Figure 2-6. at-mio-16x pgia, Figure 2-6, At-mio-16x pgia -20 – National Instruments AT-MIO-16X User Manual
Page 42
Chapter 2
Configuration and Installation
AT-MIO-16X User Manual
2-20
© National Instruments Corporation
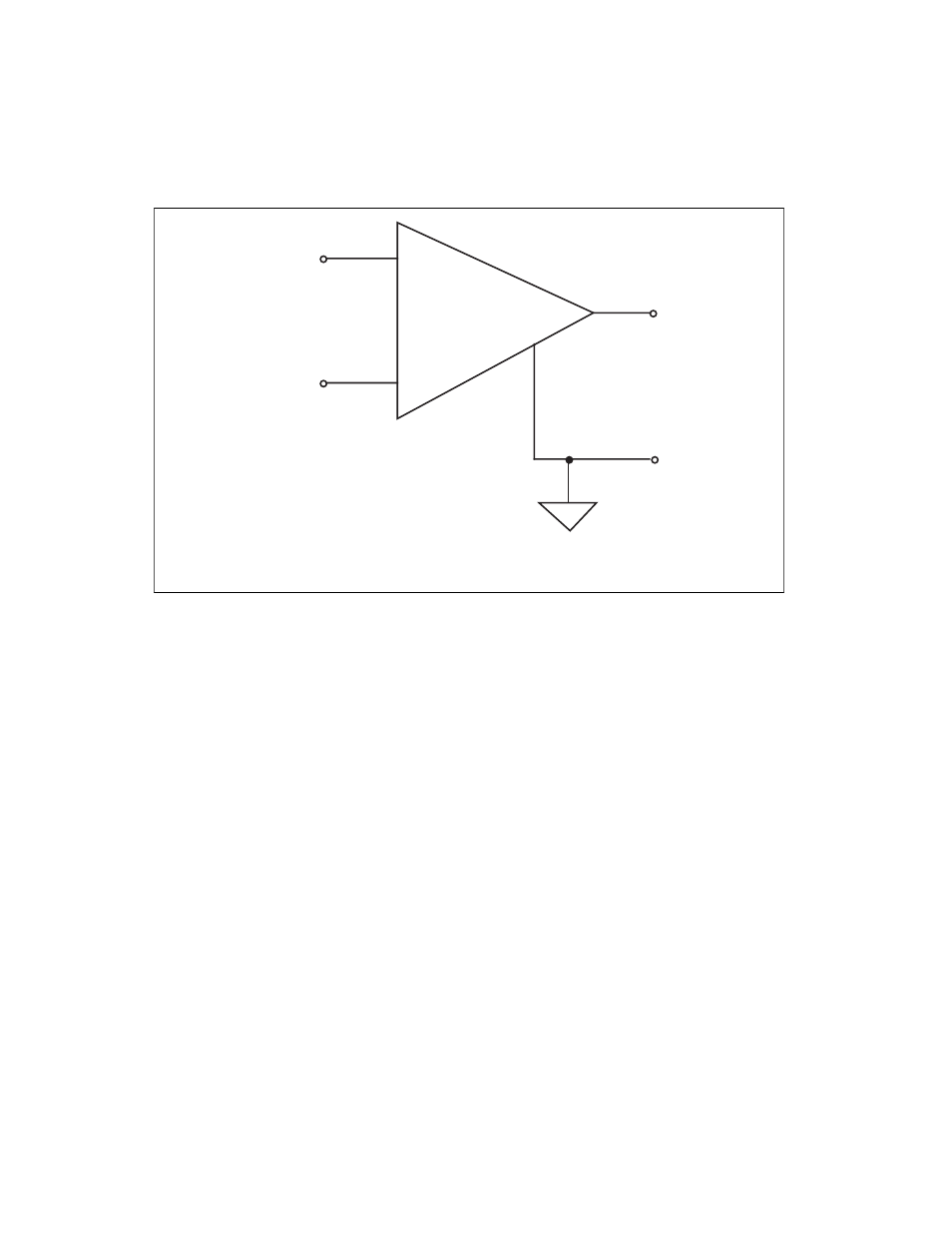
Figure 2-6. AT-MIO-16X PGIA
The AT-MIO-16X PGIA applies gain and common-mode voltage
rejection, and presents high-input impedance to the analog input signals
connected to the AT-MIO-16X board. Signals are routed to the positive
(+) and negative (–) inputs of the PGIA through input multiplexers on
the AT-MIO-16X. The PGIA converts two input signals to a signal that
is the difference between the two input signals multiplied by the gain
setting of the amplifier. The amplifier output voltage is referenced to
the AT-MIO-16X ground. The AT-MIO-16X ADC measures this
output voltage when it performs A/D conversions.
All signals must be referenced to ground, either at the source device or
at the AT-MIO-16X. If you have a floating source, the AT-MIO-16X
should reference the signal to ground by using the RSE input mode or
the DIFF input configuration with bias resistors (see the Differential
Connections for Nonreferenced or Floating Signal Sources section later
in this chapter). If you have a grounded source, the AT-MIO-16X
should not reference the signal to AI GND. The AT-MIO-16X board
avoids this reference by using the DIFF or NRSE input configurations.
Programmable Gain
+
+
-
-
Vin+
Vin
-
V
m
Measured
Voltage
Vm =
[
Gain
Gain = 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100
GAIN
Vin
+
Vin
-
-
]
*
