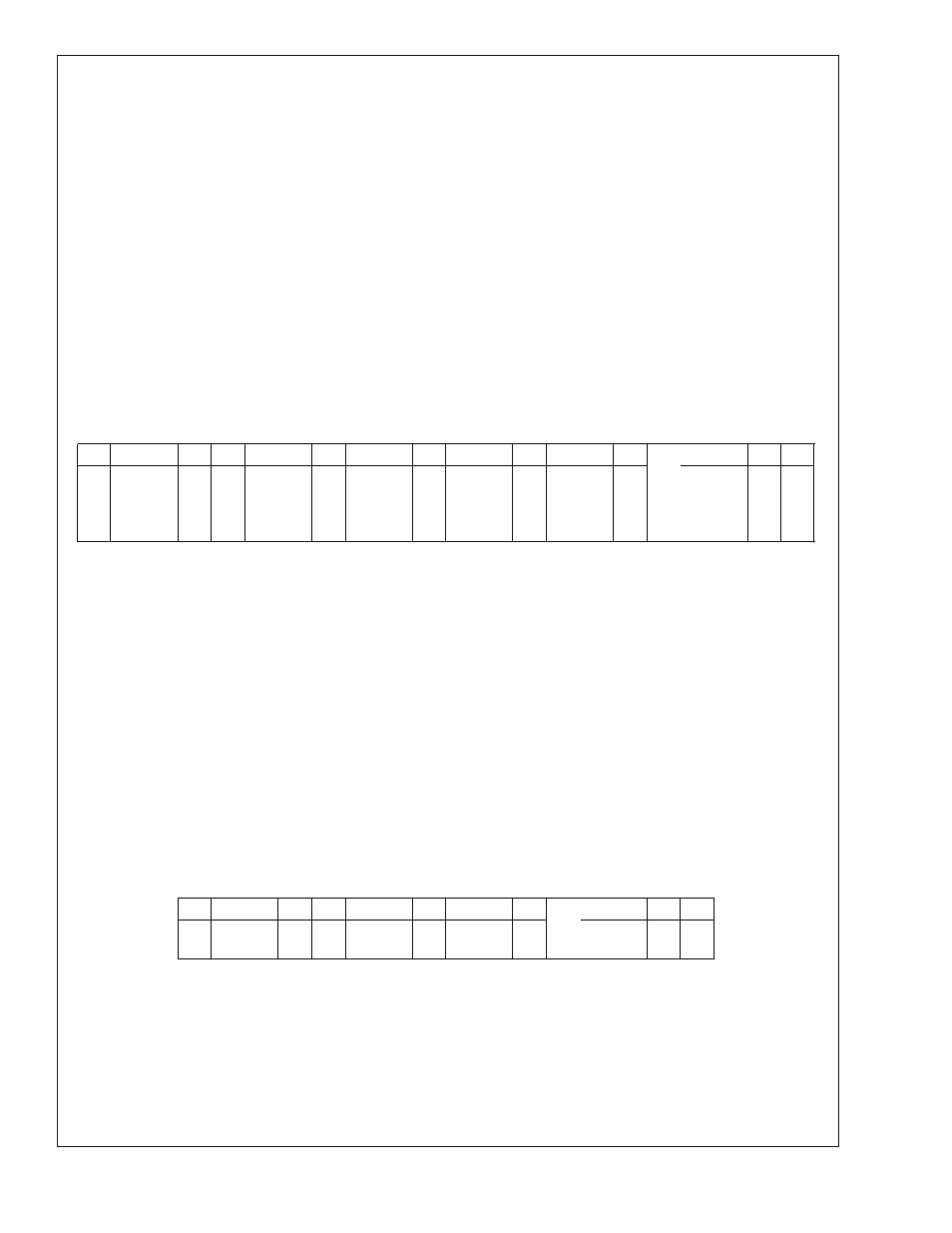
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
A
12
13
S
Slave
Address
W
A
Command
F0h
(Block
Write)
A
Byte
Count
(N)
A
Data
Byte 1
(Start
Address)
A
Data
Byte 2
A
A
Data
Byte N
A
P
Special Notes
1.
Any attempts to write to bytes beyond normal address space are acknowledged by the LM93 but are ignored.
2.
Block writes do not wrap from address FFh back to 00h the address remains at FFh.
3.
The Byte Count field is ignored by the LM93. The master device may send more or less bytes and the LM93 accepts them.
4.
The SMBus specification requires that block writes never exceed 32 data bytes. Meeting this requirement means that only 31
actual data bytes can be sent (the register address counts as one byte). The LM93 does not care if this requirement is met.
14.5.3.4 I
2
C
™
Block Write
In this transaction the master sends a block of data to the LM93 as follows:
1.
The master device asserts a START condition.
2.
The master sends the 7-bit slave address followed by the write bit (low).
3.
The addressed slave device asserts ACK.
4.
The master sends the starting address of the block write.
5.
The slave asserts ACK after each data byte.
6.
The master sends data byte 1.
7.
The slave asserts ACK.
8.
The master continues to send data bytes and the slave asserts ACK for each byte.
9.
The master asserts a STOP condition to end the transaction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
S
Slave
Address
W
A
Register
Address
A
Data
Byte 1
A
A
Data
Byte N
A
P
Special Notes:
1.
Any attempts to write to bytes beyond normal address space are acknowledged by the LM93 but are ignored.
2.
Block writes do not wrap from address FFh back to 00h the address remains at FFh.
LM93
www.national.com
21
