Prefixes (control, For mo, Prefixes (control:, data:, l:, g:) – Grass Valley Xpanel Vertigo Suite v.4.8 User Manual
Page 116: Lookup table properties
6-14
Xpanel User Manual
Adding a data source to an object
Prefixes (Control:, Data:, L:, G:)
When setting some properties or parameters, Xpanel uses prefixes to specify the origins of
objects and data. While you can type these in along with the object name or data source,
Xpanel’s drag and drop functionality makes it unnecessary for the most part by
automatically filling all required information.
The following table identifies the most common prefixes used:
Lookup table properties
Objects that have a D
ATA
S
OURCE
property, most likely also have a L
OOKUP
T
ABLE
and
L
OOKUP
T
ABLE
L
OCATION
properties.
Lookup tables are created in Xstudio, the Vertigo Suite’s template authoring application,
and they provide a way of defining replacement values for incoming data. For example, an
object that is being fed the full city names from a live data source, cross references the city
name against a lookup table and then displays the city’s abbreviation. Refer to the Xstudio
User Manual for instructions on how to create and use Lookup tables.
In the context of using lookup table in Xpanel, if lookup tables are saved on the same
Xmedia Server that Xpanel is connected to, you can use these lookup tables to replace the
values coming into an object linked to a data source. How you apply a lookup table depends
on where the data is coming from:
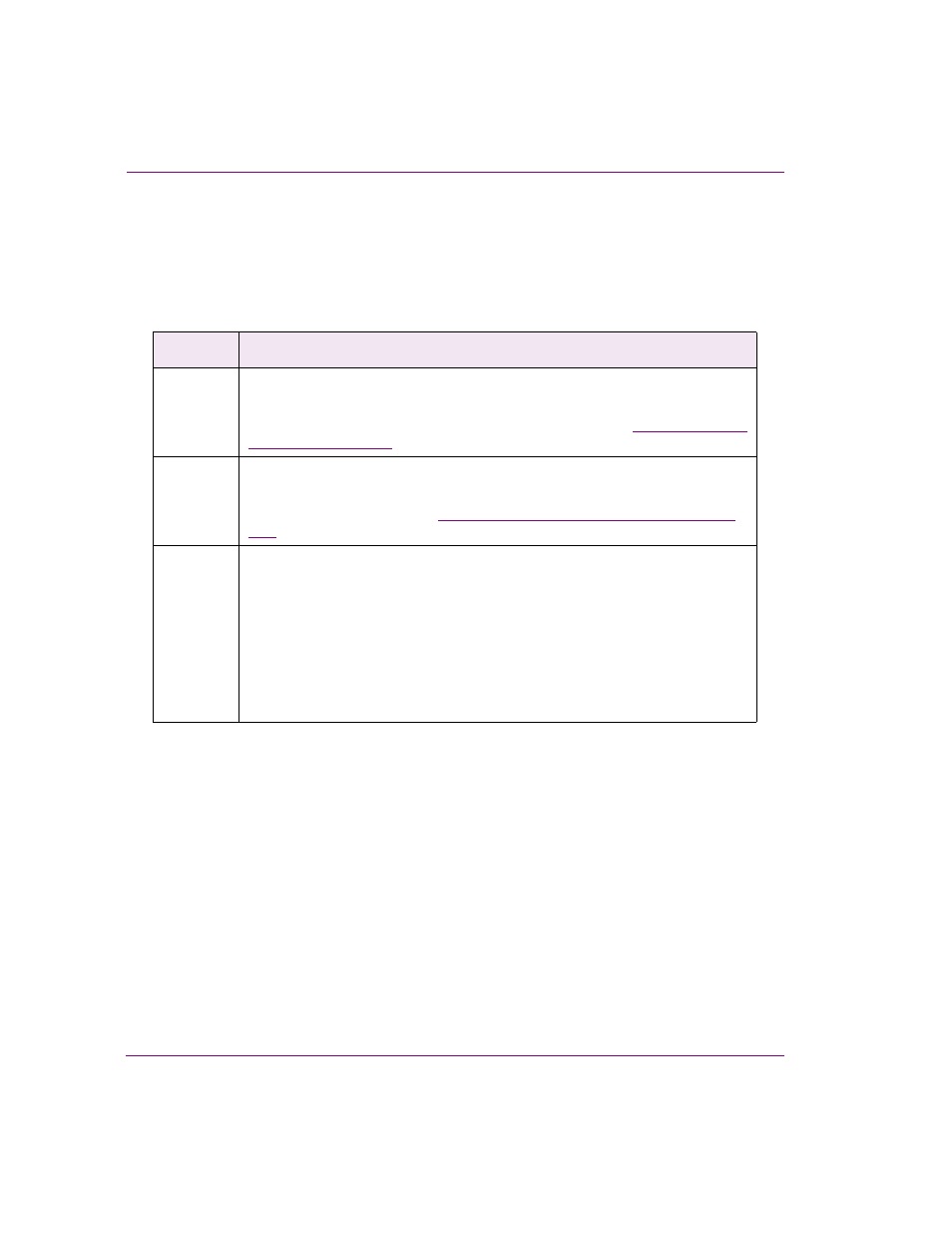
Prefix
Signifies
Control:
A control object, e.g. Control:MyControlObject.
This prefix is commonly used in the Action Editor to identify the control object that
the action’s parameters apply to (e.g. T
ARGET
or S
OURCE
.
Data:
A data item from the Data Server, e.g. Data:Schools:SchoolsClosed(1,1).
This prefix is commonly used in the D
ATA
S
OURCE
property to identify the data item
that is linked to an object. See
“Linking data entities to a panel object” on page
L:
G:
•
A local data server variable, e.g. L:SelectedStock.
•
A global data server variable, e.g. G:StationID.
Local and global database variables are created on the fly whenever a reference
to one is made in a property value or action parameter. It is also possible for
controls to set the value of these variables such that other controls may read them.
Local database variables can only be used within the control panel that created
them and are destroyed when the panel exits Production mode. Global database
variables, on the other hand, are shared amongst all control panels and remain in
the database even after exiting Production mode.
