ZyXEL Communications P-334W User Manual
Page 37
Prestige 334W User’s Guide
Getting to Know Your Prestige
1-3
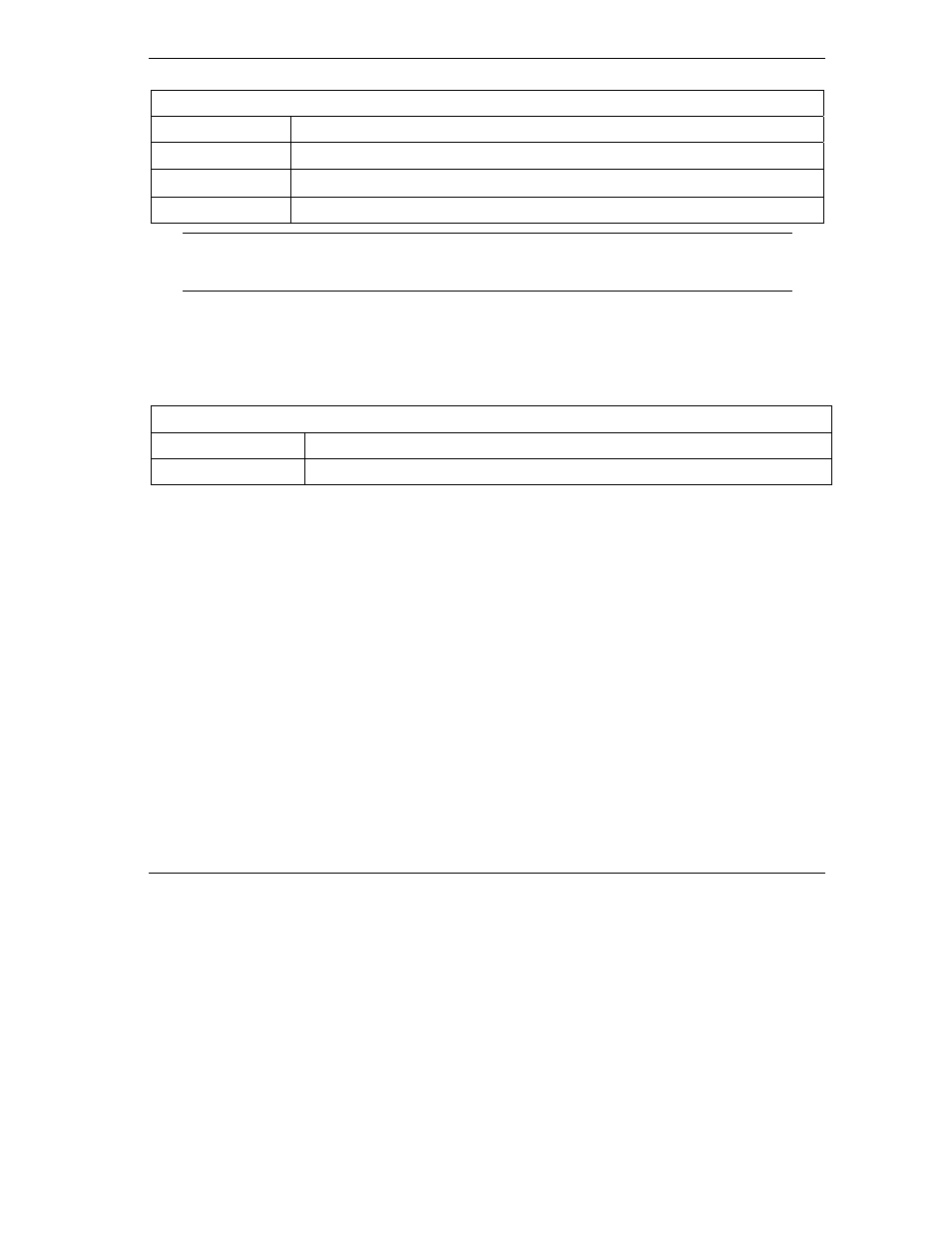
IEEE 802.11b
Data Rate (Mbps)
Modulation
1
DBPSK (Differential Binary Phase Shift Keyed)
2
DQPSK (Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
)
5.5 / 11
CCK (Complementary Code Keying)
The Prestige may be prone to RF (Radio Frequency) interference from other 2.4
GHz devices such as microwave ovens, wireless phones, Bluetooth enabled
devices, and other wireless LANs.
802.11g Wireless LAN Standard
The Prestige, complies with the 802.11g wireless standard and is also fully compatible with the 802.11b
standard. This means an 802.11b radio card can interface directly with an 802.11g device (and vice versa)
at 11 Mbps or lower depending on range. 802.11g has several intermediate rate steps between the
maximum and minimum data rates. The 802.11g data rate and modulation are as follows:
IEEE 802.11g
Data Rate (Mbps)
Modulation
6/9/12/18/24/36/48/54 OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)
Packet Filtering
The packet filtering mechanism blocks unwanted traffic from entering/leaving your network.
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)
Using the standard TCP/IP protocol, the Prestige and other UPnP enabled devices can dynamically join a
network, obtain an IP address and convey its capabilities to other devices on the network.
Call Scheduling
Configure call time periods to restrict and allow access for users on remote nodes.
PPPoE
PPPoE facilitates the interaction of a host with an Internet modem to achieve access to high-speed data
networks via a familiar "dial-up networking" user interface.
PPTP Encapsulation
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a network protocol that enables secure transfer of data from a
remote client to a private server, creating a Virtual Private Network (VPN) using a TCP/IP-based network.
PPTP supports on-demand, multi-protocol and virtual private networking over public networks, such as the
Internet. The Prestige supports one PPTP server connection at any given time.
